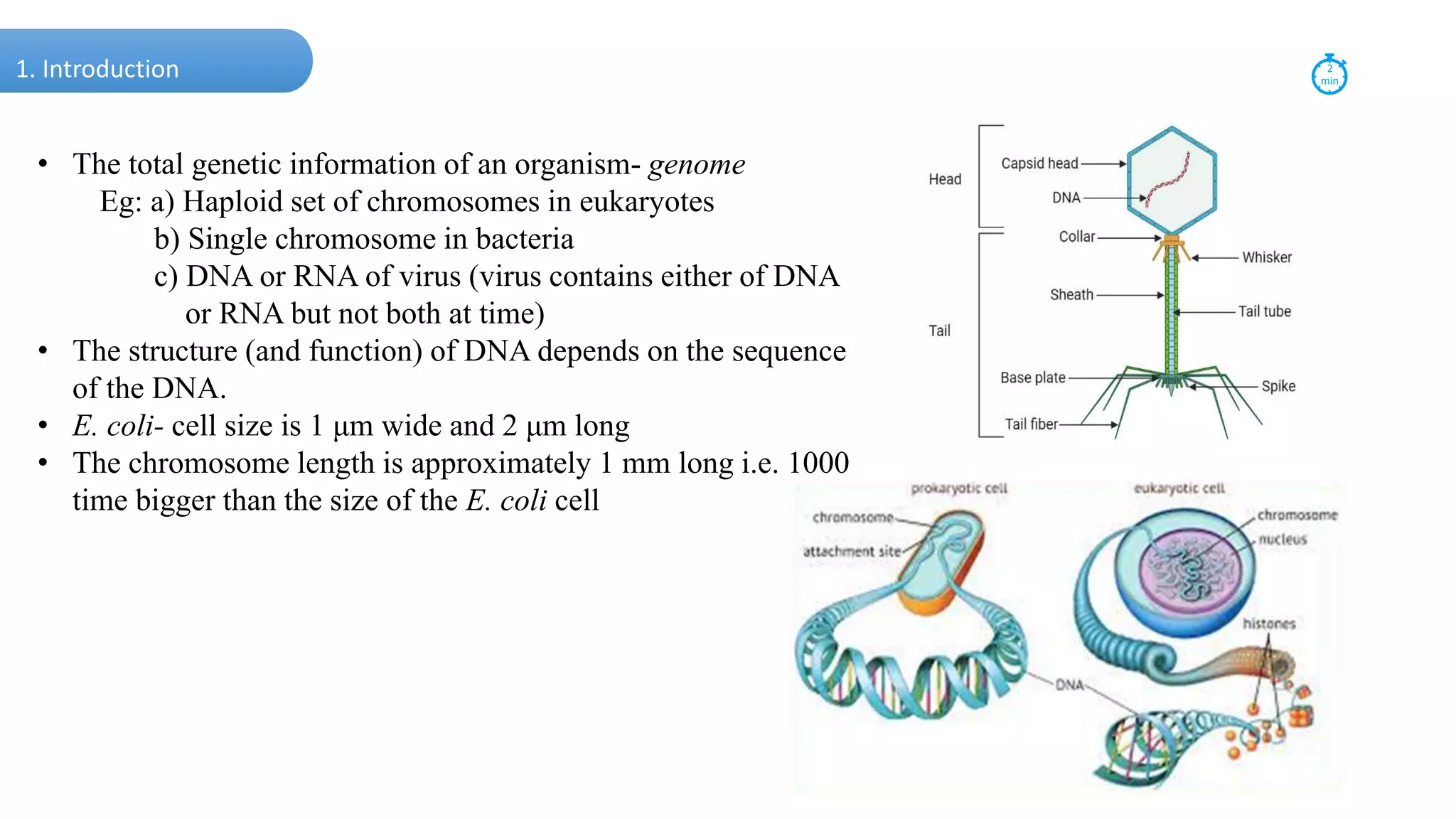
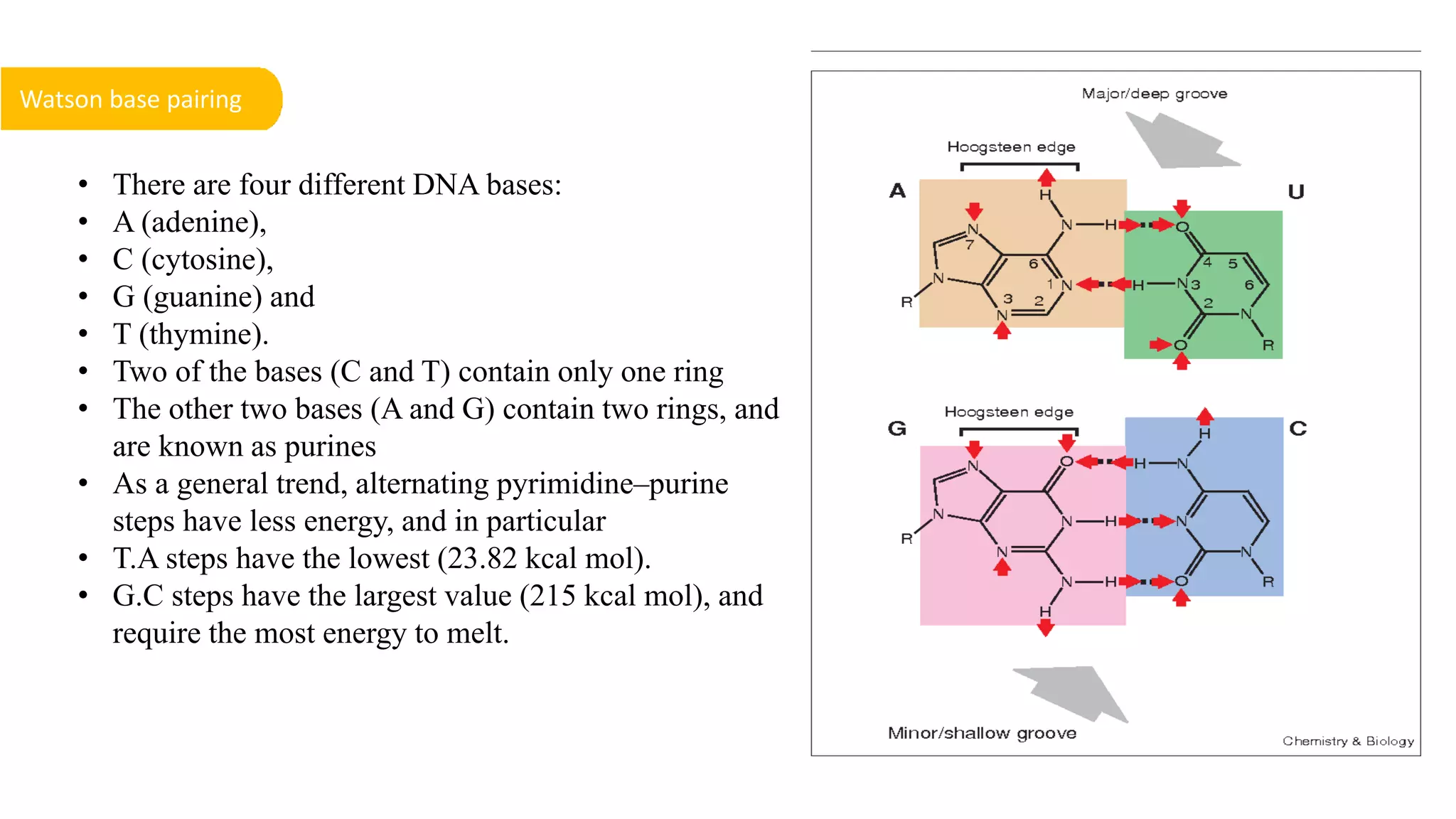
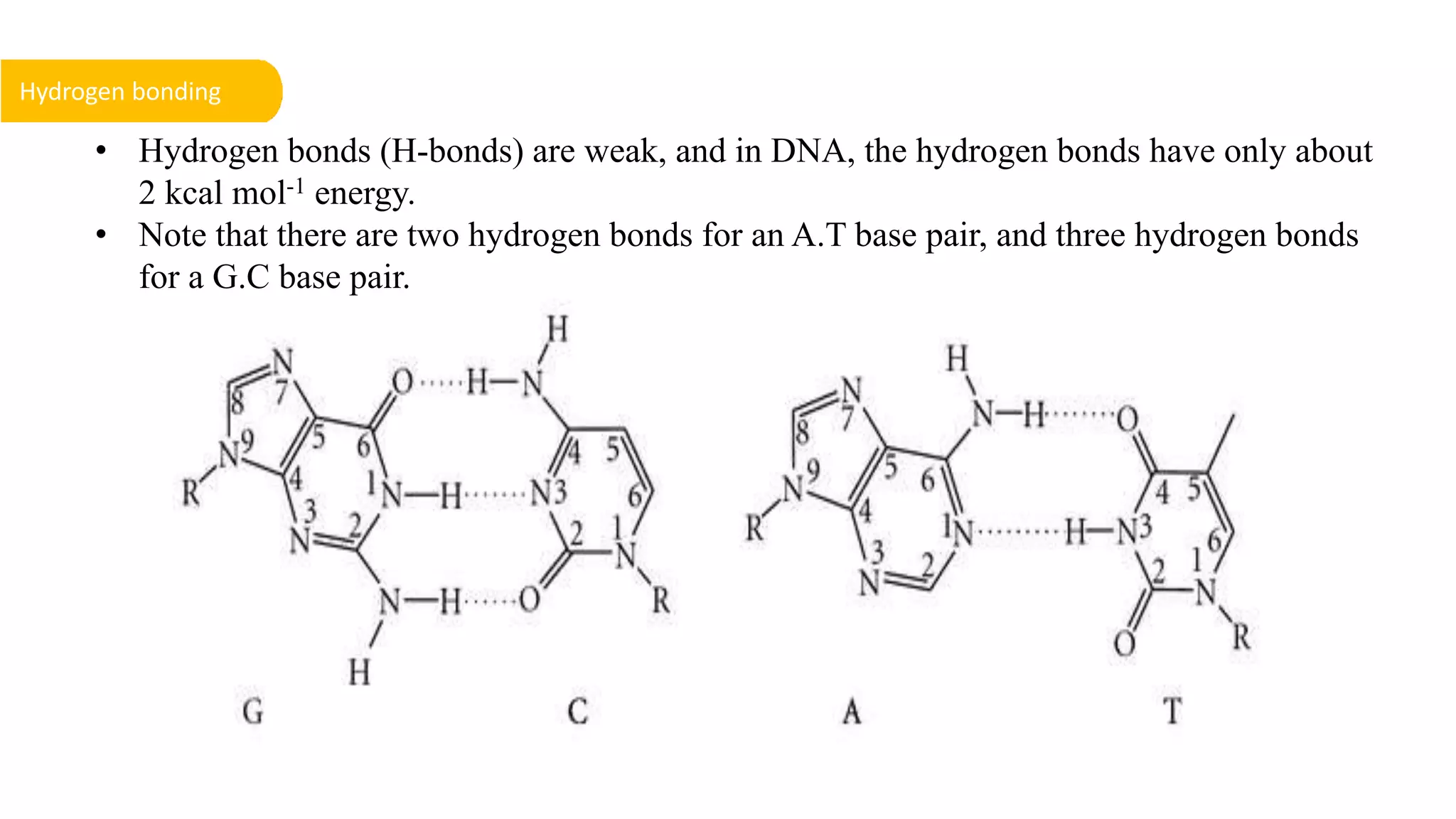
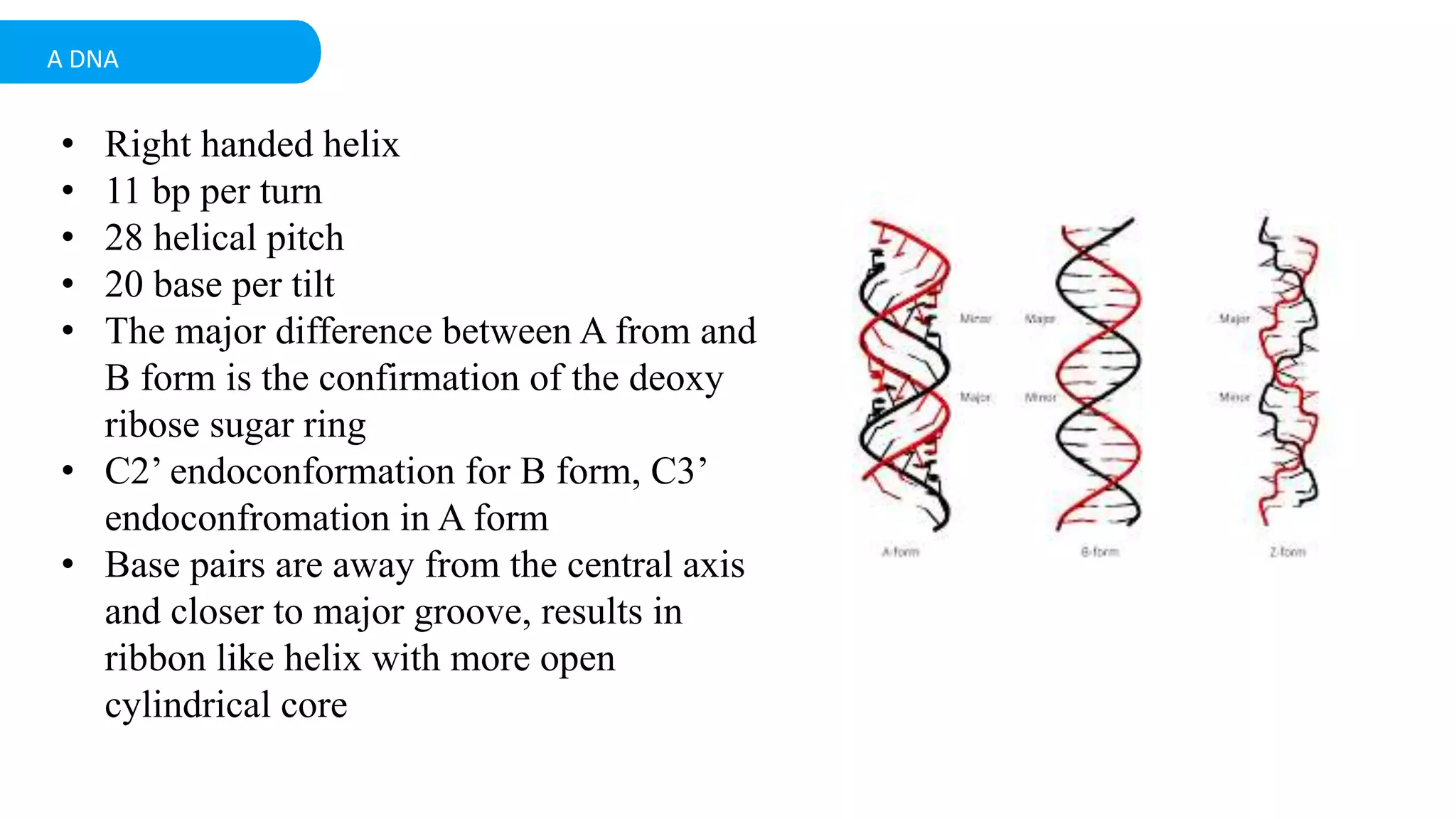
