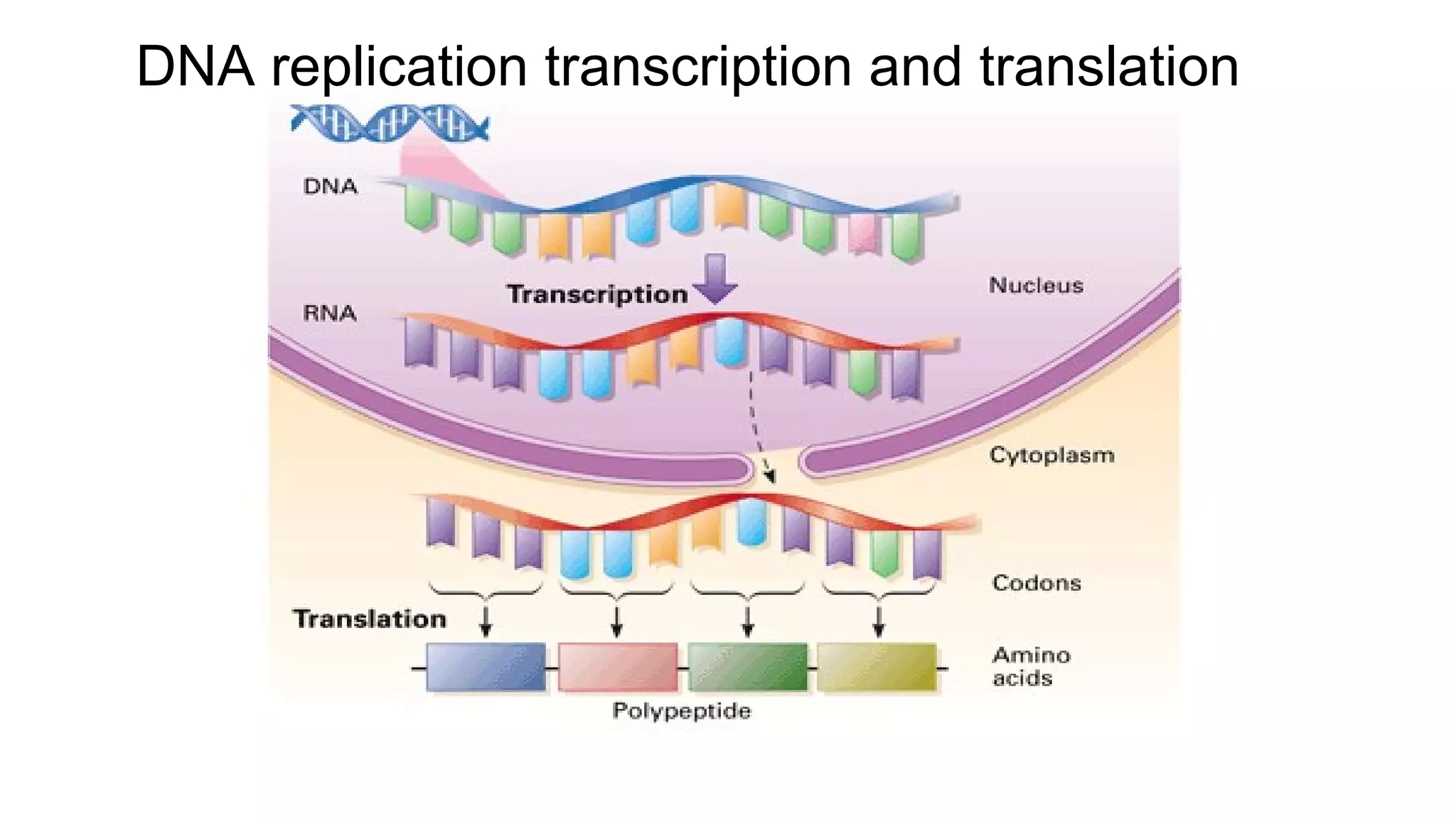
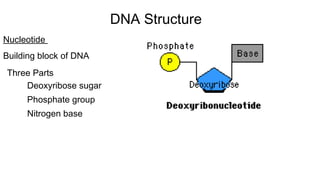
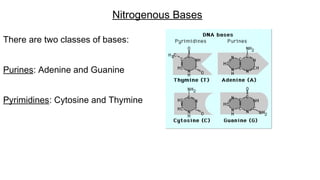
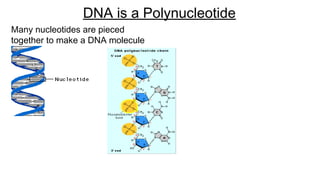
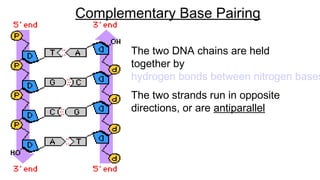
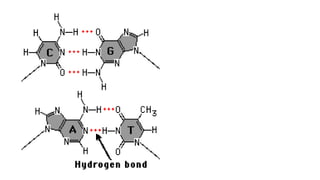
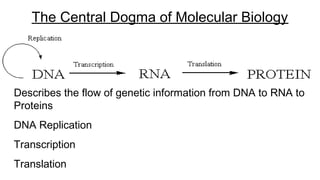
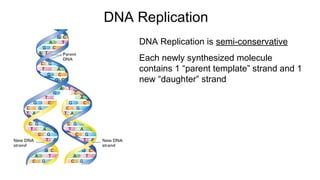
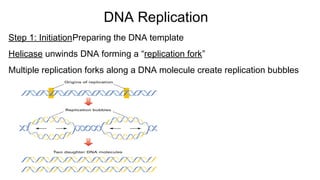
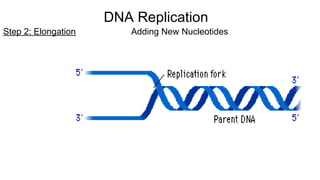
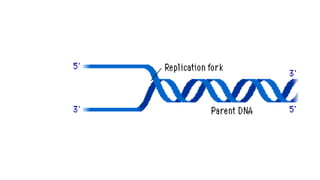
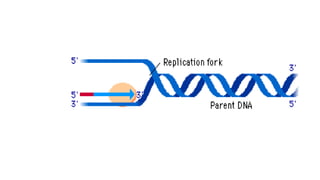
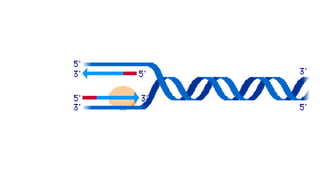
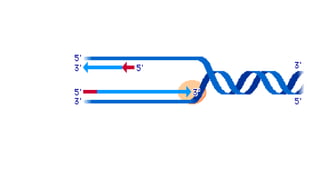
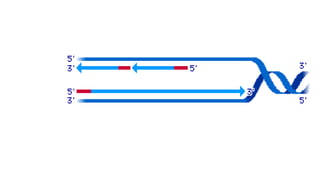
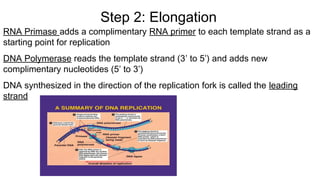
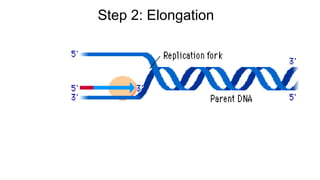
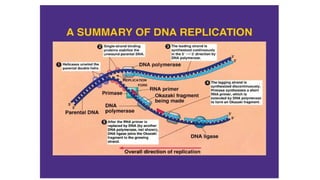
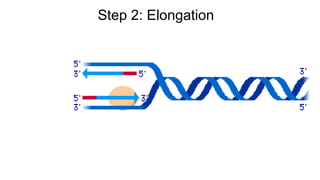
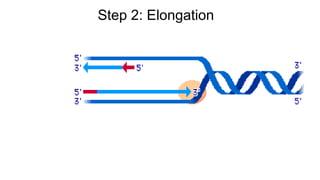
