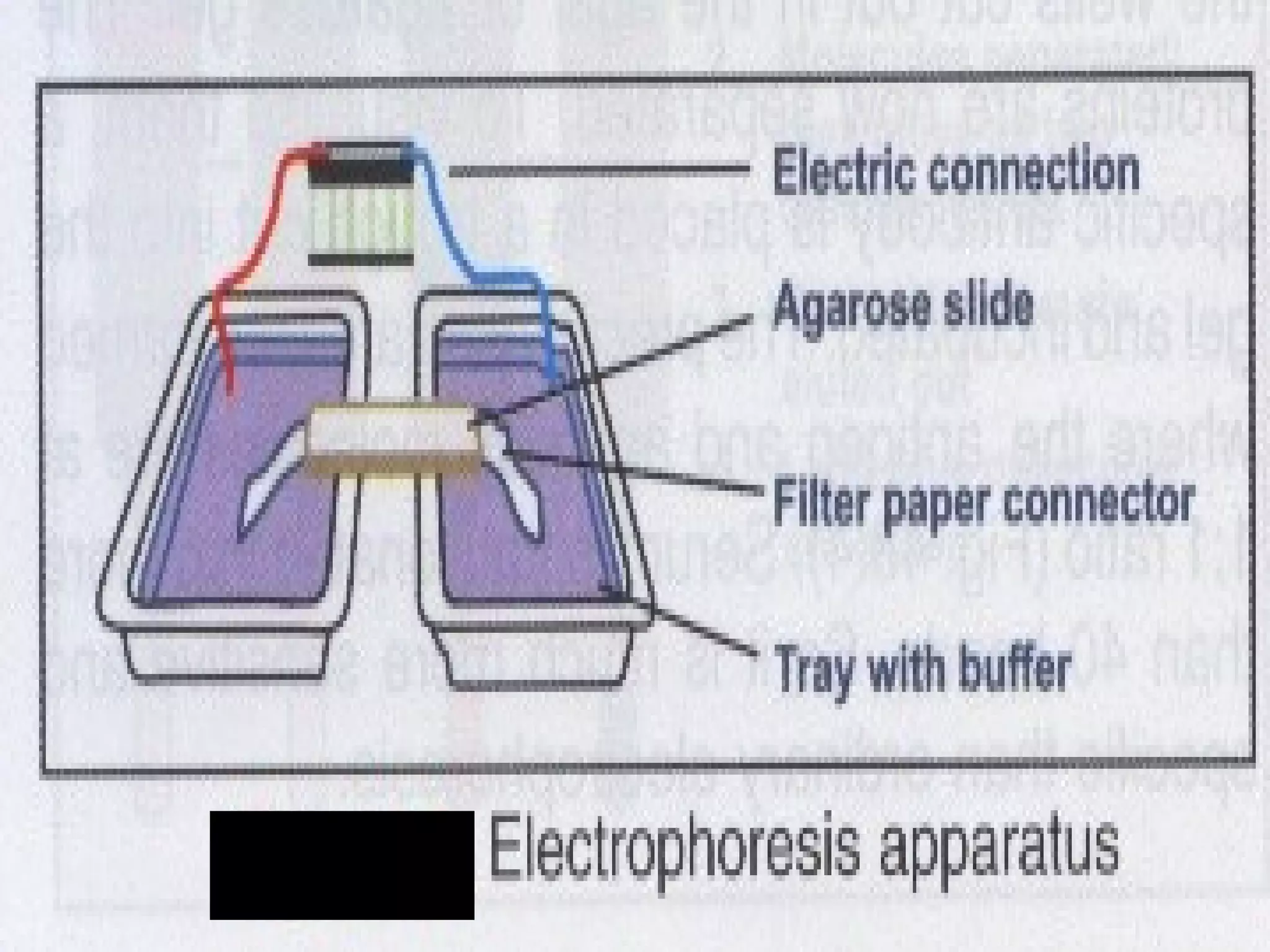
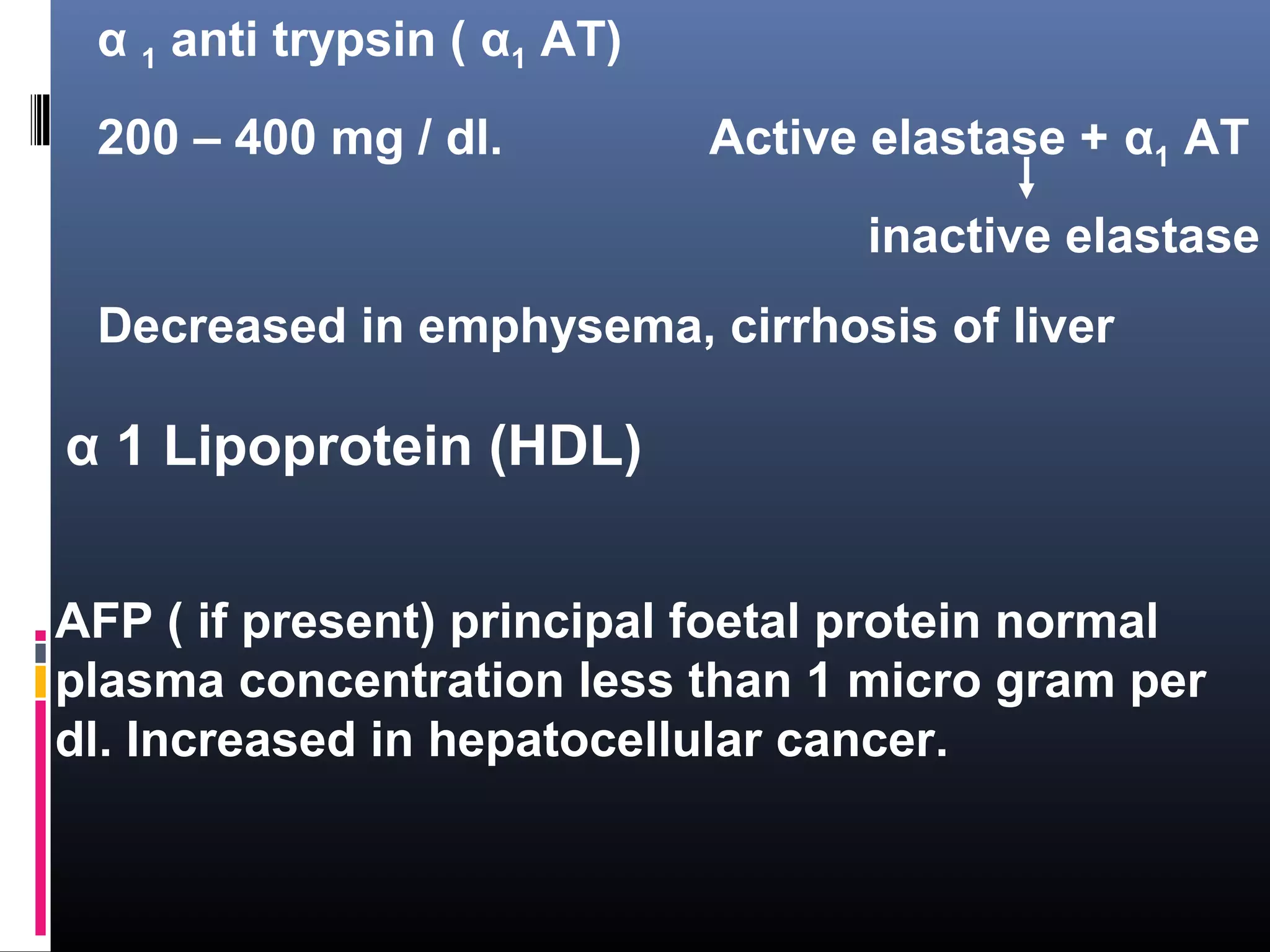
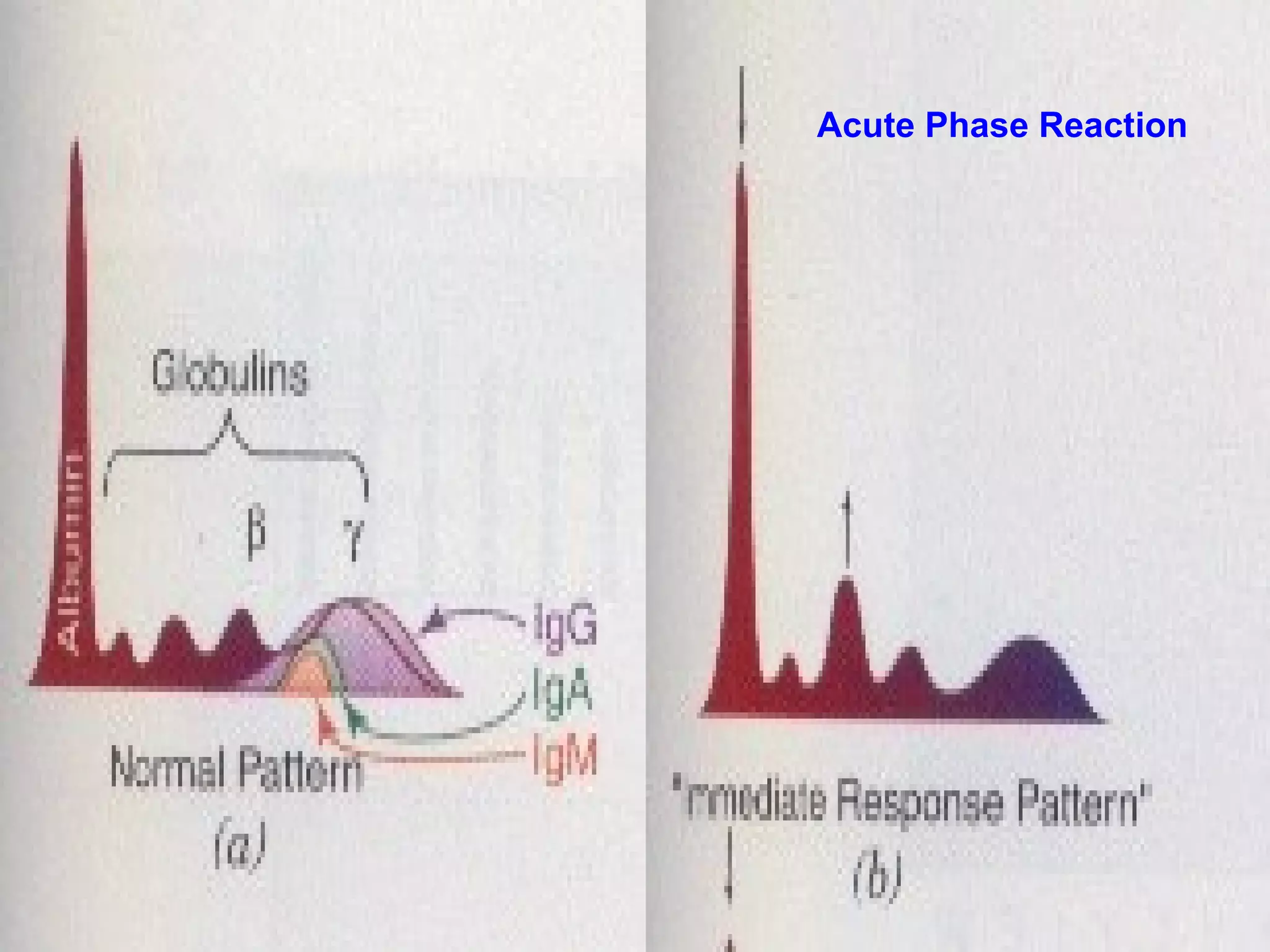
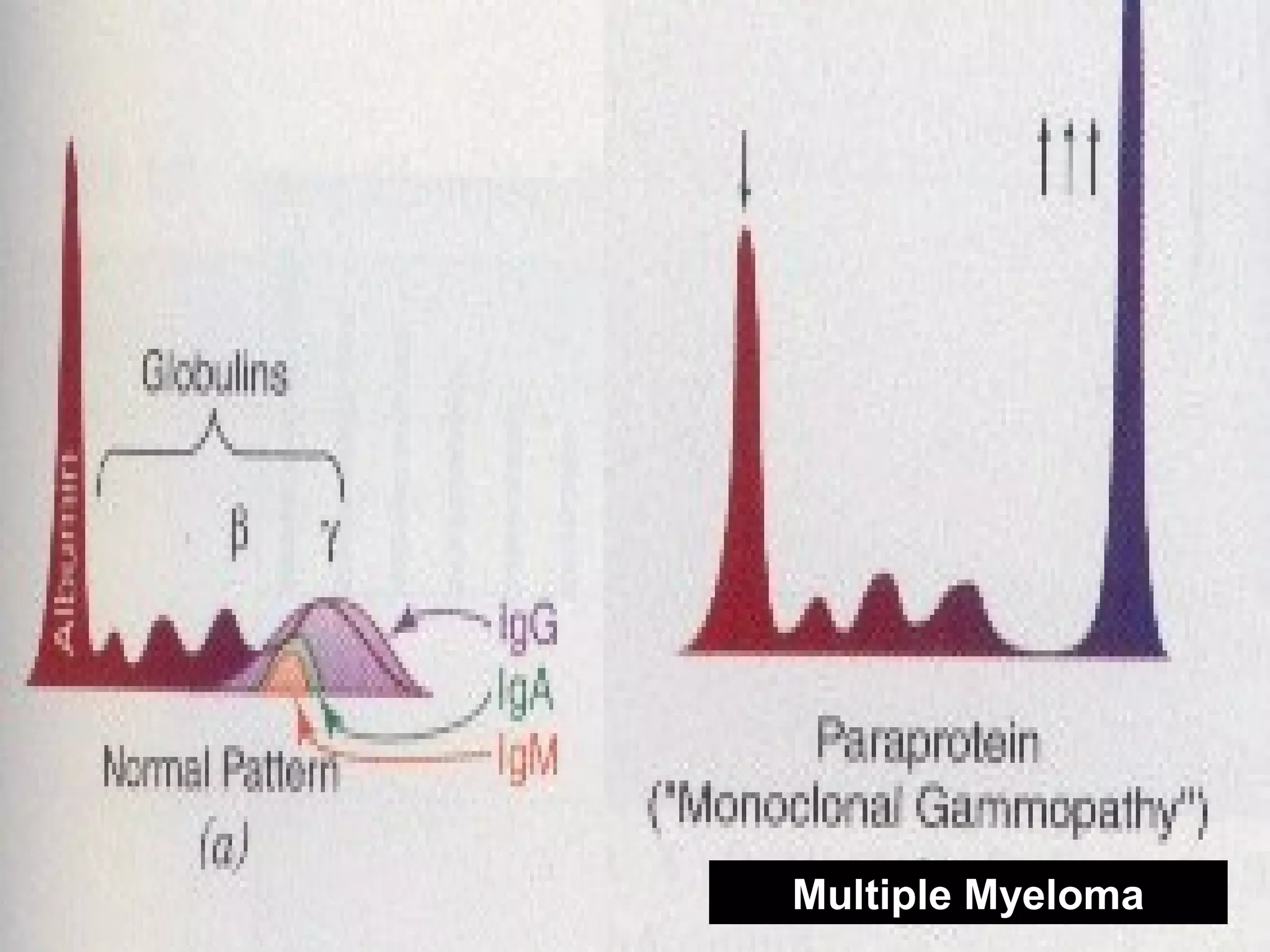
