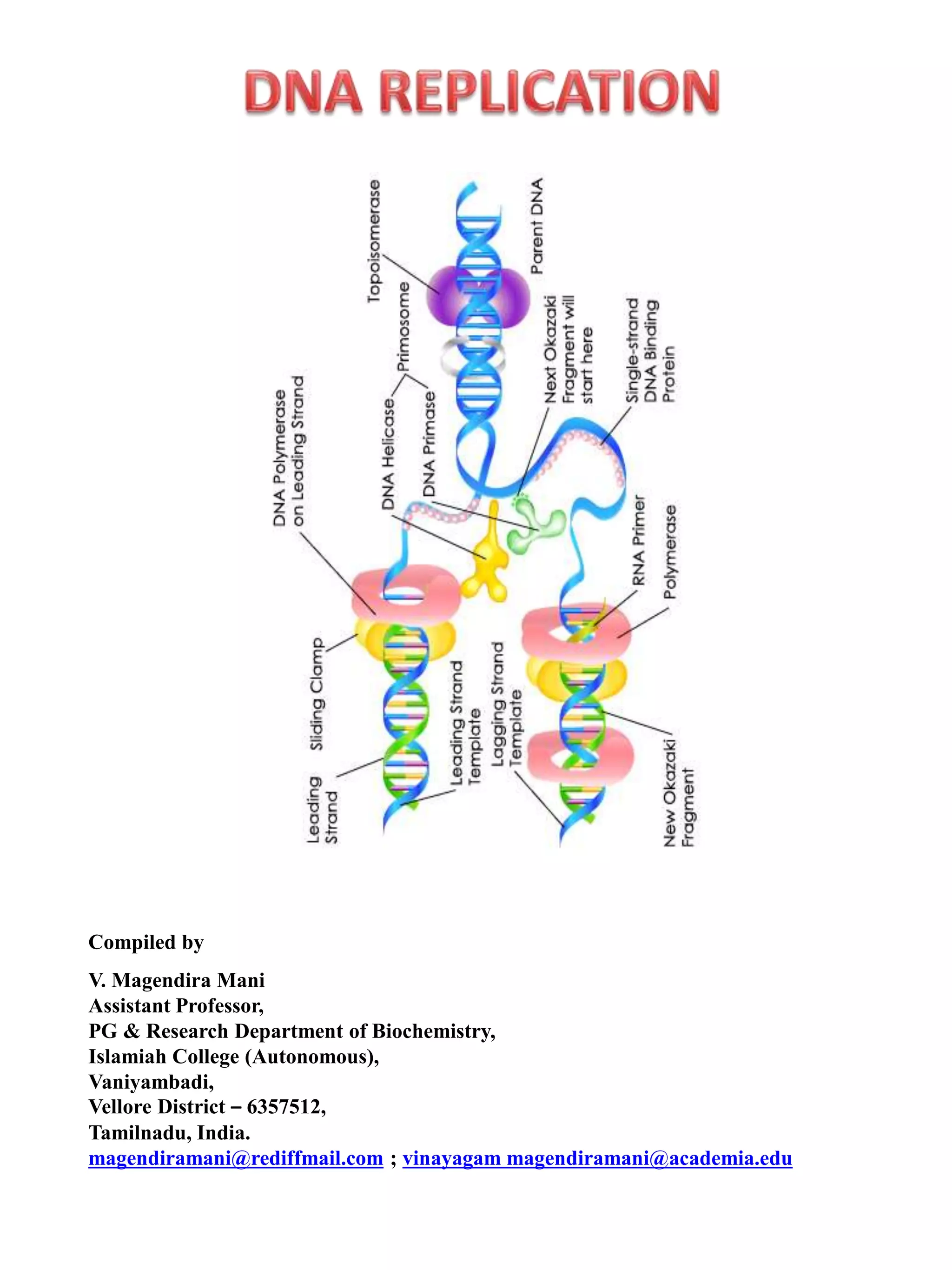
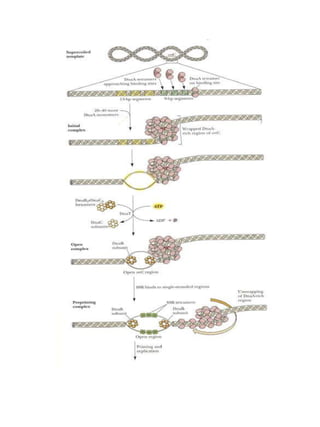
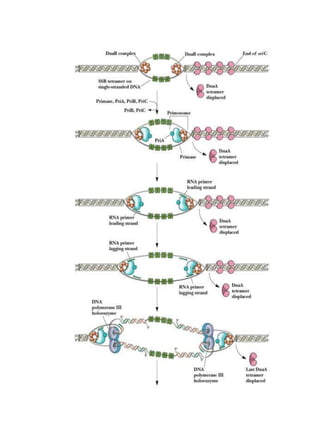
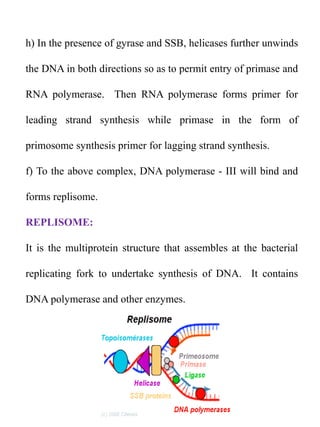
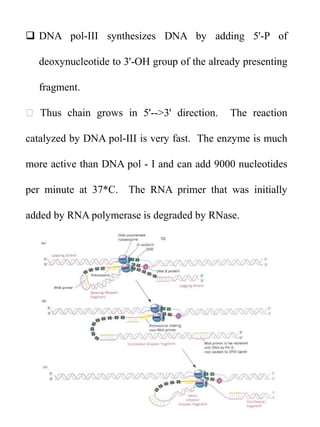
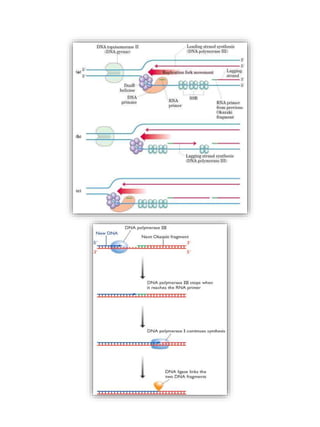
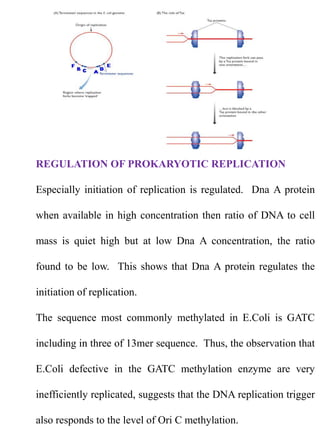
Replication in prokaryotes occurs through three main stages - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation begins at a specific origin of replication site called OriC, where DnaA protein binds and unwinds the DNA, forming an open complex. Elongation then proceeds bidirectionally as DNA polymerase synthesizes leading and lagging strands. Termination occurs when the replication forks from opposite directions meet. The entire replication process in E. coli takes around 40 minutes to complete replication of its genome.