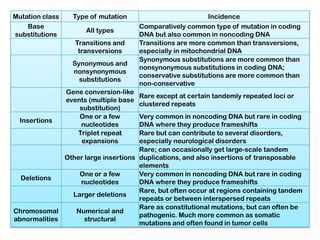
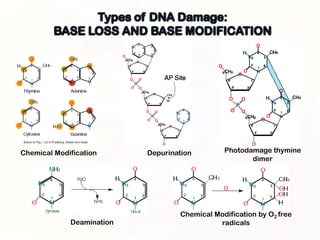
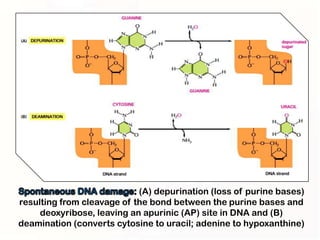
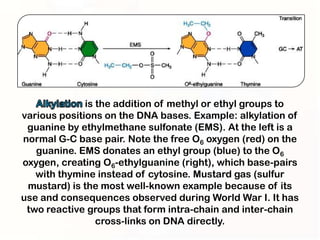
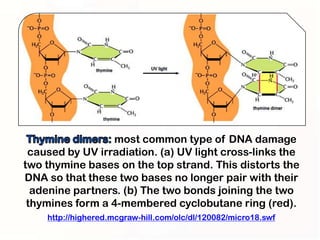
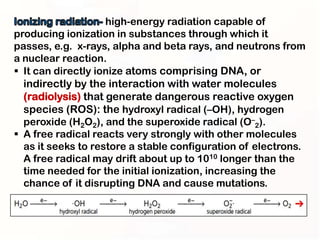
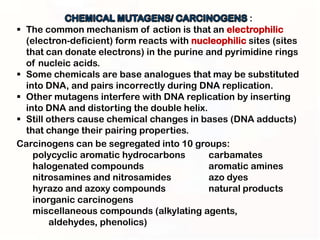
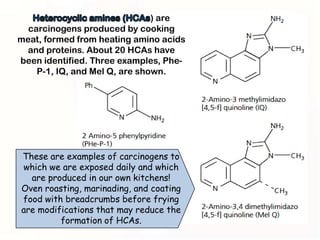
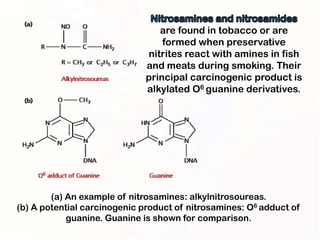
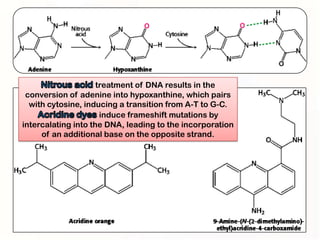
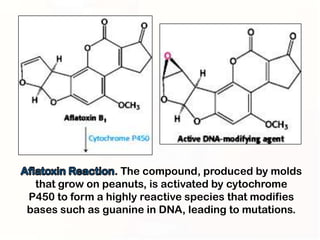
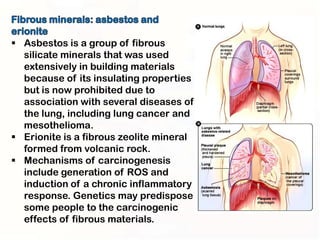
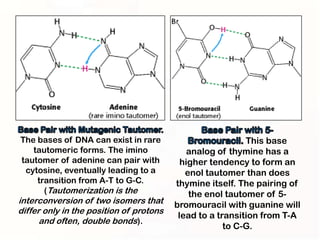
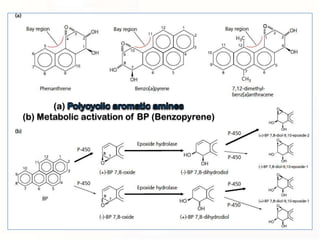
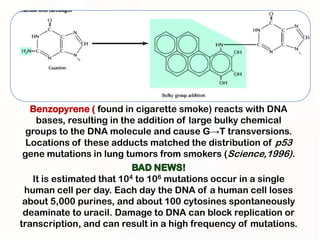
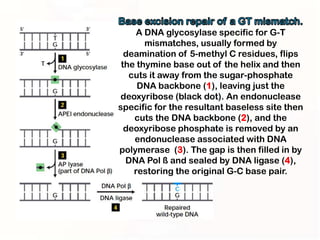
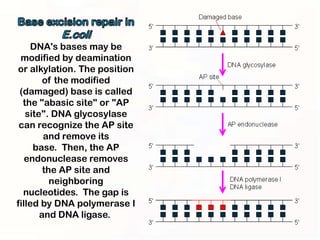
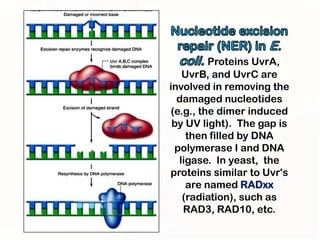
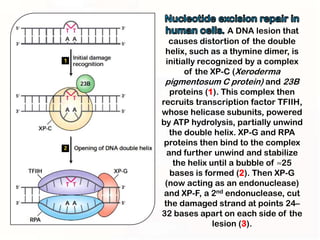
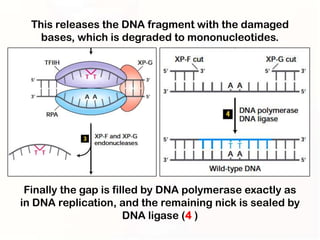
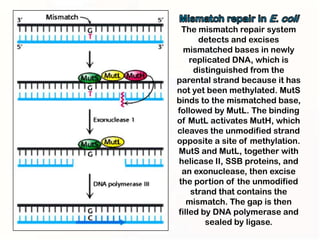
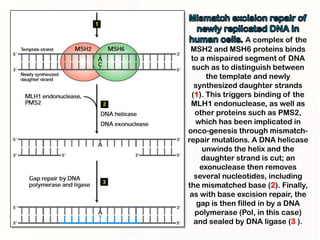
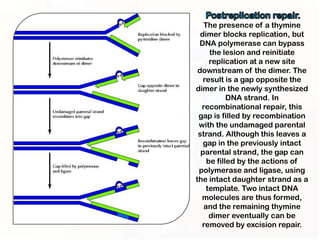
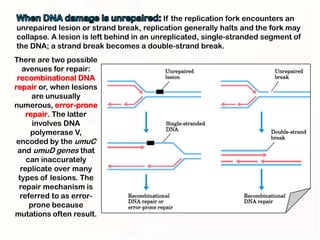
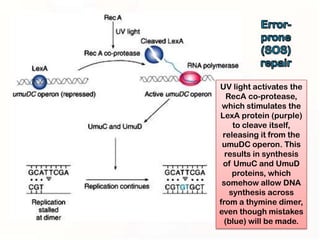
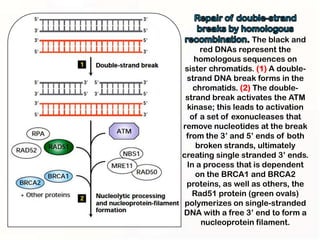
