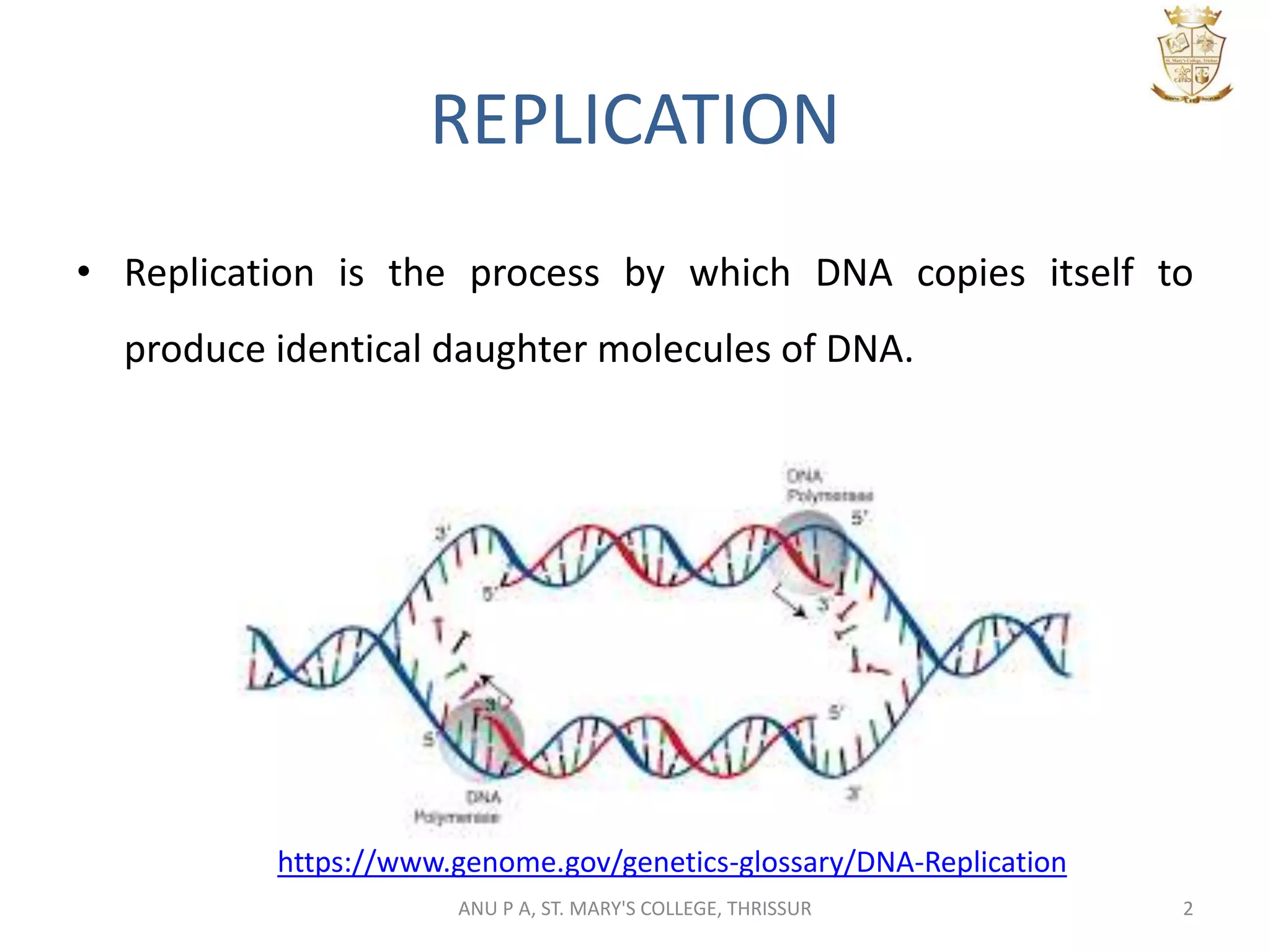
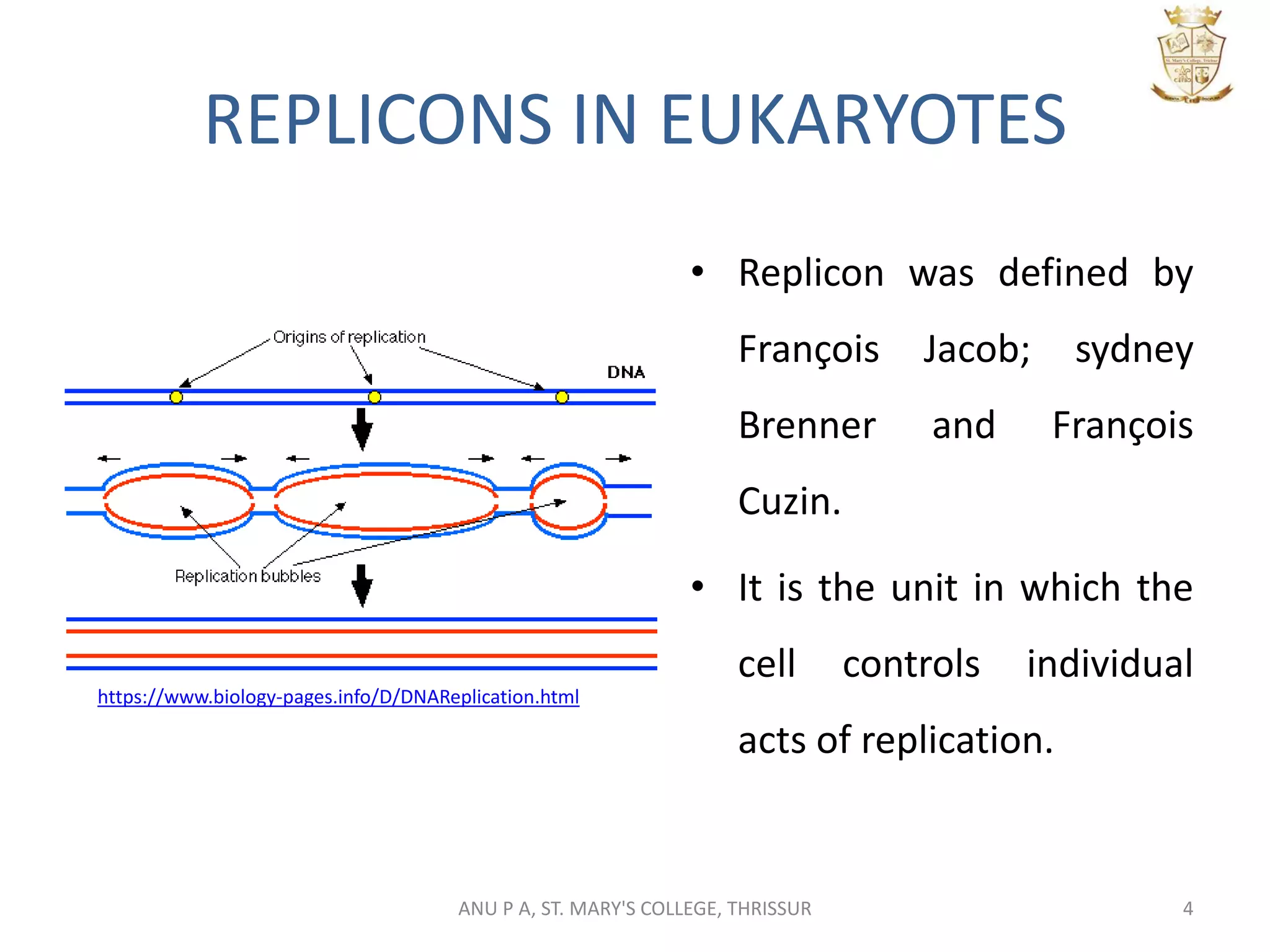
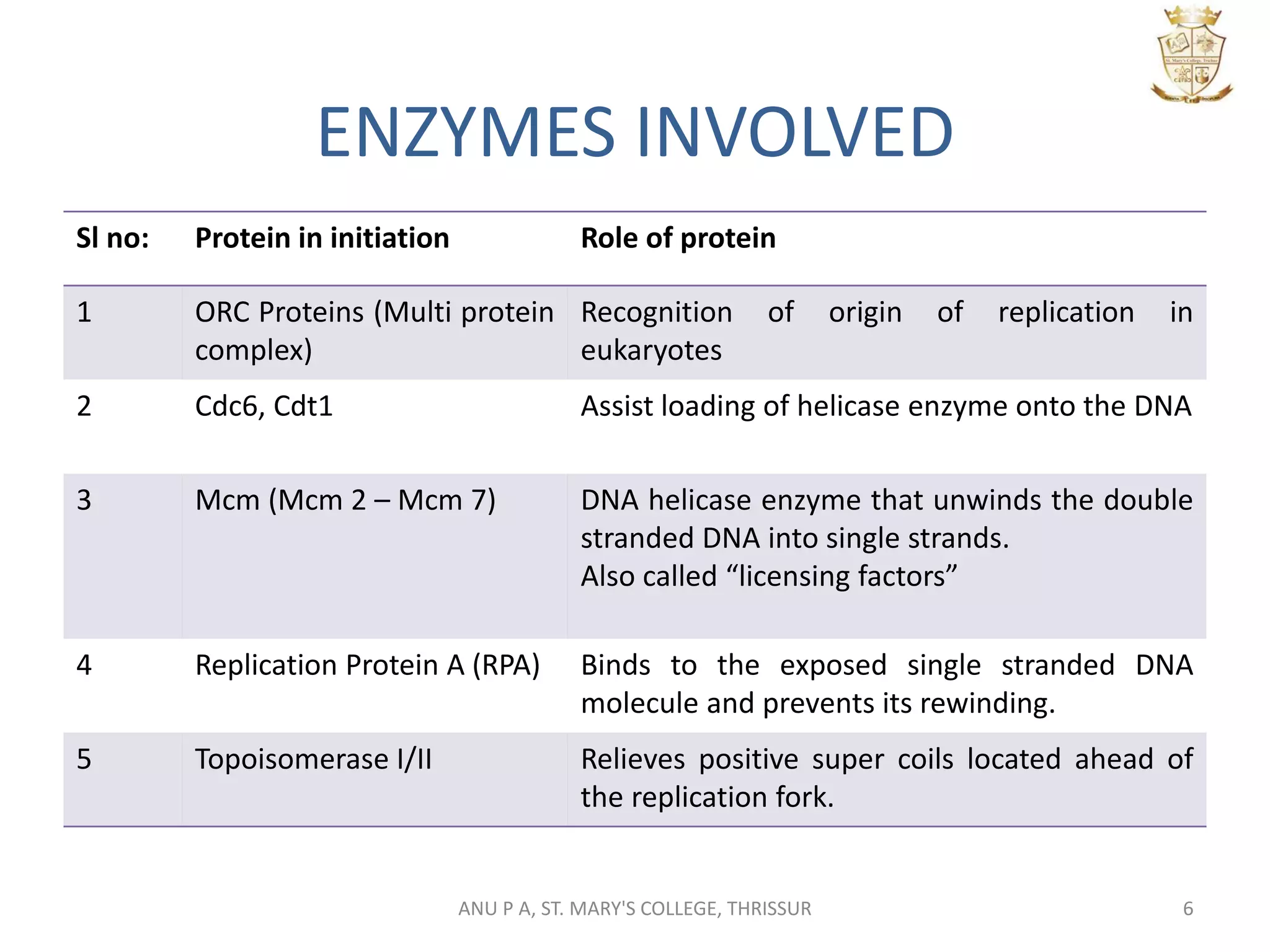
