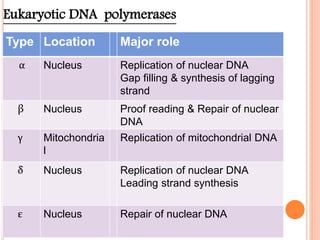
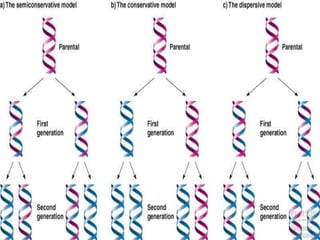
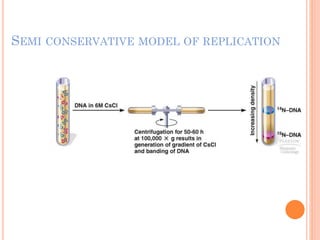
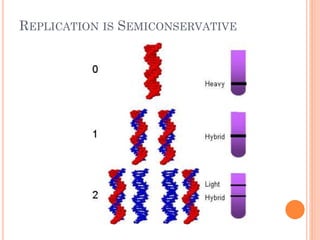
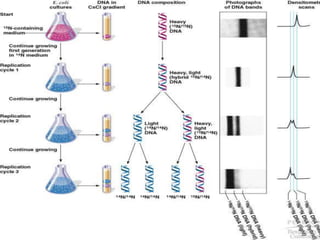
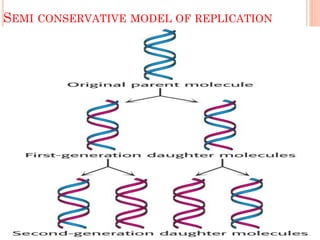
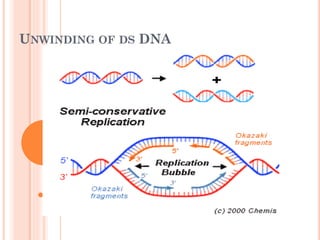
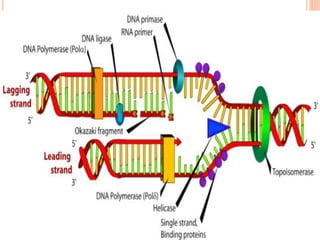
DNA replication is a highly regulated process that occurs semiconservatively before cell division. It involves unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicases, followed by synthesis of new strands complementary to each parental strand. This is carried out by DNA polymerases that add nucleotides according to base pairing rules. In eukaryotes, the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in fragments called Okazaki fragments which are later joined by DNA ligase. DNA replication ensures faithful transmission of genetic material to daughter cells.



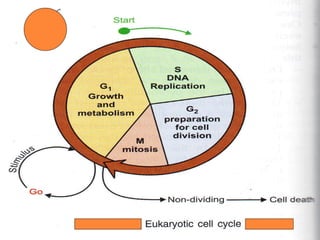
![CELL - CYCLE
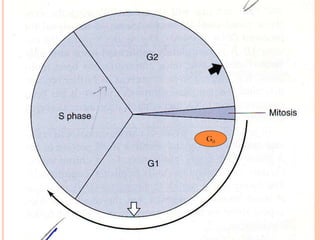
Cell cycle is a sequence of events that occur in
a cell during cell division.
It results in formation of 2 identical daughter
cells.
Duration of cell cycle varies from cell to cell.
It occurs in 4 phases
G1 PHASE [ gap-1]
S PHASE [synthetic]
G2 PHASE [gap-2]
M PHASE [ mitotic]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/replication-140330123617-phpapp01/85/Replication-6-320.jpg)