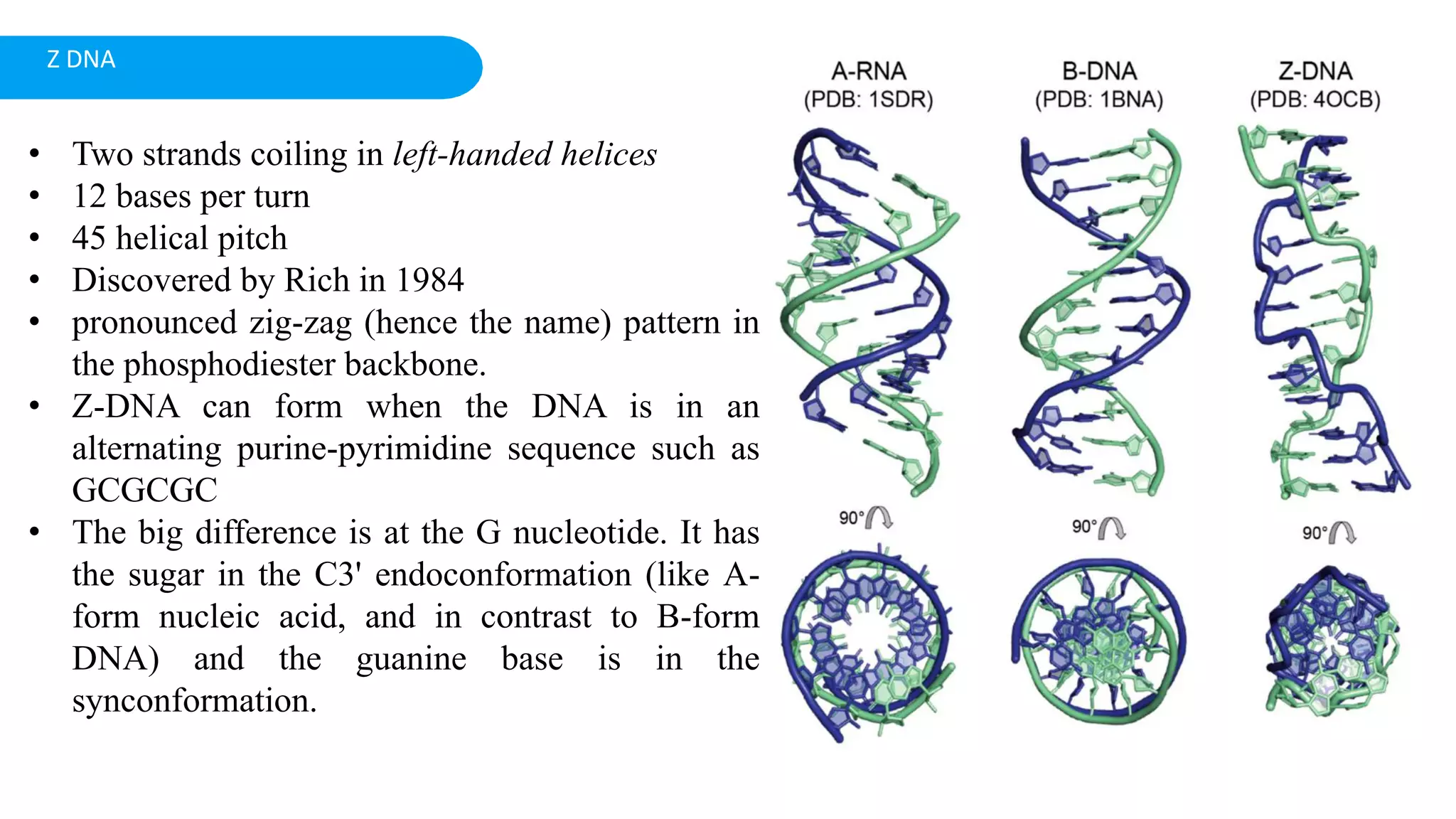
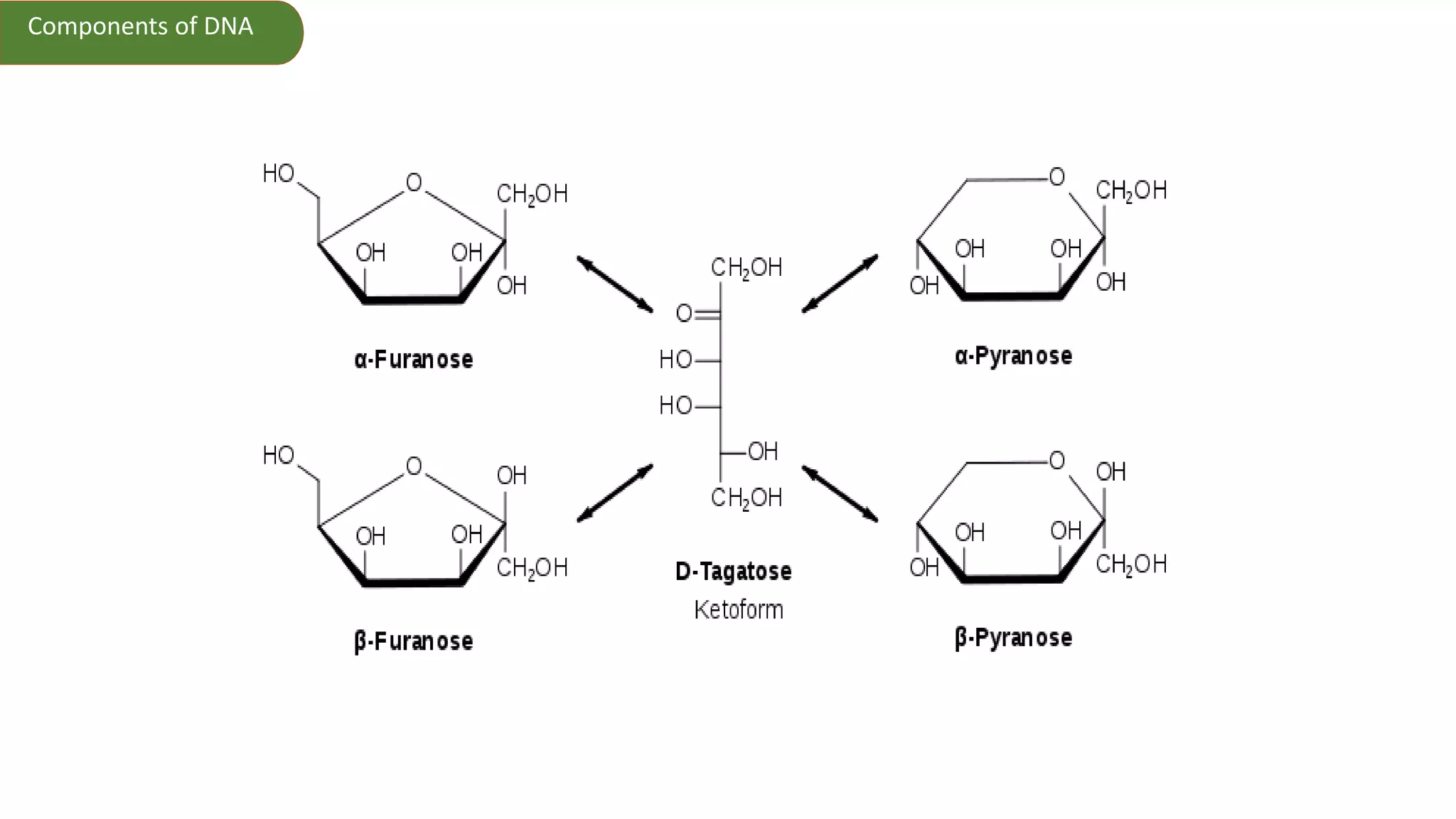
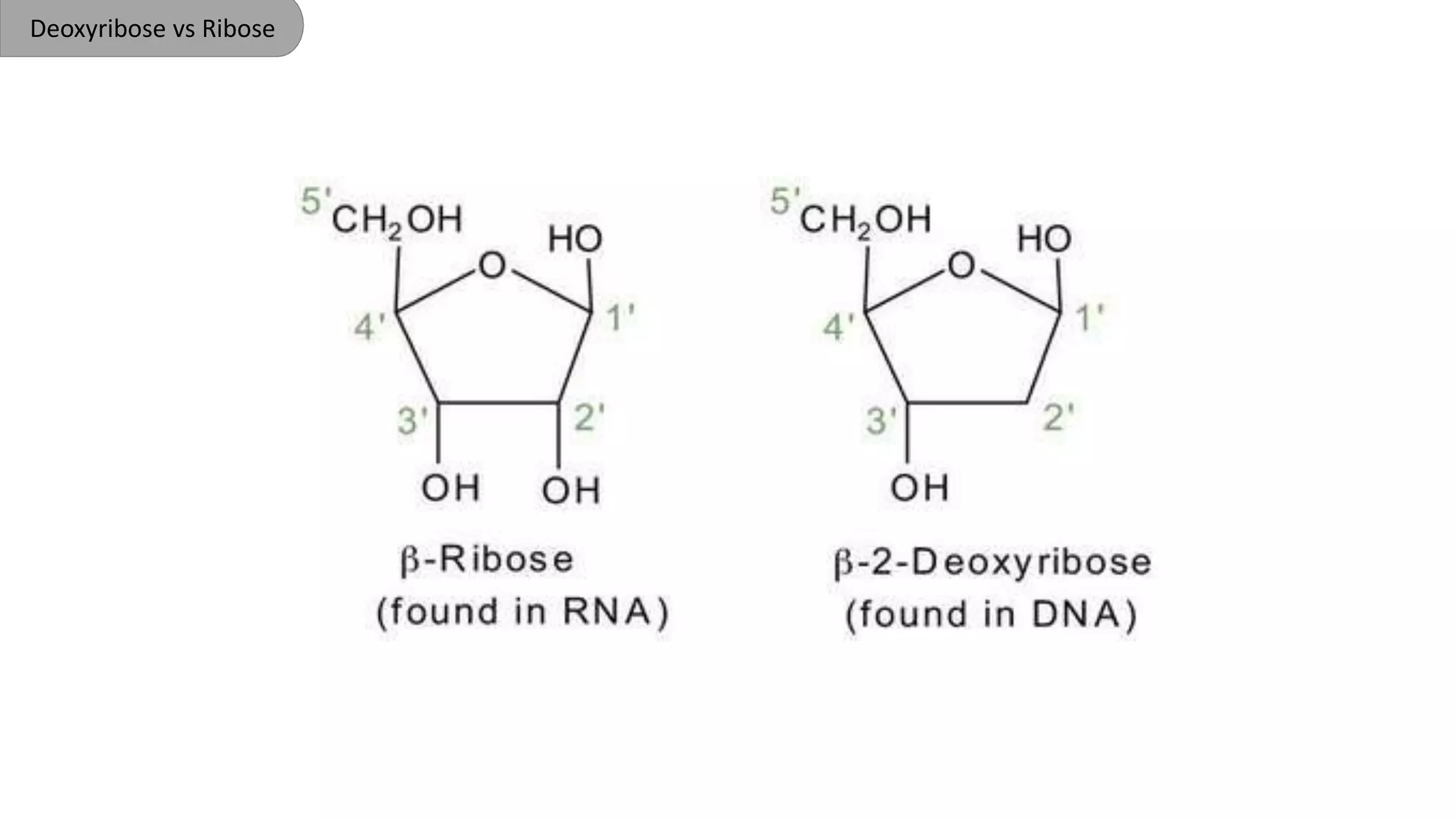
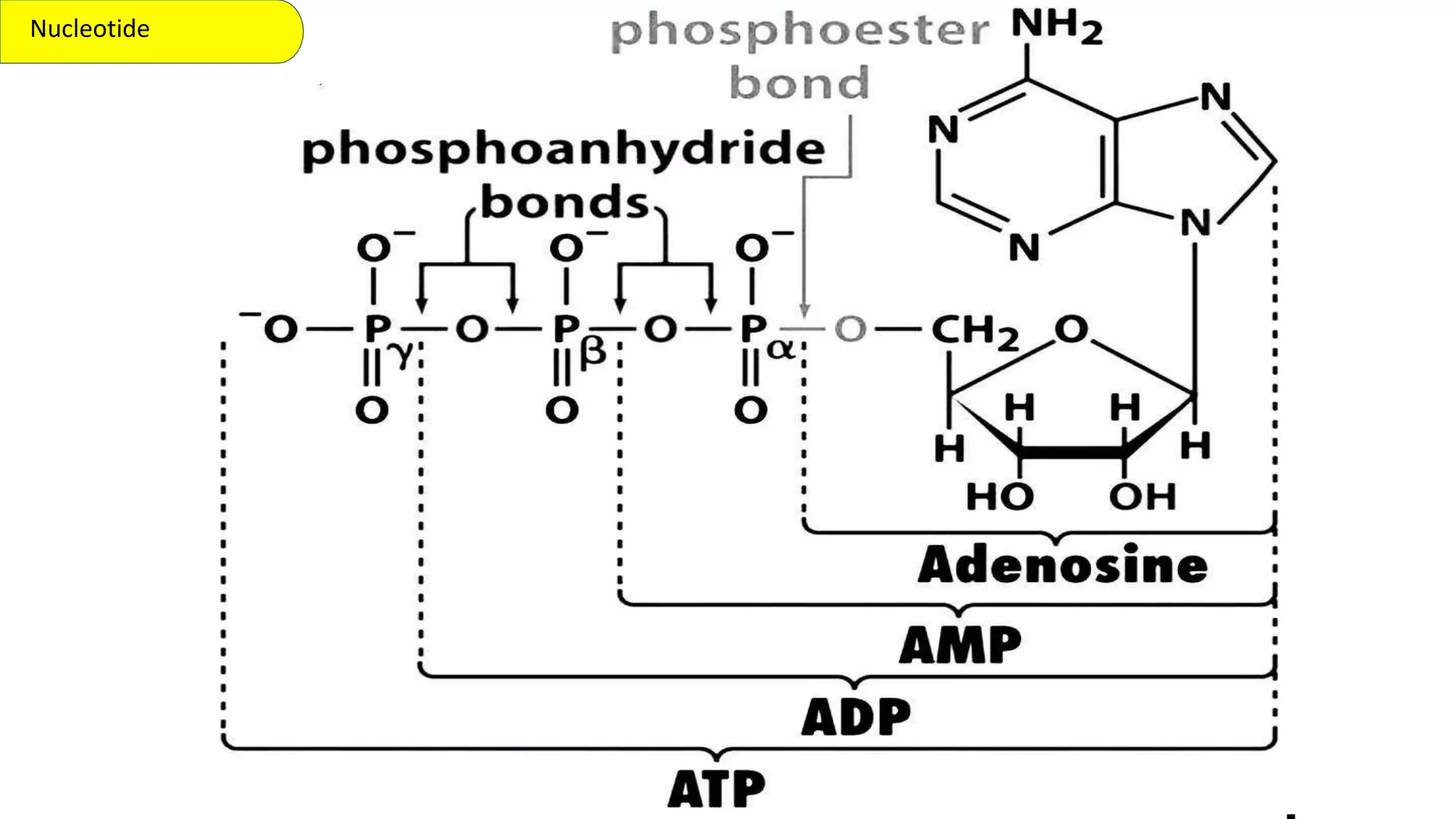
