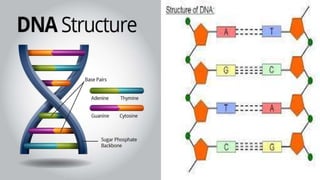
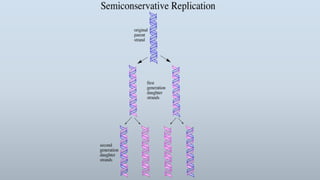
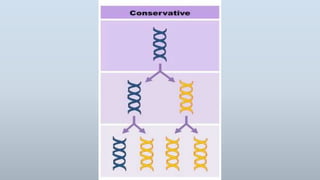
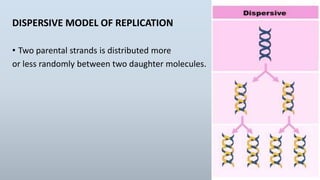
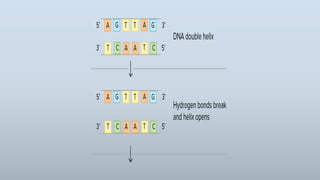
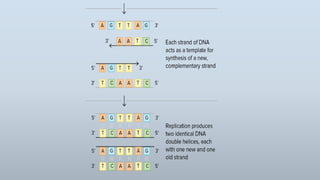
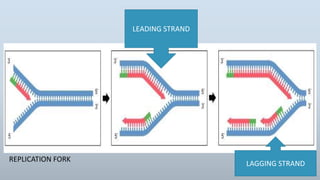
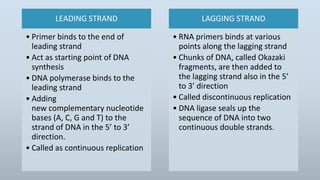
DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division. There are three models of DNA replication: semiconservative, conservative, and dispersive. In semiconservative replication, the two parental DNA strands separate and each acts as a template to make a new complementary strand, resulting in two double-stranded daughter molecules each with one original and one new strand. The steps of replication involve unwinding the DNA double helix, forming a replication fork, and synthesizing new strands in the 5' to 3' direction along the leading and lagging strands through the use of primers, DNA polymerase, and DNA ligase.