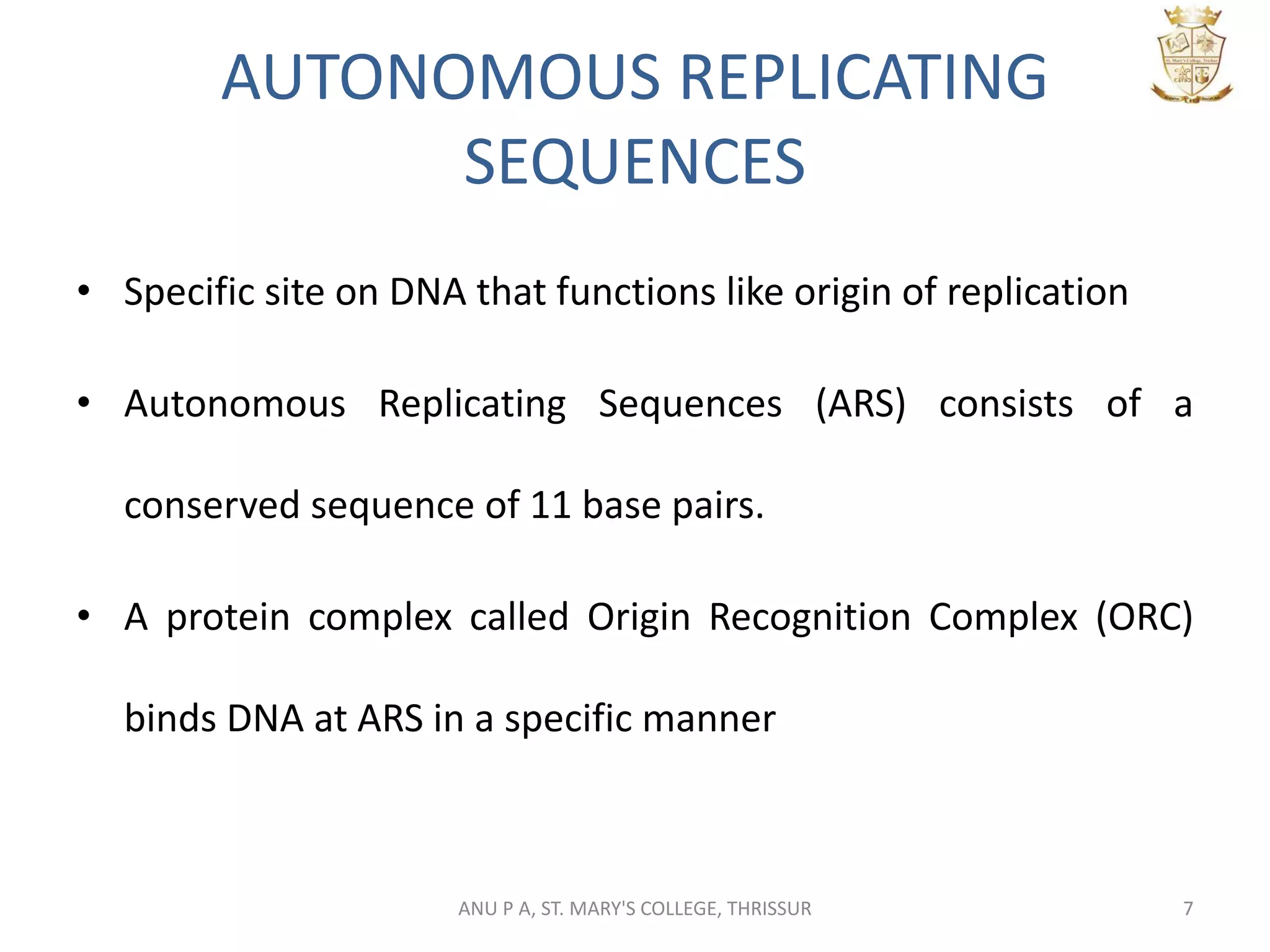
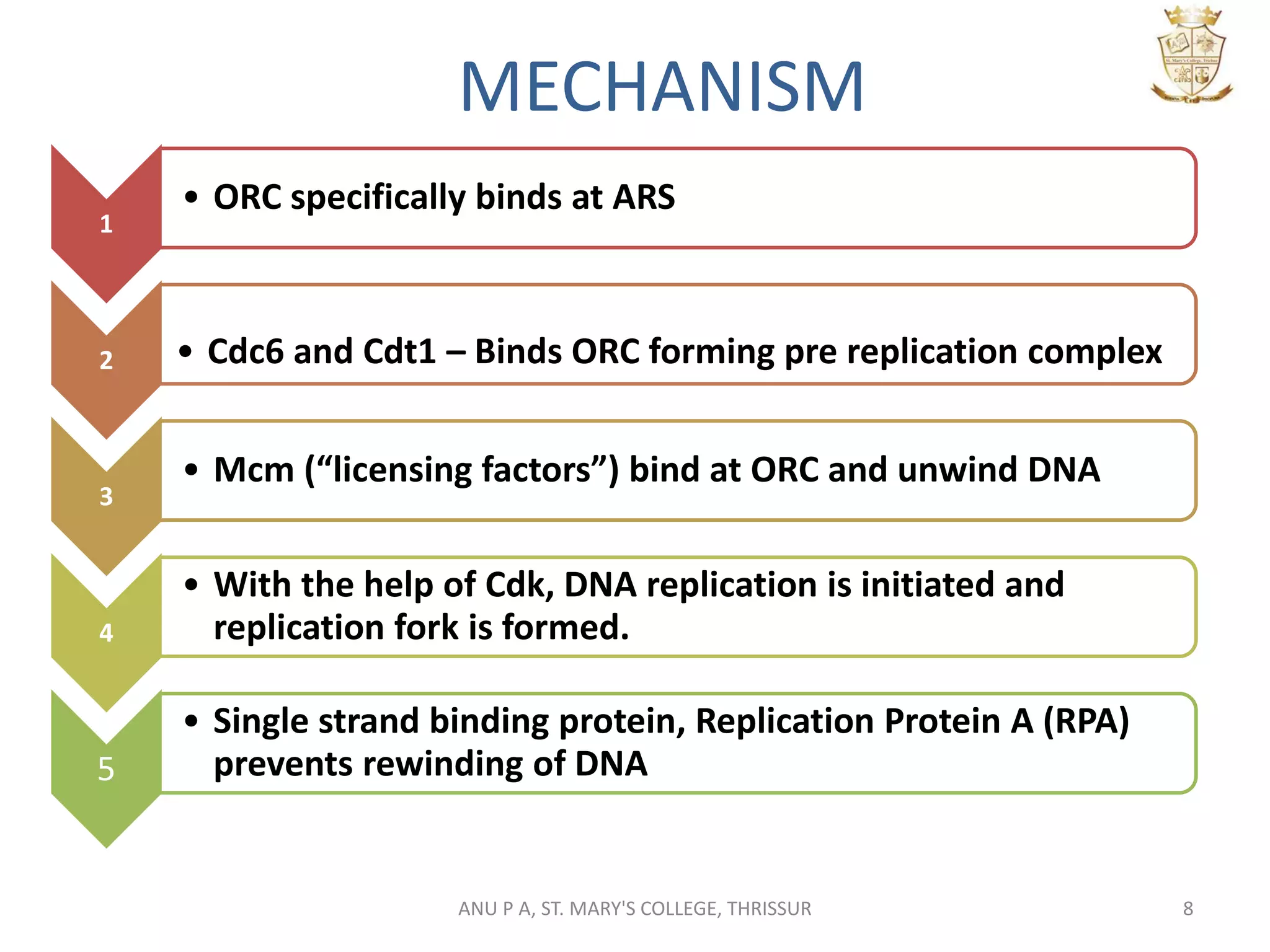
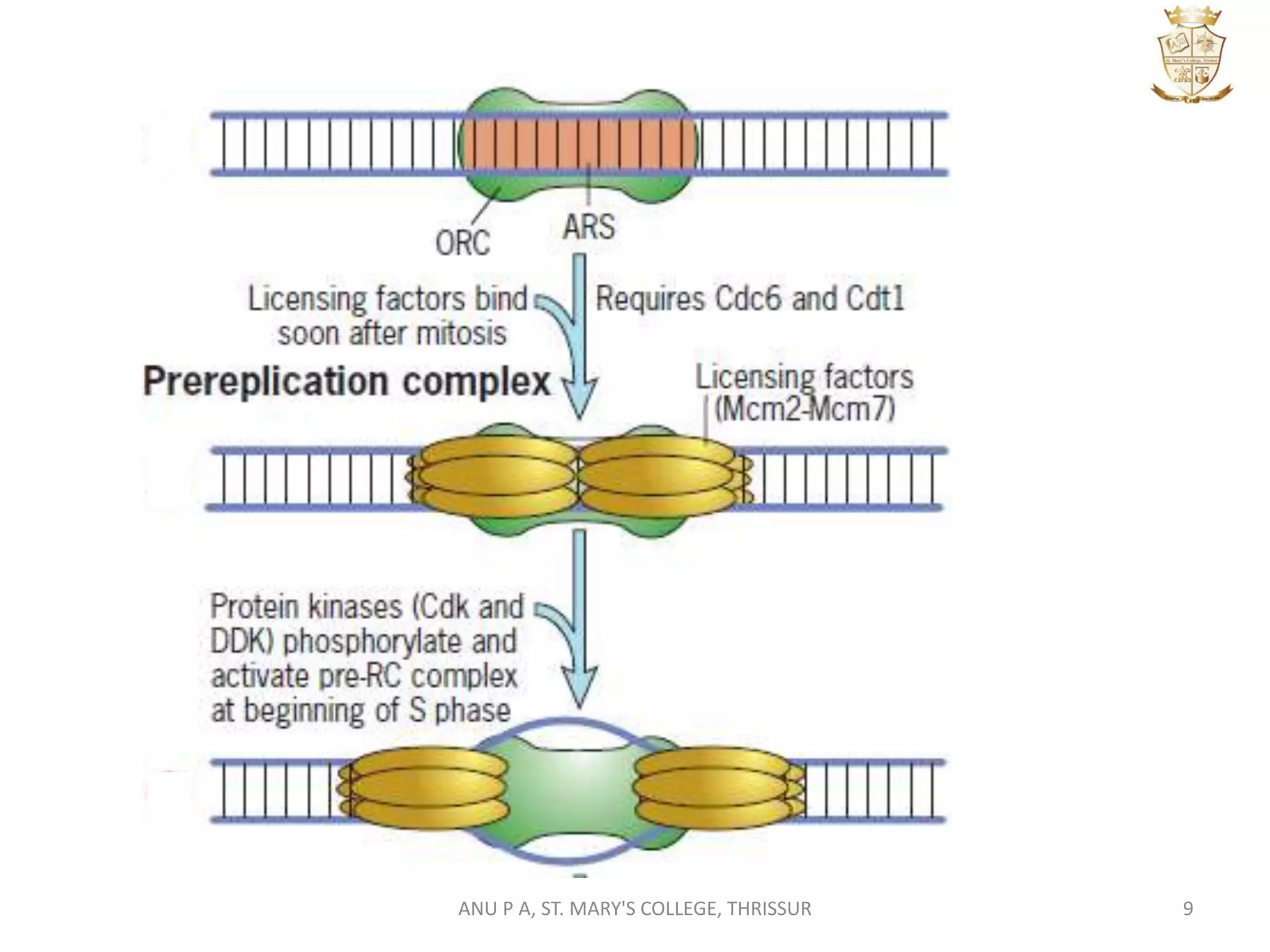