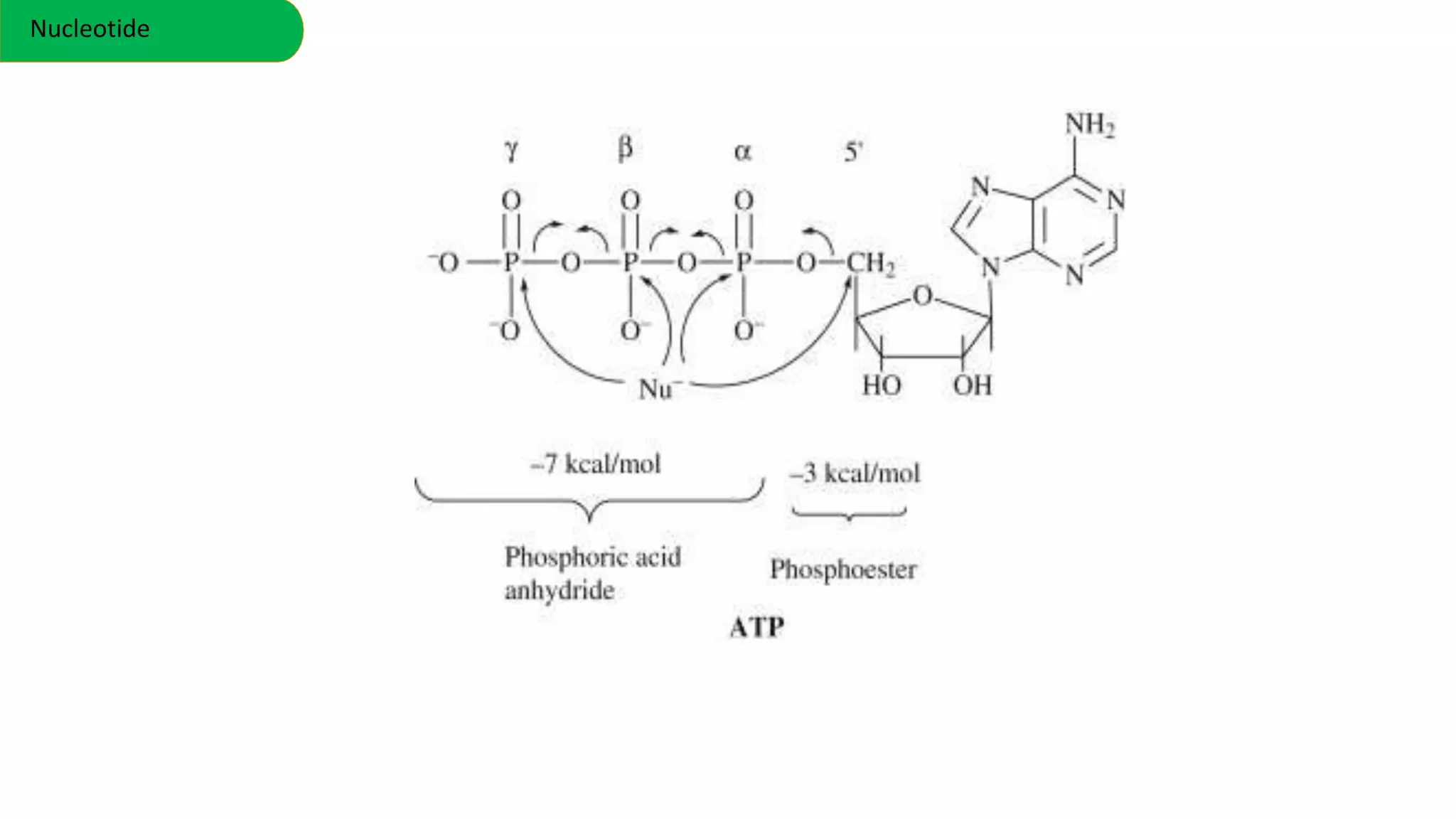
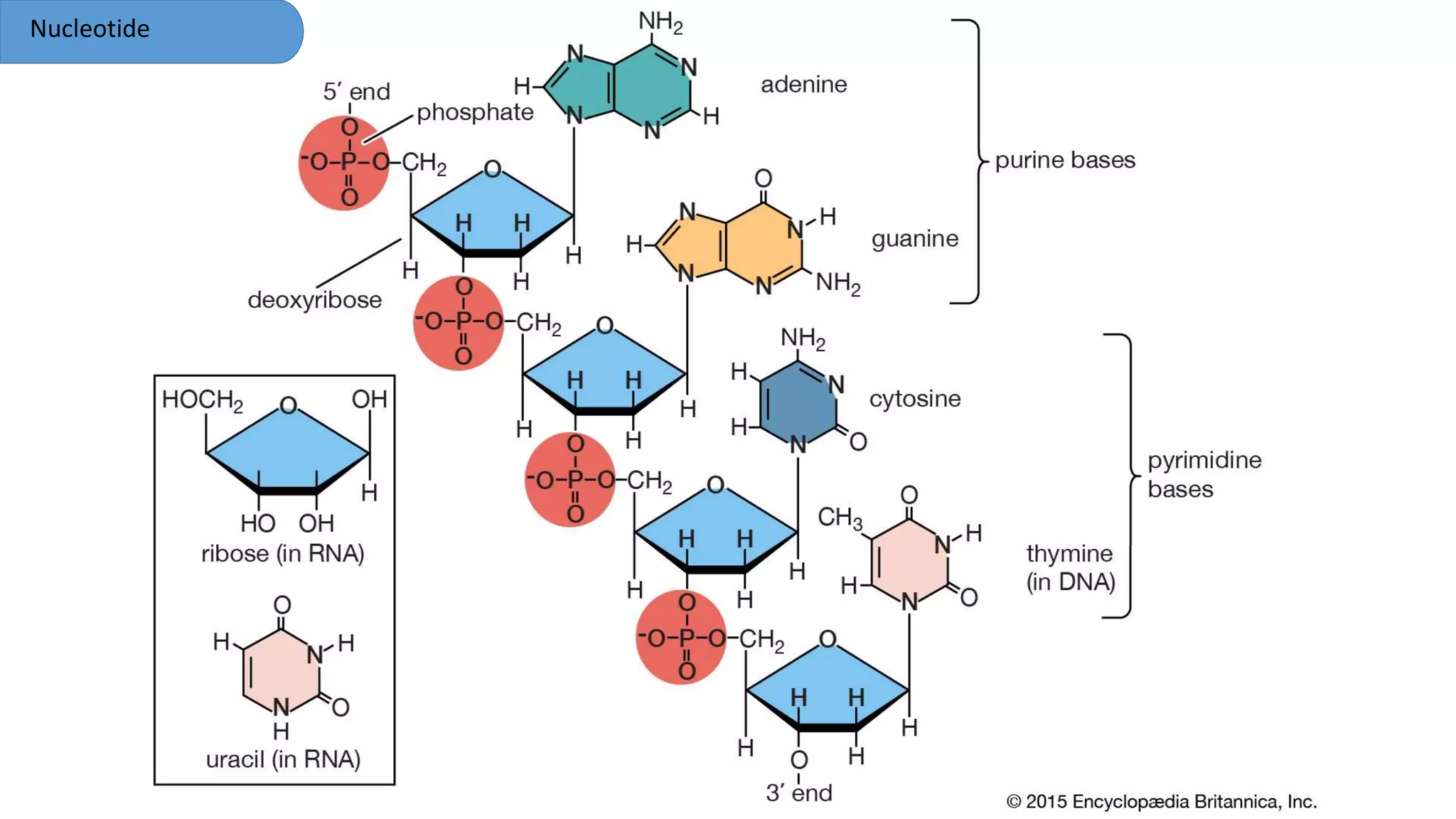
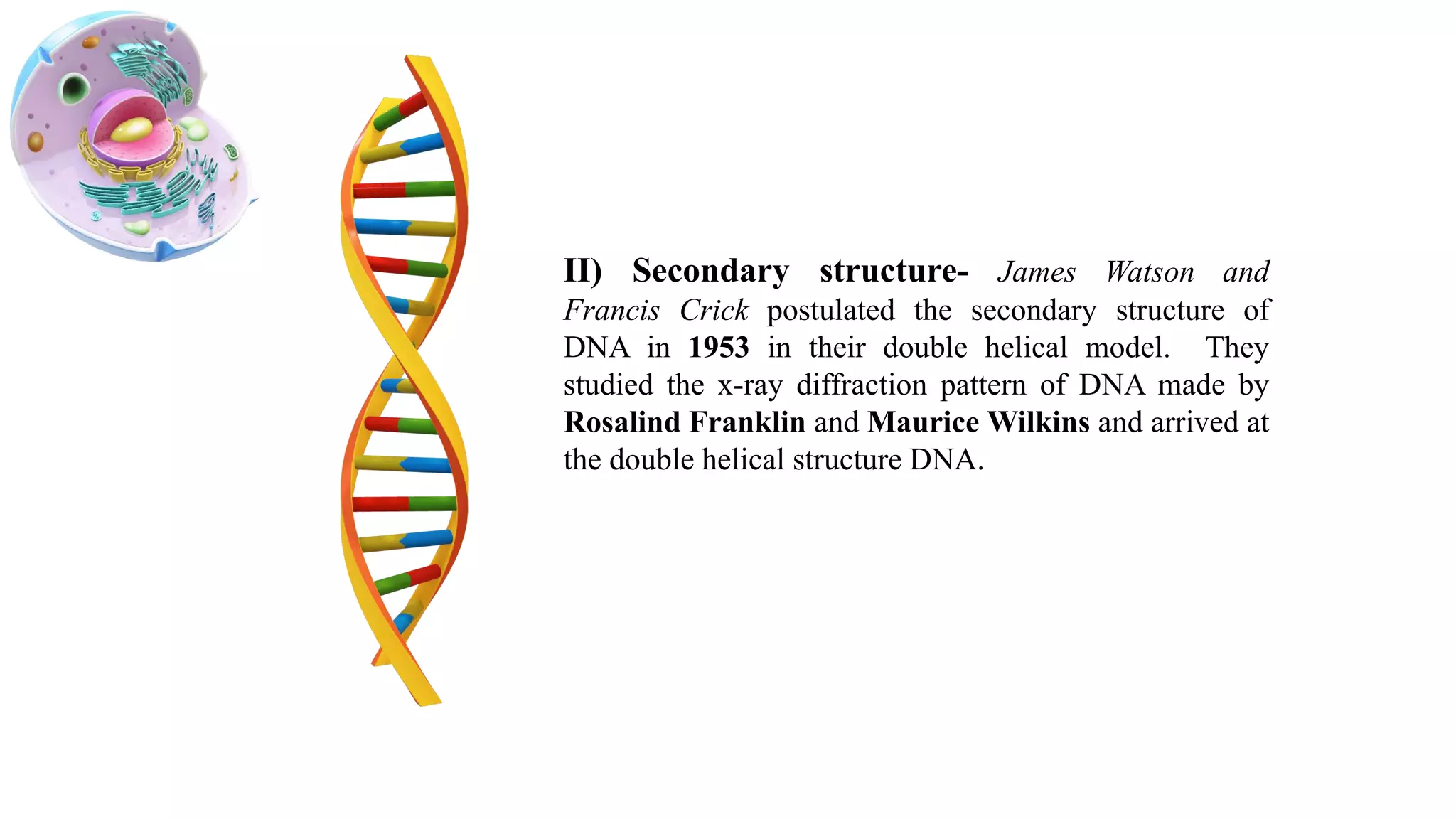
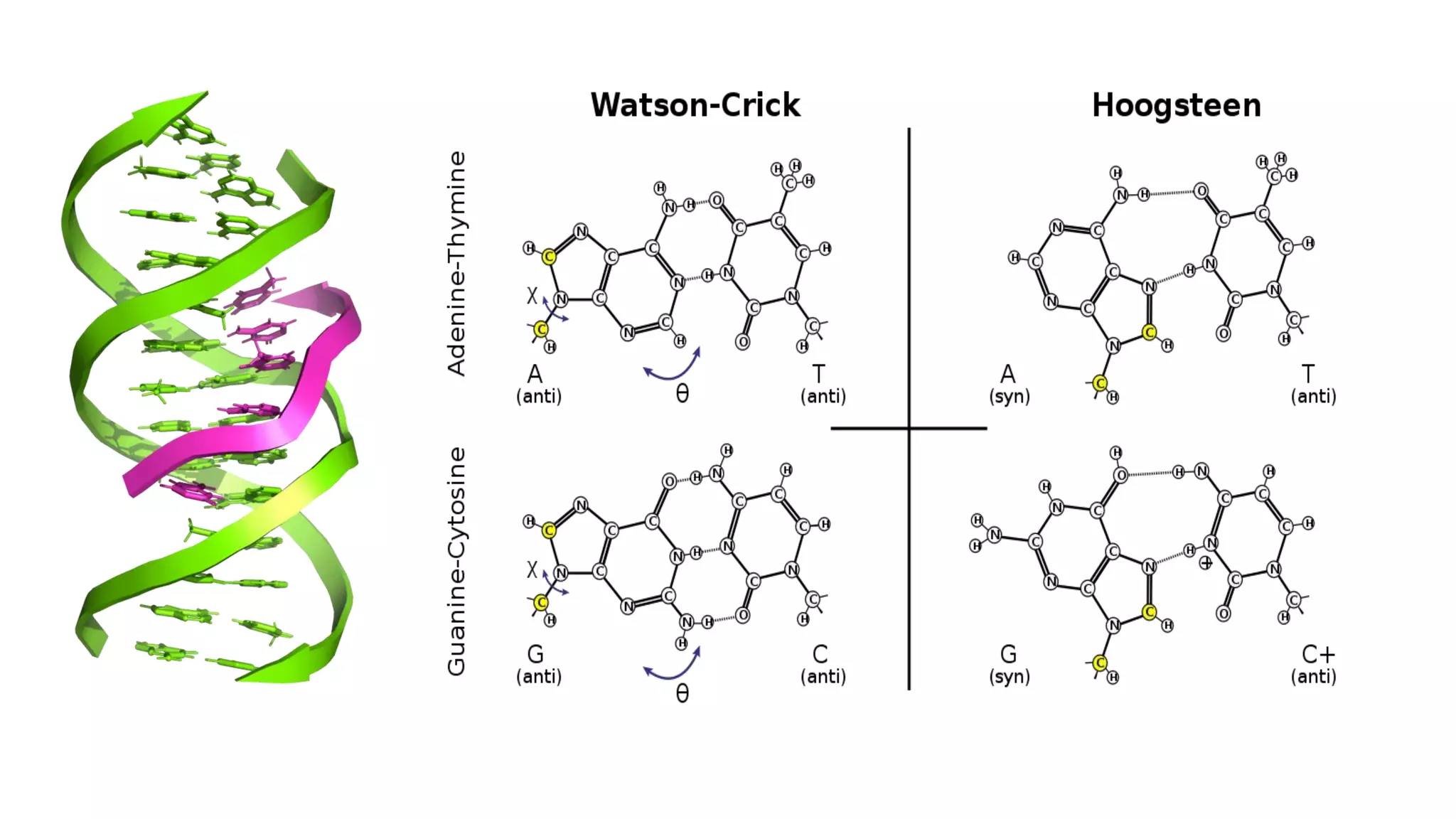