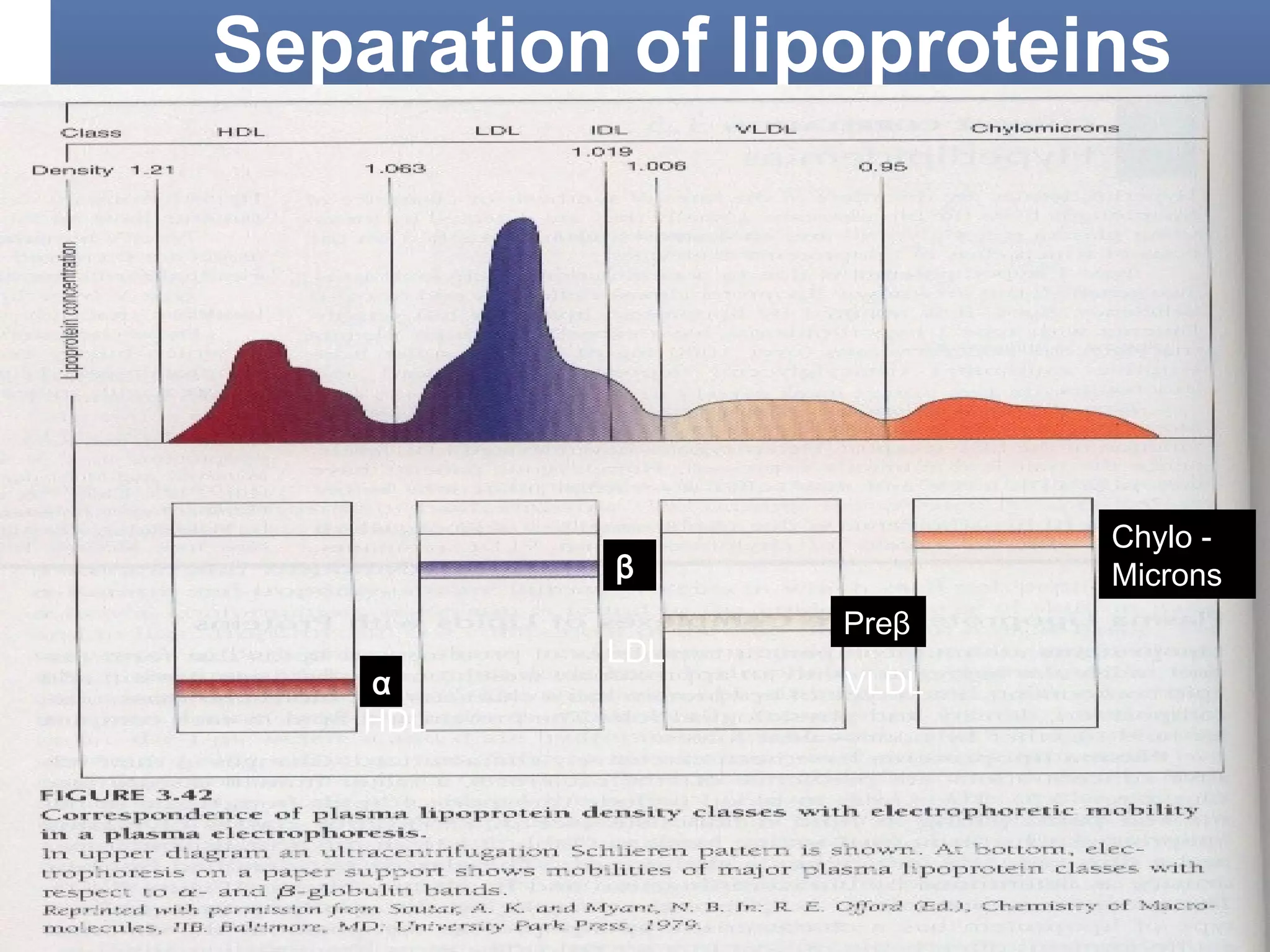
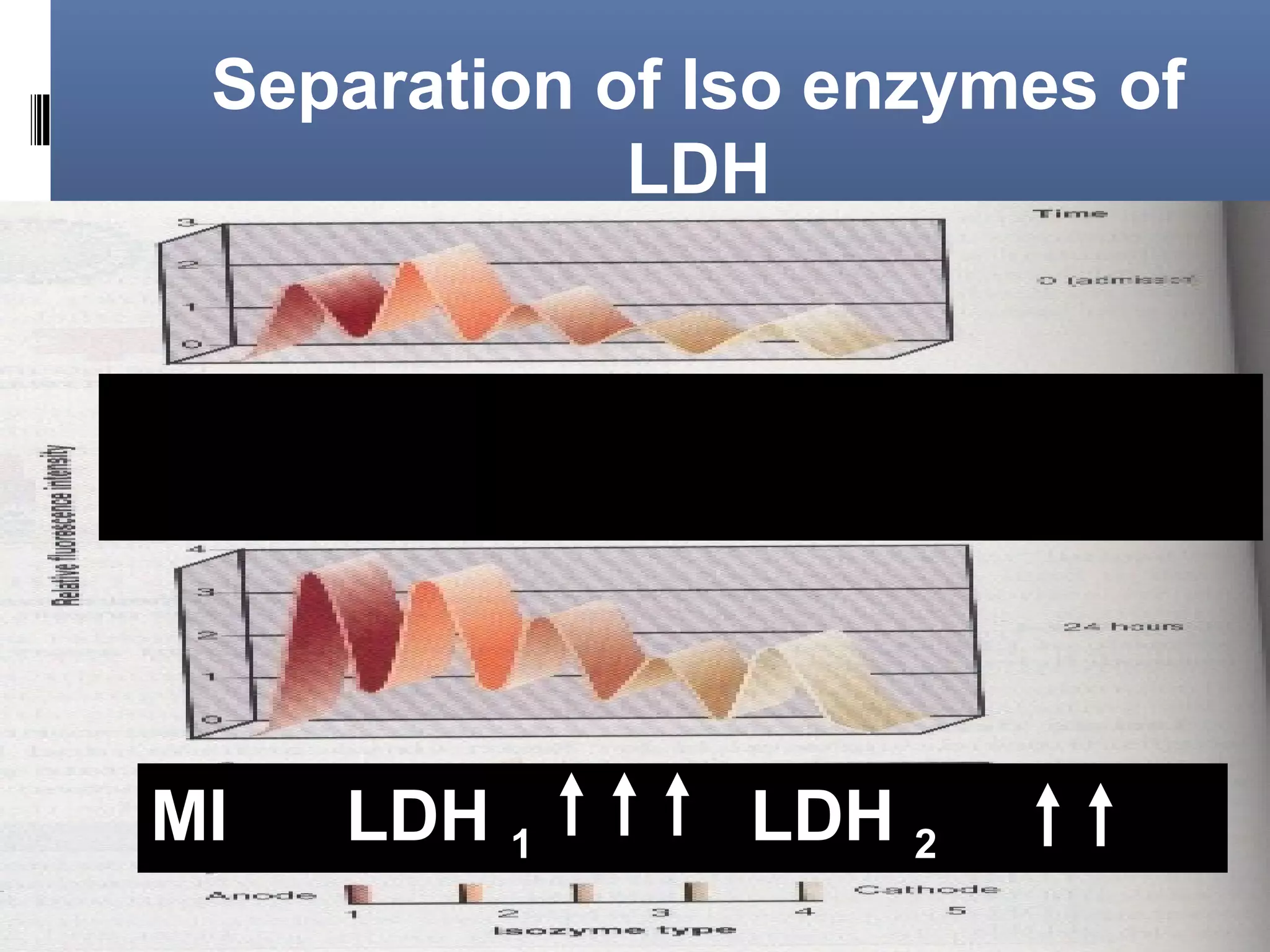
This document discusses electrophoresis, which separates charged compounds using an electric field. It moves negatively charged proteins in serum towards the anode at pH 8.6. Applications include separating serum proteins, lipoproteins, hemoglobin variants, and isoenzymes. Zone electrophoresis is commonly used and involves applying samples to a support medium like paper, cellulose acetate, or polyacrylamide gel. After separation, proteins are visualized through staining and quantified using densitometry. Serum protein electrophoresis is used to analyze the albumin and globulin percentages. Abnormal patterns can indicate conditions like multiple myeloma or liver cirrhosis.