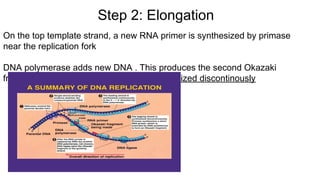
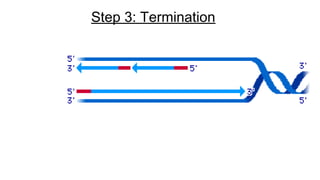
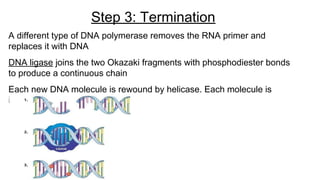
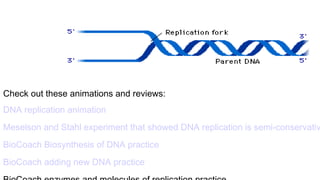
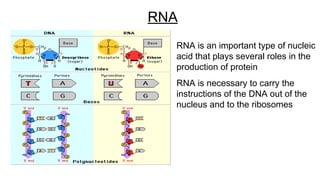
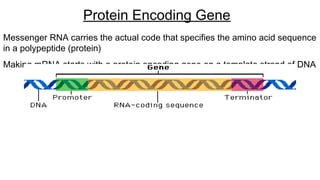
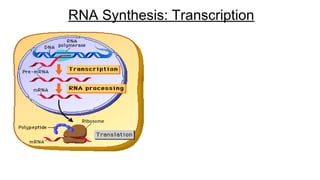
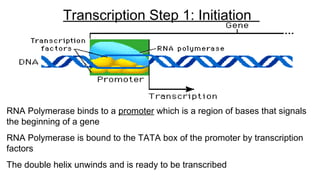
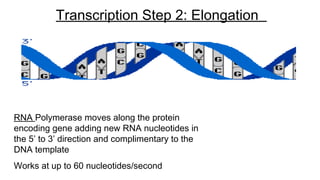
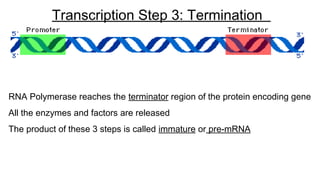
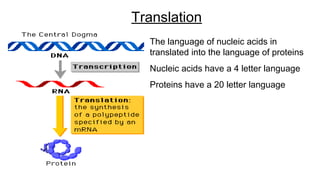
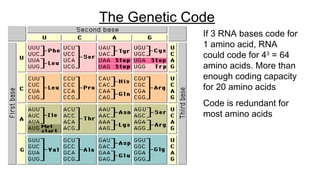
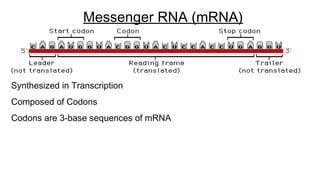
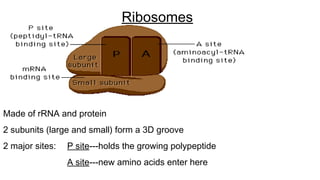
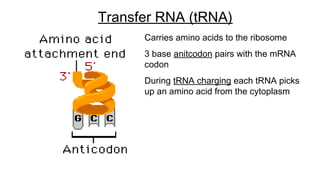
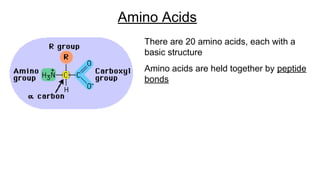
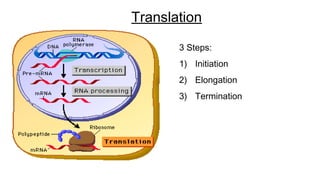
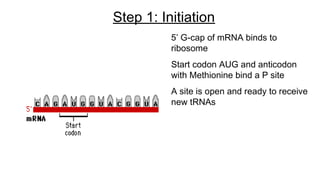
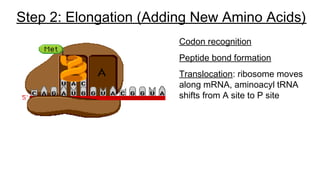
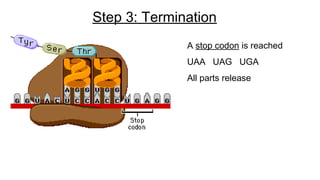
