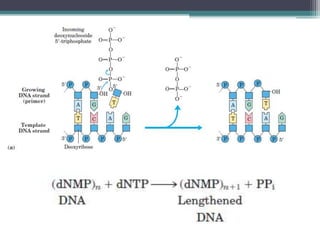
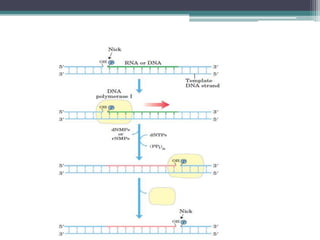
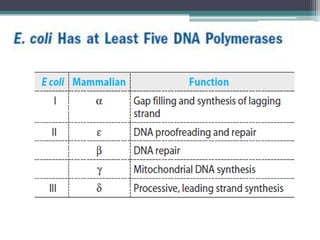
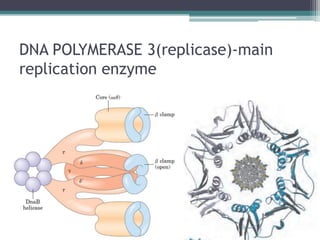
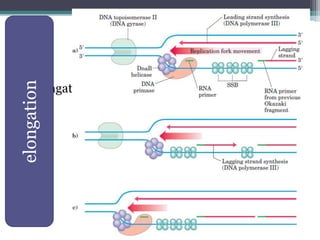
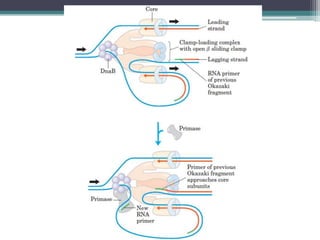
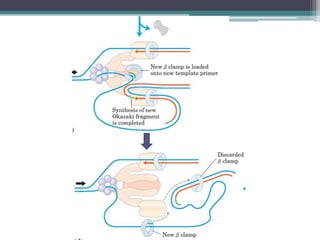
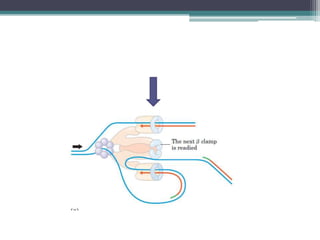
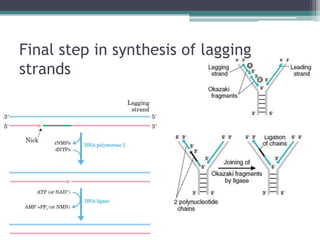
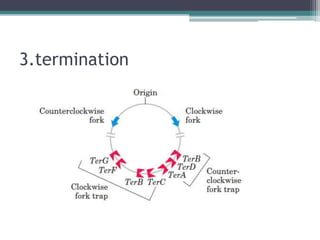
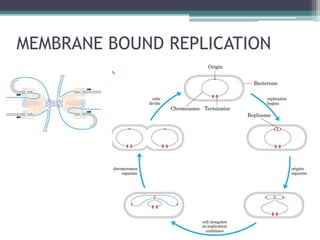
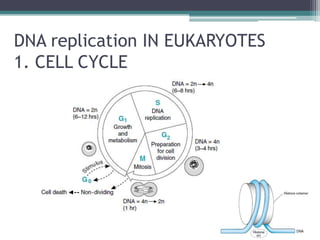
DNA replication is the process by which DNA copies itself to produce identical daughter molecules. Some key points:
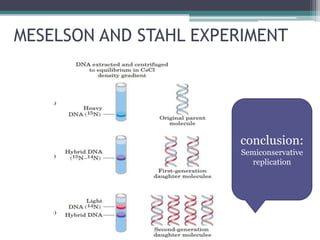
- The Meselson-Stahl experiment provided evidence that replication is semiconservative.
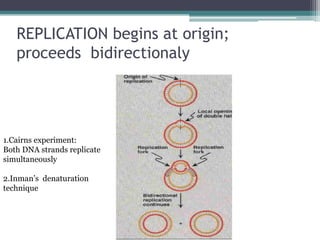
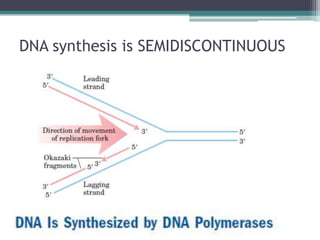
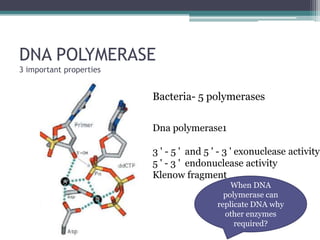
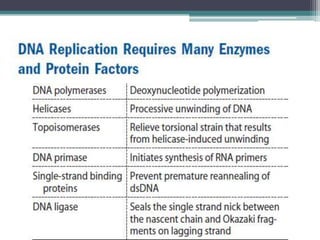
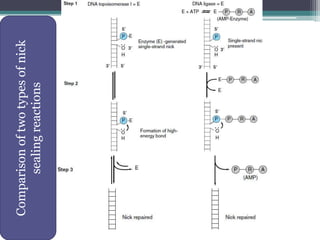
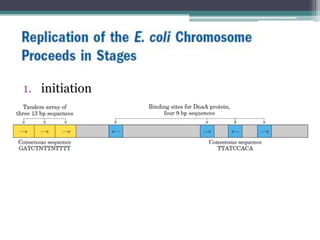
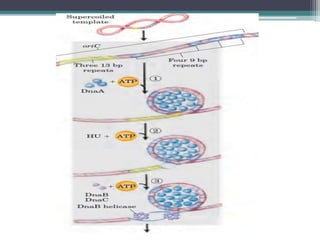
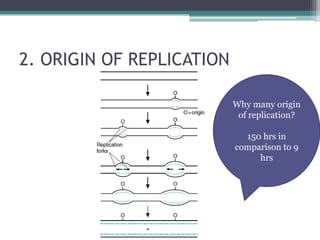
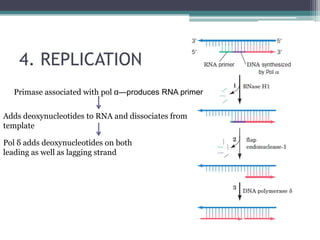
- Replication begins at the origin and proceeds bidirectionally. DNA polymerase is the main enzyme that carries out replication.
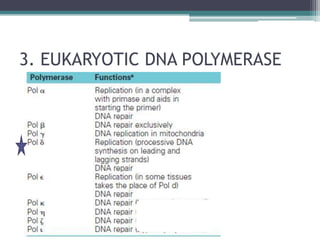
- Replication in eukaryotes involves multiple origins of replication, several DNA polymerases, and other proteins like PCNA and RFC. It also must coordinate with packaging DNA into chromatin and replication of mitochondrial DNA.
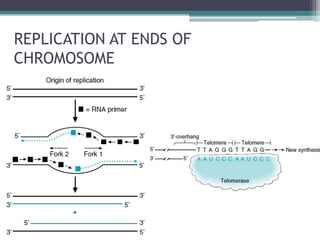
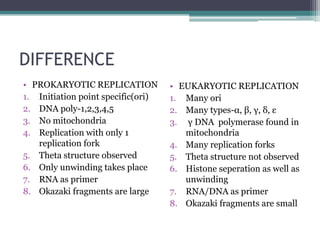
- Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic replication include the number of replication forks, presence of histones, and size of Okazaki fragments.