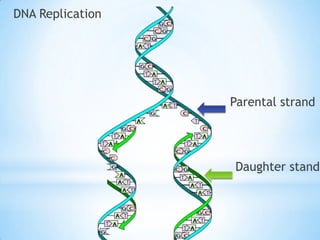
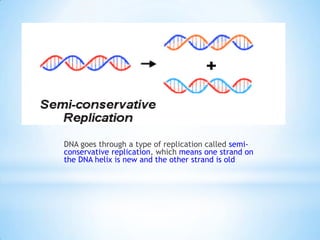
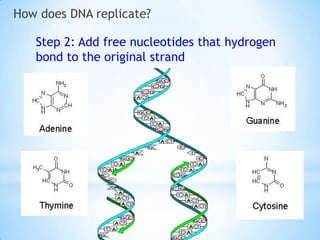
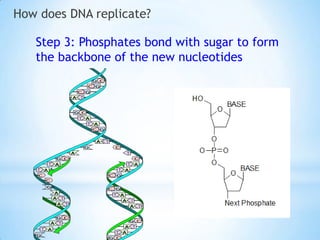
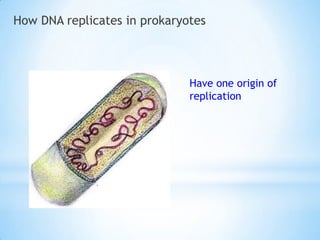
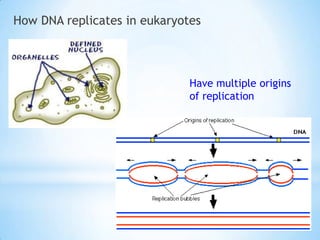
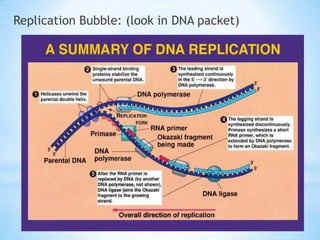
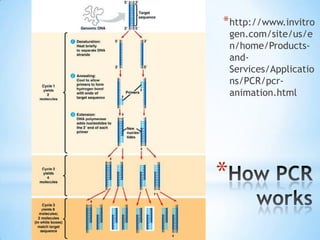
The document provides instructions for a DNA replication activity involving student teams competing to make copies of DNA strands using the fewest nucleotides. The objective is for each team to end up with two DNA strands taped to the whiteboard. Rules prohibit talking during the activity and allow two minutes for strategy discussion beforehand. The activity aims to demonstrate the speed of DNA replication in human versus bacterial cells.