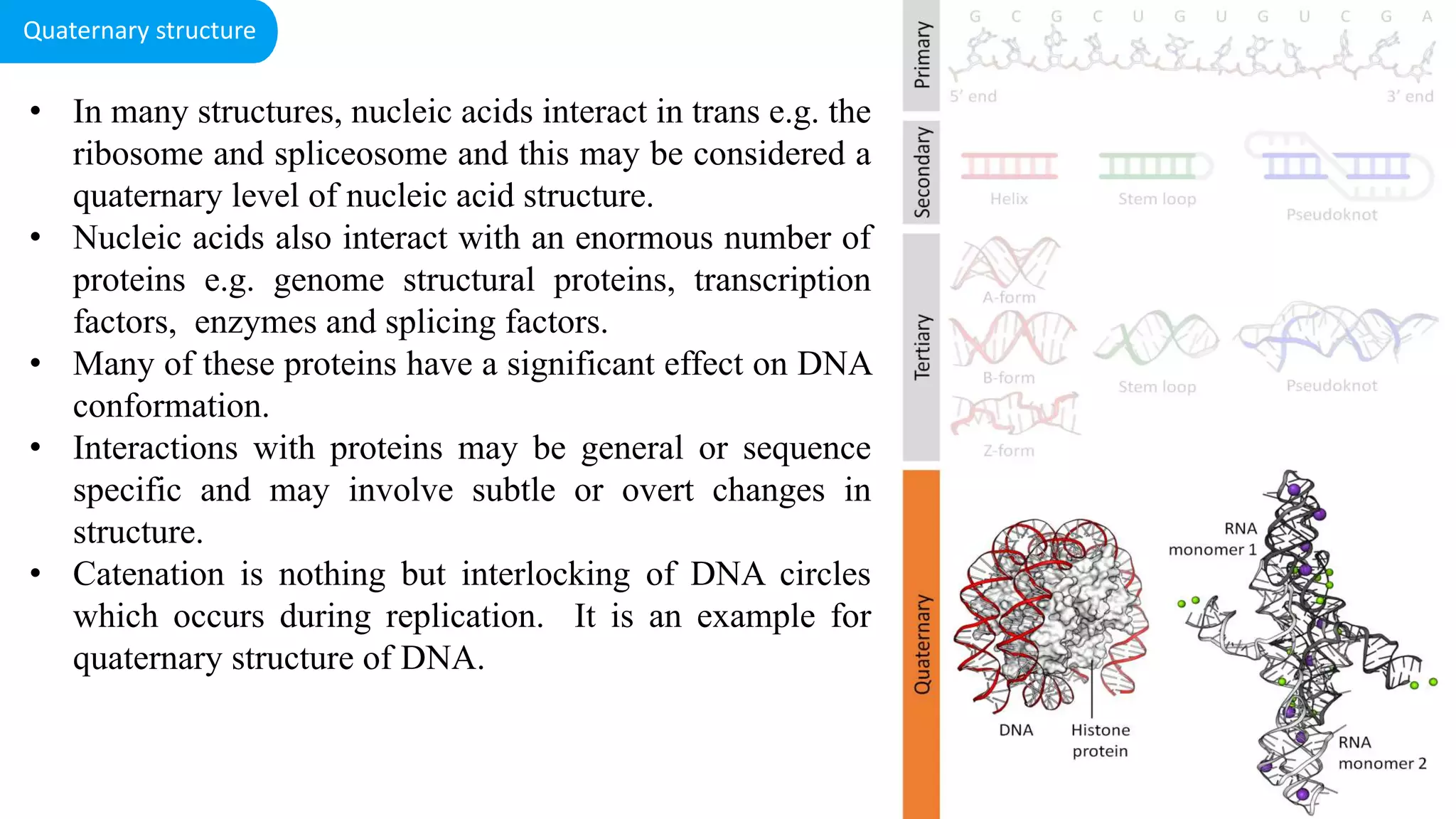
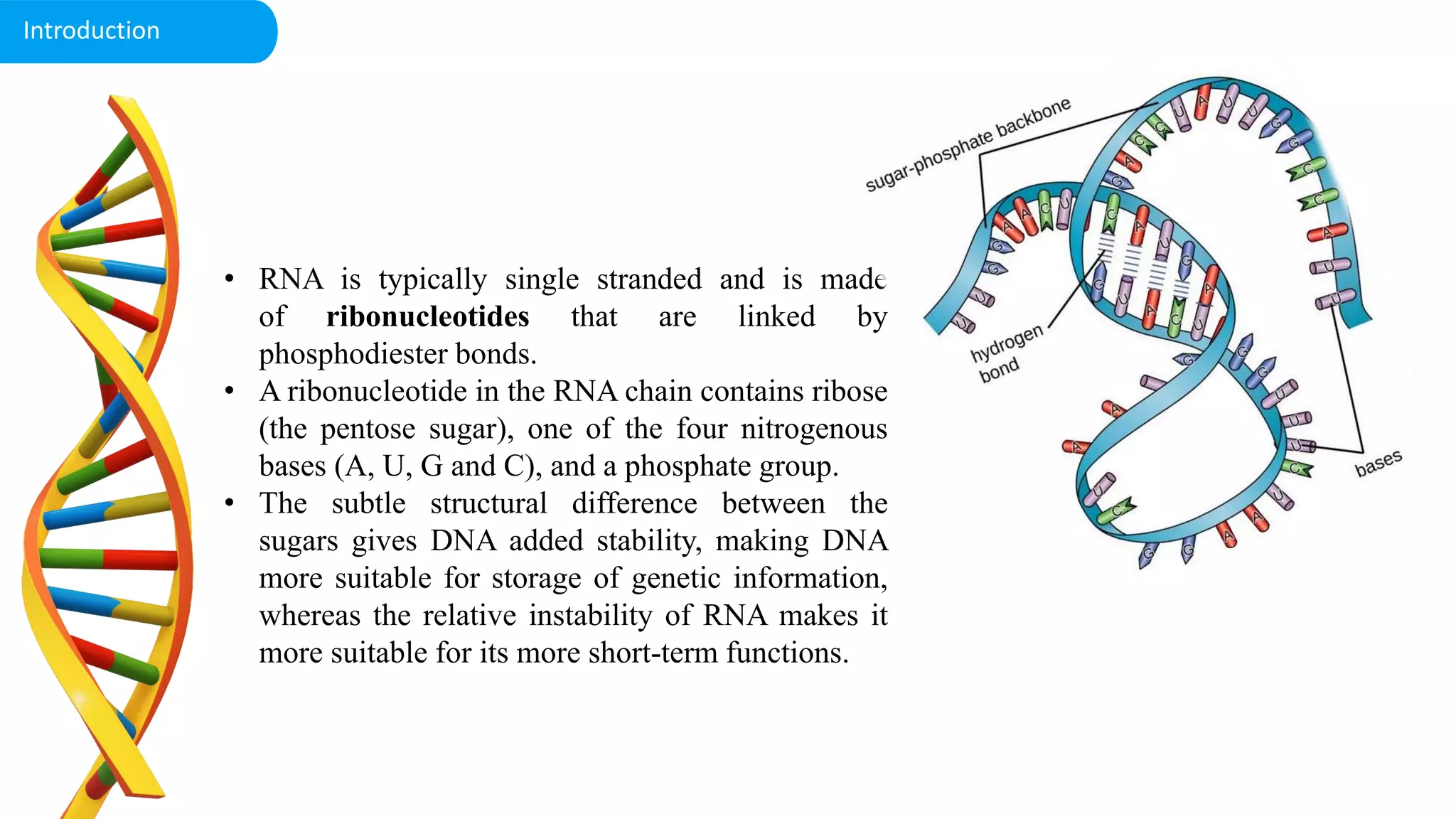
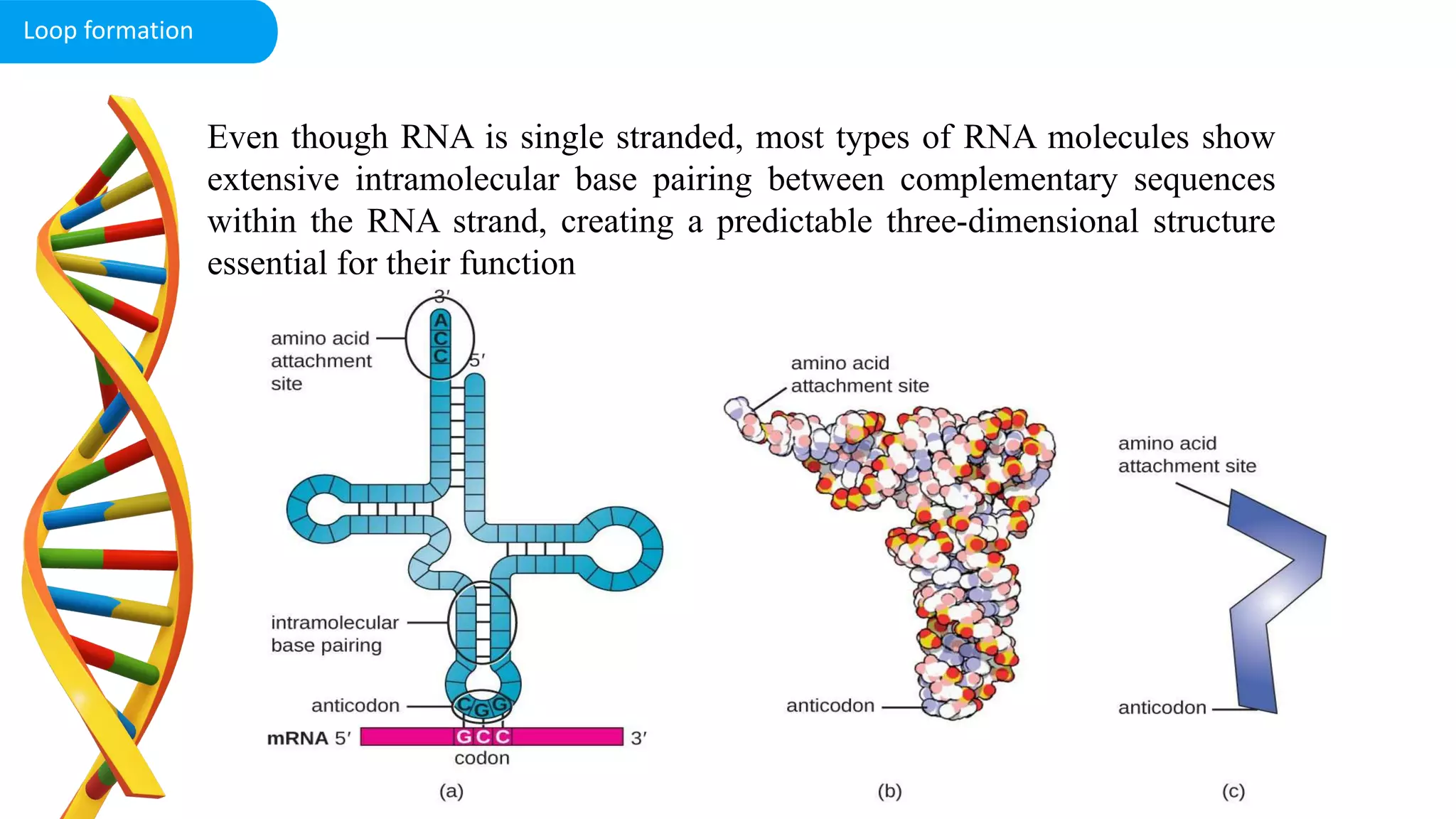
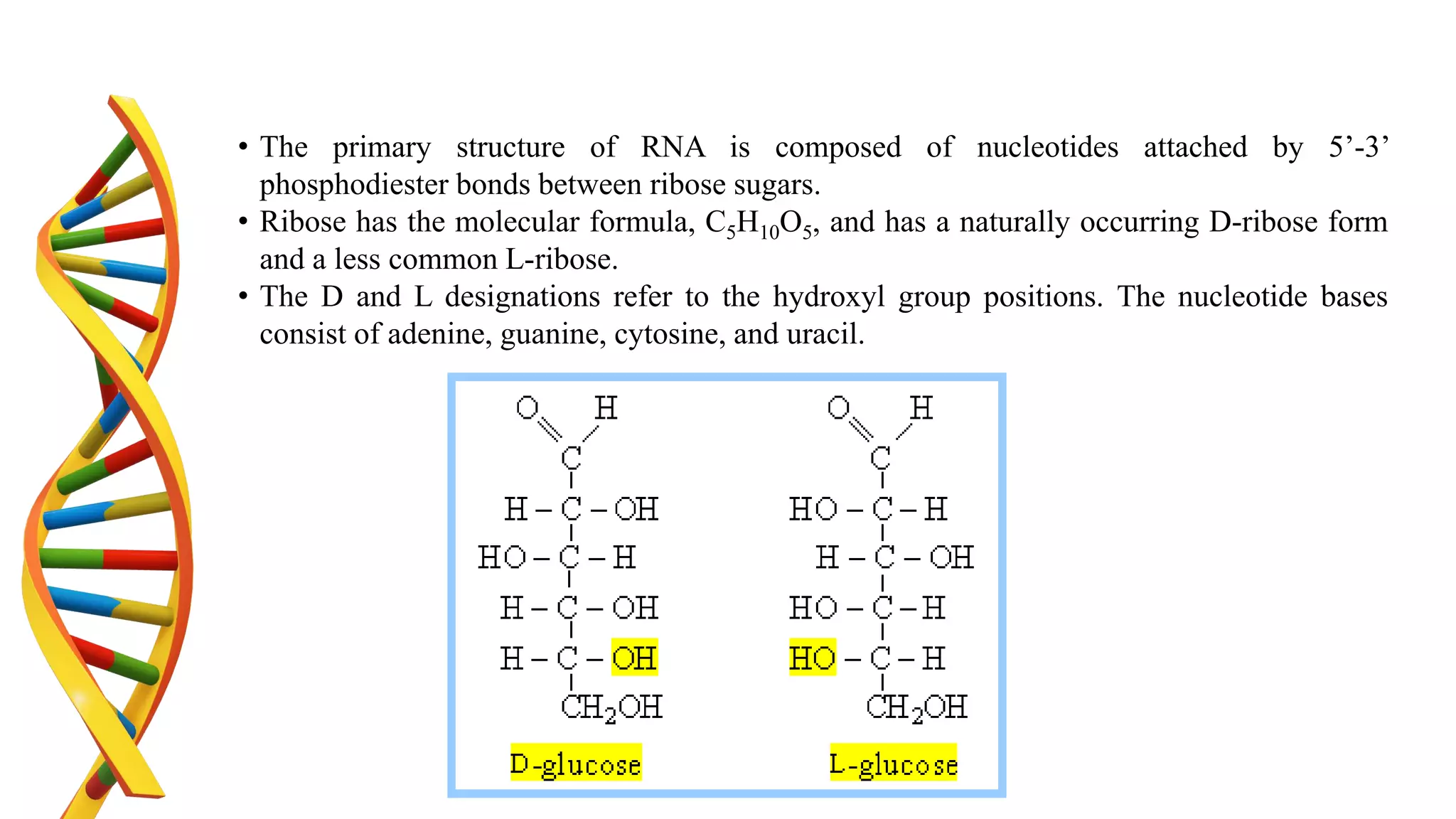
DNA is the genetic material found in cells. It exists in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in the form of a double helix composed of two strands bound together by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous base pairs. The four bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. DNA can take on different structures depending on its sequence and environment, including A, B, C, D, E, and Z forms. Eukaryotic DNA is linear and contained within the nucleus, while prokaryotic DNA exists as a single circular chromosome. RNA also exists as a single strand and plays important roles in protein synthesis and gene regulation.