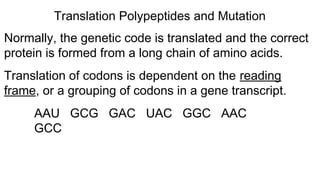
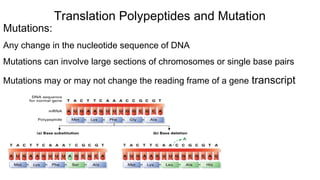
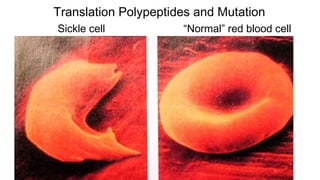
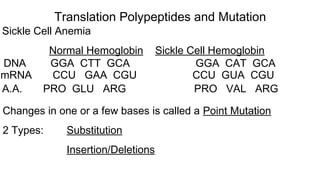
DNA is made up of nucleotides containing nitrogen bases, sugars and phosphates. The bases on two DNA strands bond together through complementary base pairing between adenine and thymine, and cytosine and guanine. DNA replicates semi-conservatively through initiation, elongation, and termination steps. RNA carries instructions from DNA for protein production. Transcription involves RNA polymerase making mRNA from DNA. Translation uses mRNA, tRNAs, and ribosomes to assemble amino acids into proteins according to the genetic code of three-base codons. Mutations in DNA can alter codons and cause changes in protein sequences.