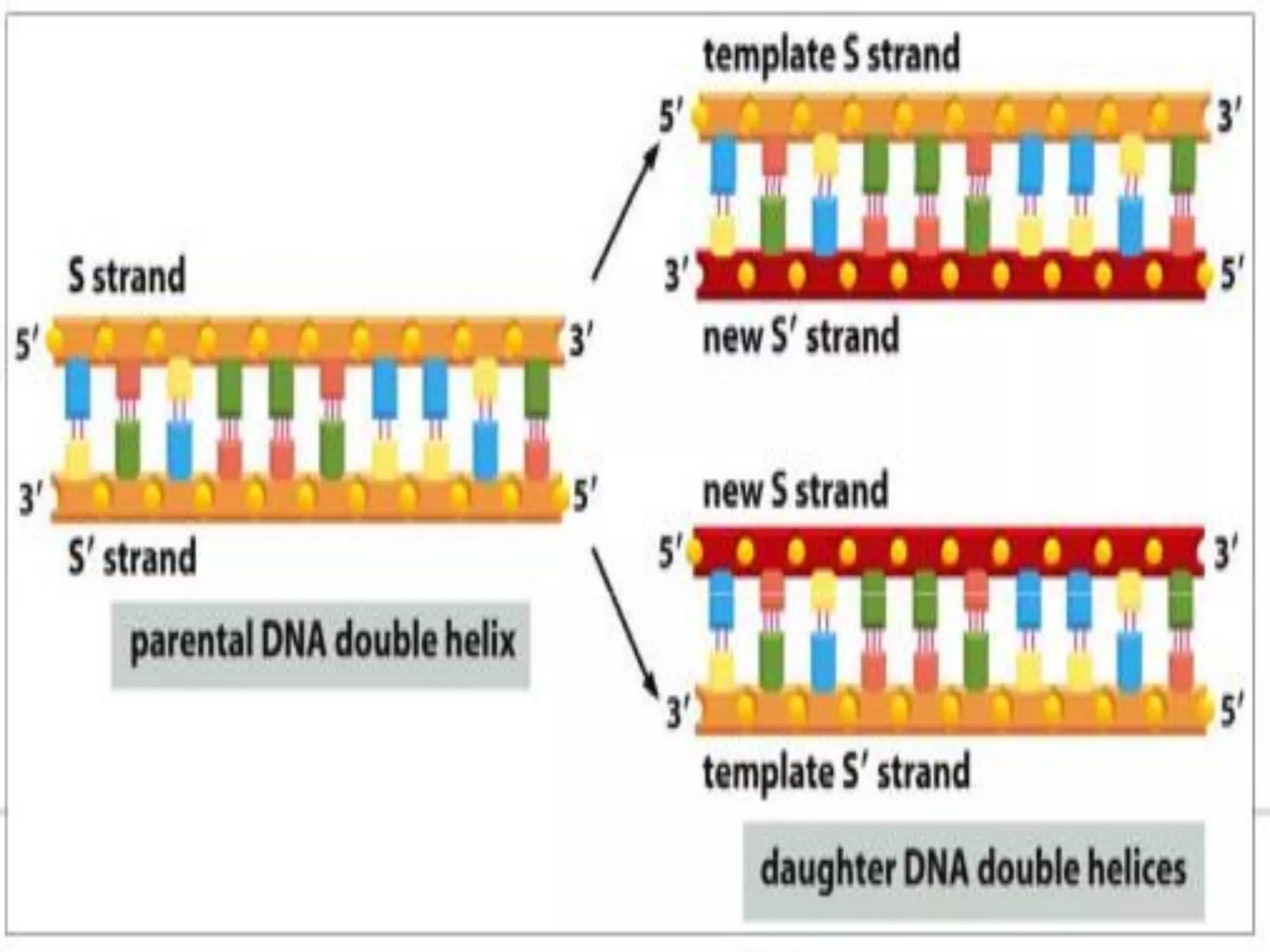
DNA replication occurs semi-conservatively to produce two identical copies of DNA before cell division. It involves unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicase, followed by synthesis of new strands complementary to the original strands. RNA primers are required for DNA polymerase to begin DNA synthesis. The leading strand is synthesized continuously while the lagging strand is synthesized in fragments called Okazaki fragments. DNA polymerase proofreads and repairs any errors with its exonuclease activity to maintain high fidelity of DNA replication.