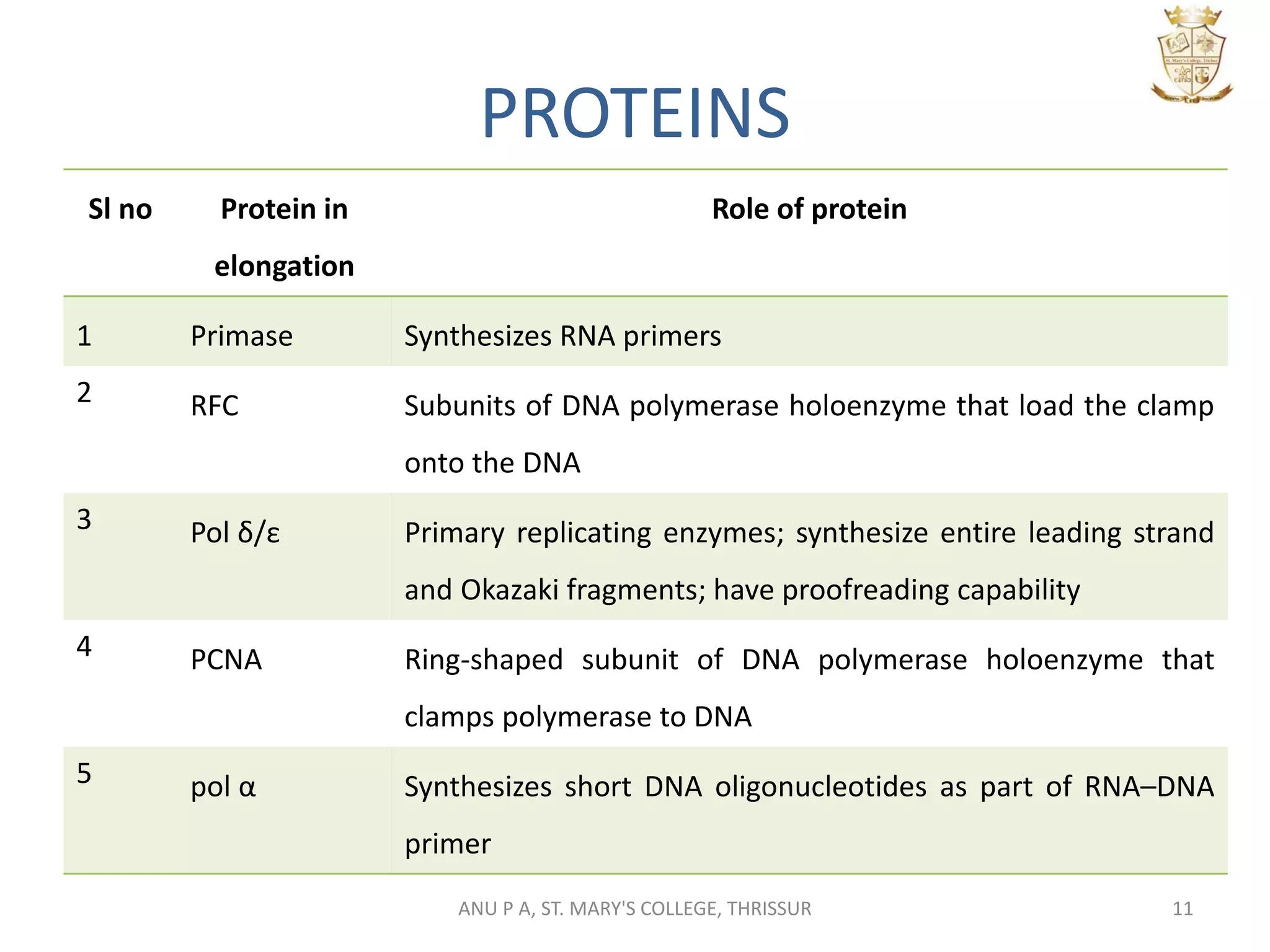
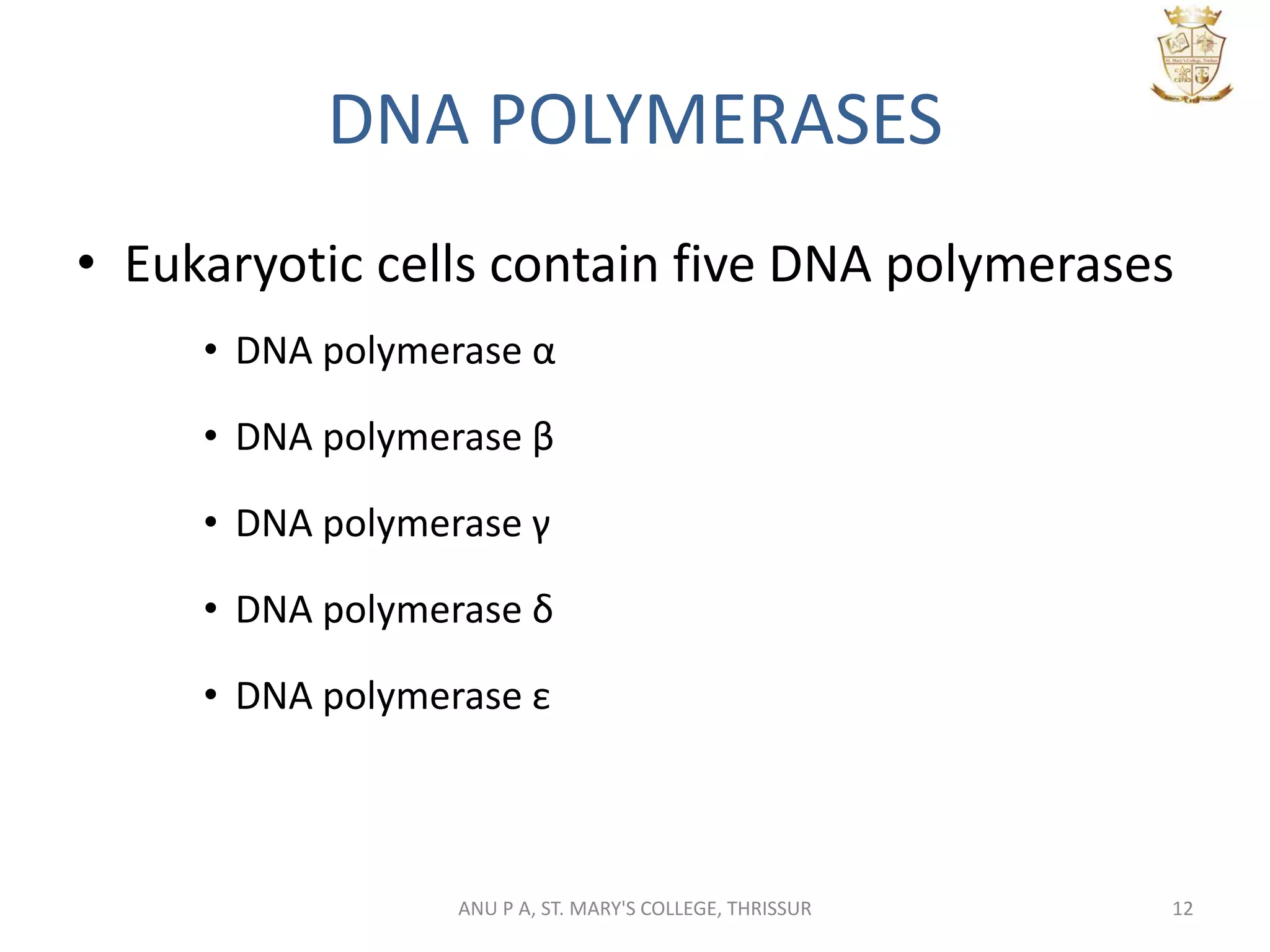
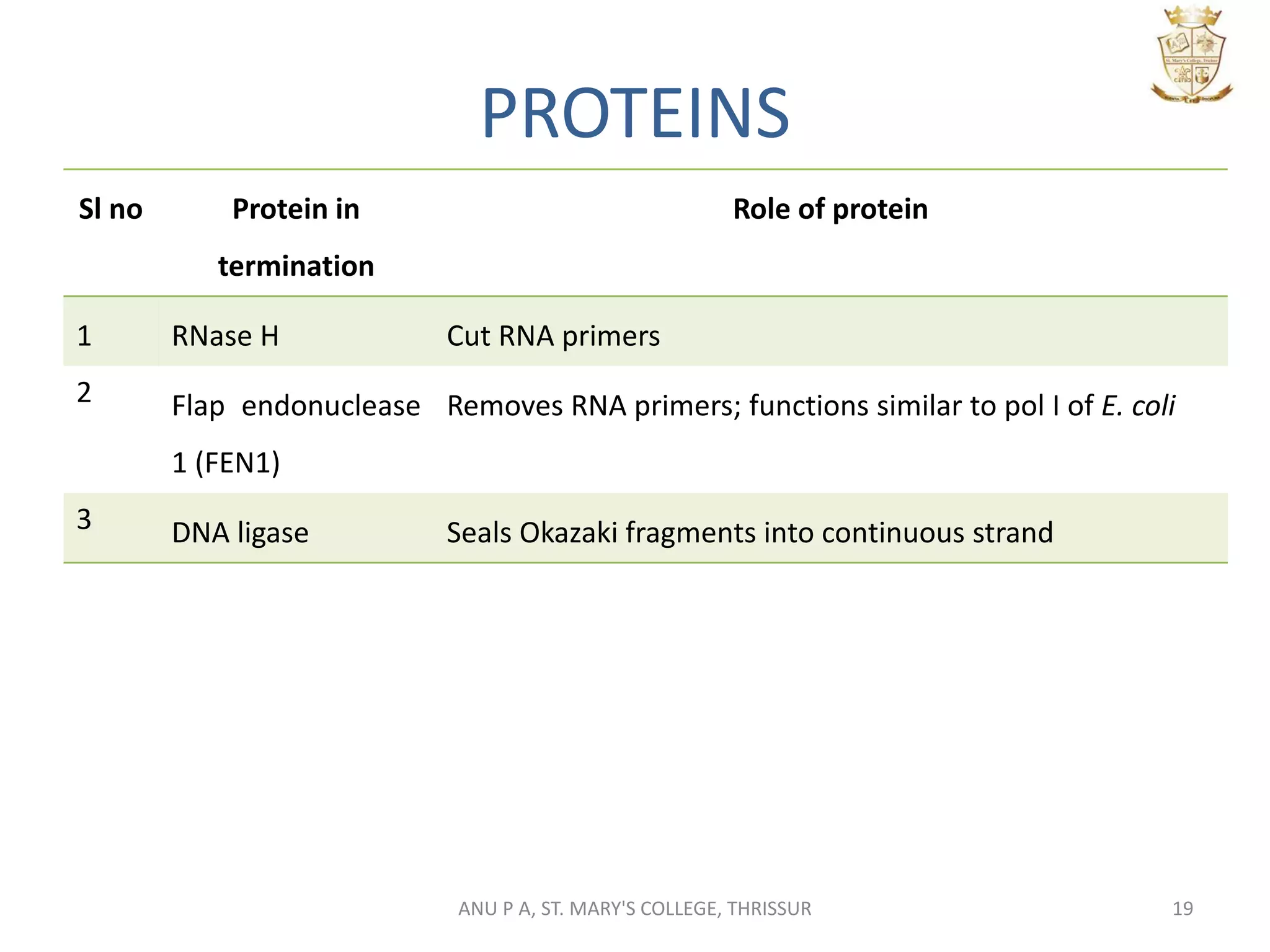
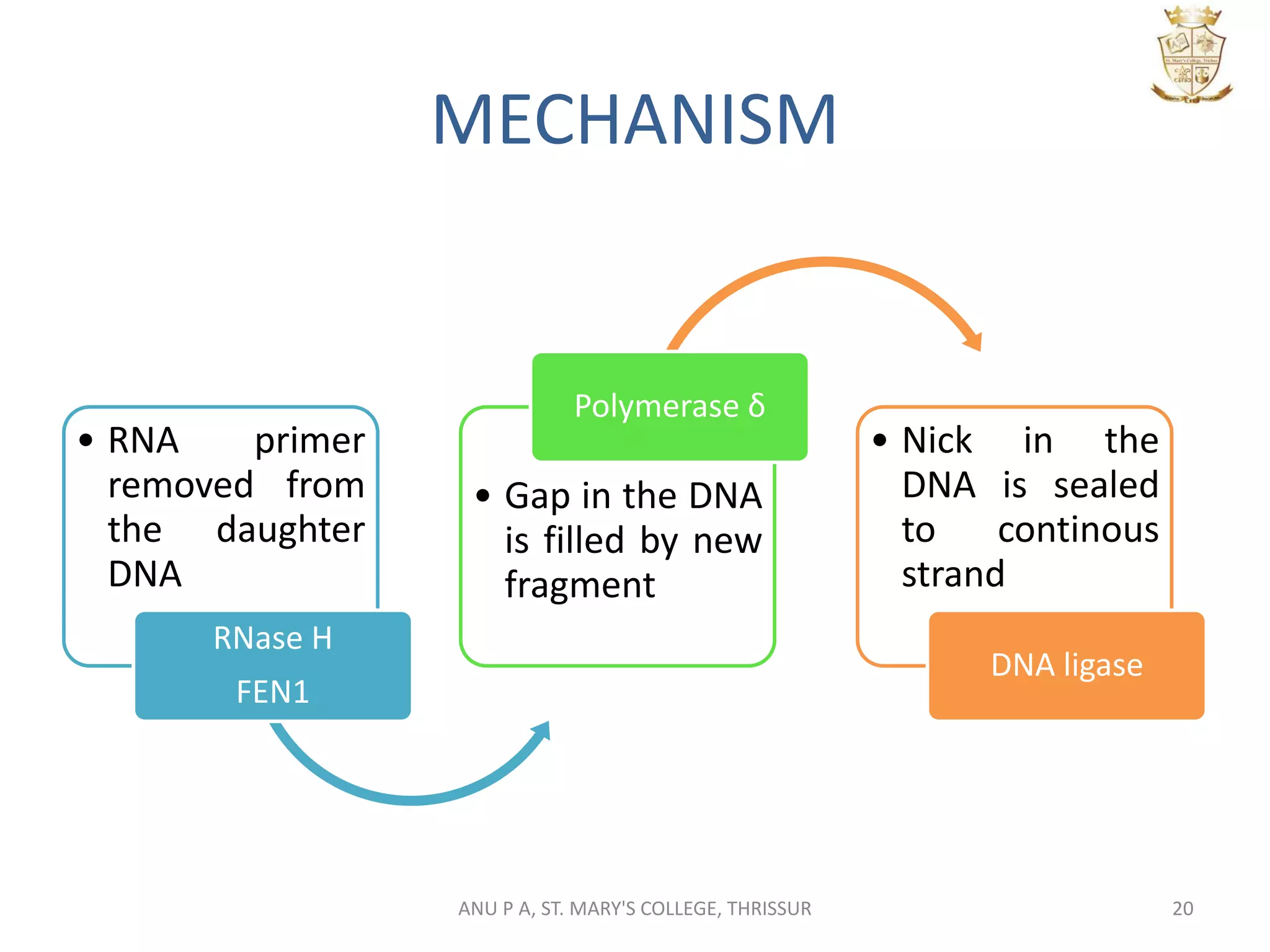
This document summarizes DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. It describes that replication occurs through replicons to overcome the slower polymerases. Replication is initiated at specific sites called autonomous replicating sequences (ARS) where the origin recognition complex (ORC) binds. Elongation uses DNA polymerases α, δ, and ε and occurs semi-discontinuously with Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand. Termination involves removing RNA primers with RNase H and sealing fragments with DNA ligase. Multiple enzymes are involved in each phase including MCM helicase, primase, DNA ligase, and DNA polymerases.