![DNA-REPLICATION
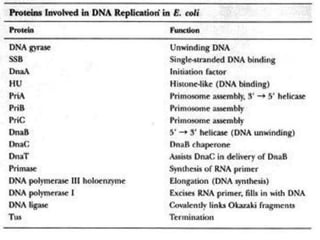
Requirements
1.Deoxyribonucleotides [ dATP, dGTP, dCTP, dTTP ]
2.Template DNA strand [parent strand]
3.RNA primer
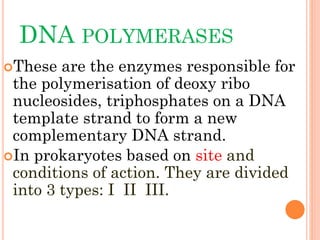
4.Enzymes DNA polymerase
Primase
Helicase
DNA Ligase
Topo-isomerases
Single Strand Binding Proteins.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/replication-140330123617-phpapp01/85/Replication-16-320.jpg)


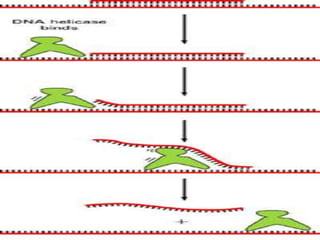
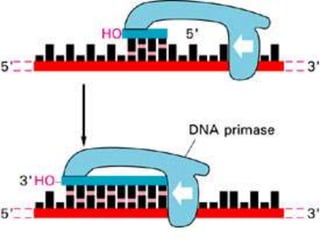