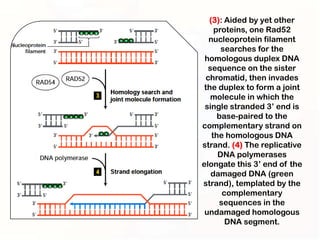
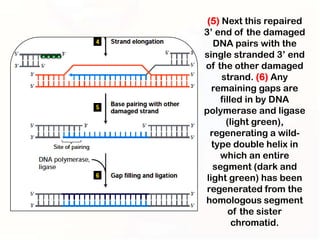
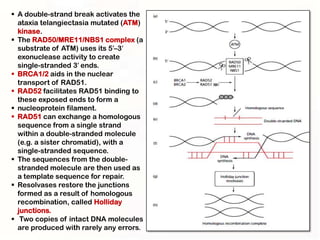
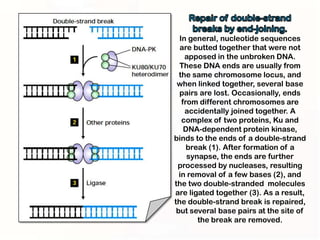
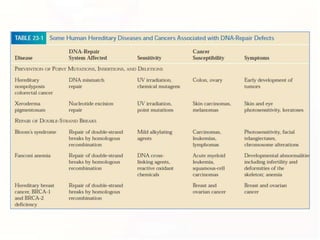
1. Mutations can occur through errors in DNA replication, repair, or recombination which can cause substitutions, insertions or deletions of DNA bases. Environmental mutagens like radiation and chemicals can also directly interact with DNA and cause mutations.
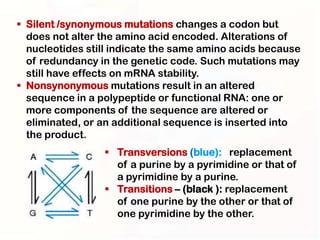
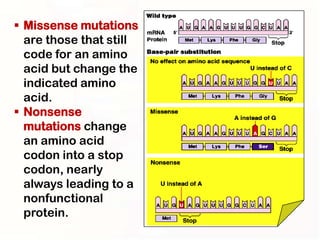
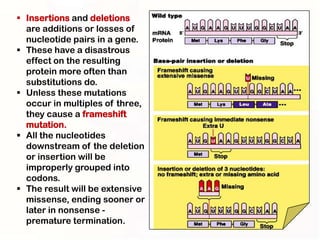
2. Some mutations involve changes to a single DNA base pair, while others are larger scale mutations affecting longer DNA segments. Point mutations may substitute one base for another, while insertions or deletions can disrupt the DNA reading frame.
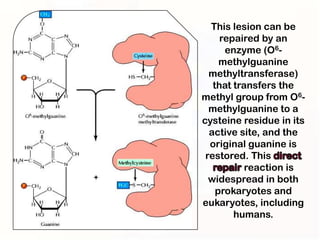
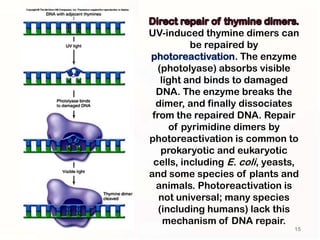
3. Cells have mechanisms like direct repair and photoreactivation to correct some mutations, but errors in these pathways can also lead to mutations if not repaired properly.