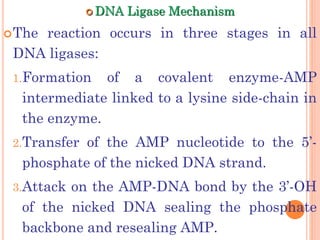






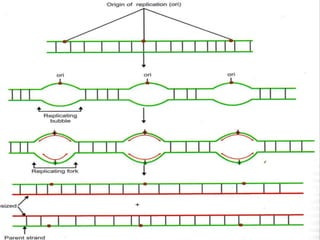
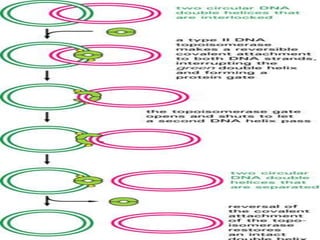
![INITIATION OF DNA-REPLICATION
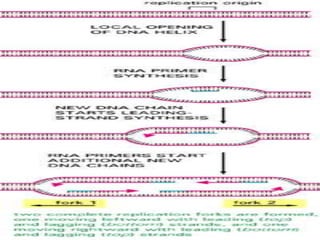
1.Identification of the origins of replication.
The origin of replication [oriC locus] rich in
AT pairs is identified.
A specific protein [Dna A] binds to the oriC and
results in unwinding of ds DNA.
Un winding of DNA results in formation of
replication bubble with 2 replication forks.
Ss binding proteins binds to DNA to each strand
to prevent re-annealing of DNA.
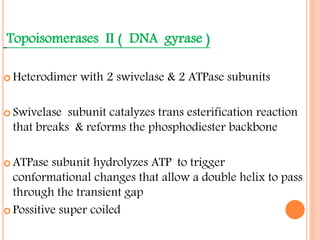
Helicases continues the process of un winding.
Topoisomerases relieve the super coils formed
during unwinding.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/replication-140330123617-phpapp01/85/Replication-38-320.jpg)
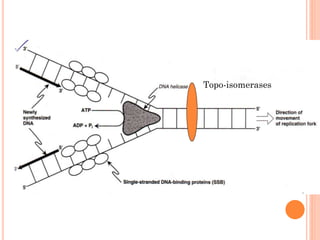
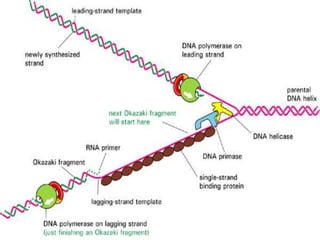
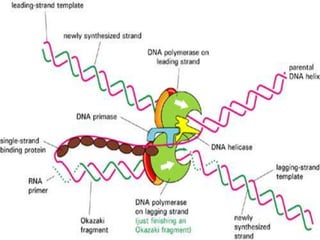
![DNA-REPLICATION
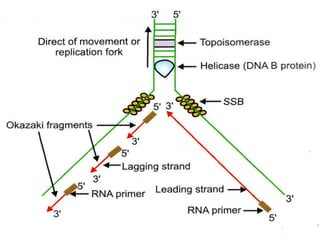
2.Fomation of replication fork
replication fork has 4 components
1.helicase [unwinds ds DNA]
2.primase [synthesizes RNA primer]
3.DNApolymerase[synthesizes DNA]
4.ss binding proteins [stabilizes the strand]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/replication-140330123617-phpapp01/85/Replication-44-320.jpg)
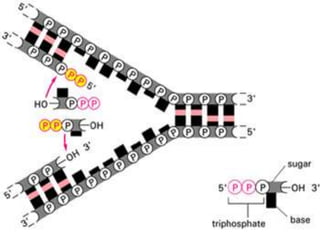
![2.ELONGATION OF DNA
Requires RNA primer, DNA template , DNAP
enzyme
and deoxyribonucleotides [dATP,dGTP ,dCTP,
dTTP]
DNA polymerase catalyze the stepwise addition of
deoxyribonucleotides to 31 end of template strand
and
thus copies the information from the template DNA.
DNAP requires RNA primer to start elongation.
DNAP copies the information from DNA template](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/replication-140330123617-phpapp01/85/Replication-45-320.jpg)
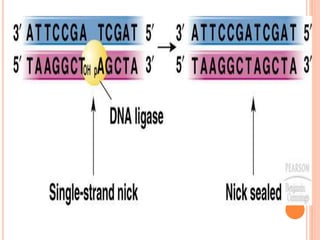
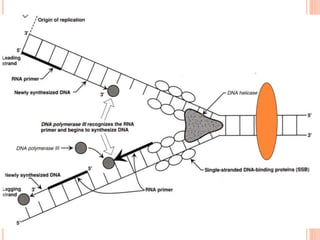
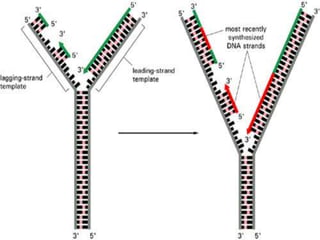
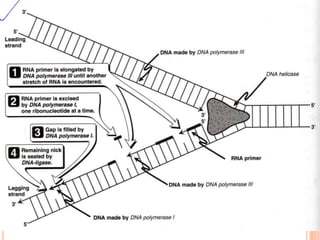
![2.ELONGATION OF DNA
1.continous synthesis occurs towards
the replication fork [leading strand] by
DNA polymerase.
2.discontinuous synthesis occurs
away from the replication fork in pieces
called as okazaki fragments which are
ligated by DNA ligase [lagging strand]. It
requires multiple RNAprimers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/replication-140330123617-phpapp01/85/Replication-46-320.jpg)


![ROLE OF TELOMERS IN
EUKARYOTIC REPLICATION
A small portion of 31 end of parent strand
is not replicated and length of
chromosome reduces.
Telomeres play a crucial role in eukaryotic
replication.
Telomeres contain the repeat sequence of
[TTAGGG]n .
They prevent the shorting of chromosome
with each cell division by an enzyme
telomerase.
Telomerase enzyme synthesizes and
maintains the telomeric DNA.
Telomerase adds repeats to 31end of DNA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/replication-140330123617-phpapp01/85/Replication-53-320.jpg)

![INHIBITORS OF REPLICATION
1.Inhibitors of DNA; Prevents un-winding of
DNA.
E.g. actinomycin, mitomycin
2.Inhibitors of deoxy-ribonucleotides;
E.g. Anti-folates [ inhibits
Purine
Pyrimidine synthesis]
3.Inhibitors of replicative enzymes;
E.g. norflox [inhibit DNA
gyrase]
ciploflox](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/replication-140330123617-phpapp01/85/Replication-57-320.jpg)