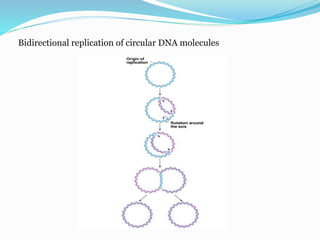
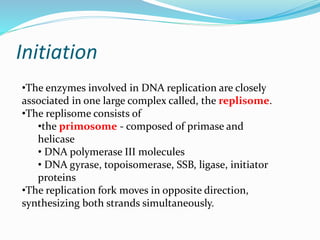
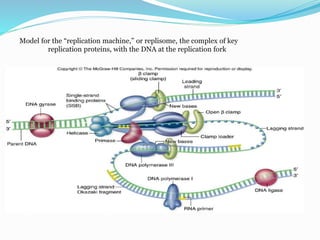
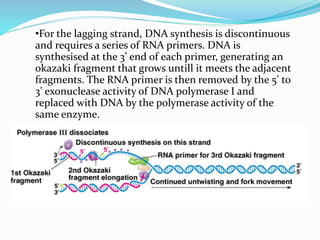
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It involves unwinding the double helix at an origin of replication and using each parental strand as a template to synthesize new daughter strands. This results in two identical copies of the DNA molecule. Replication is semi-conservative, meaning each new DNA molecule contains one original parental strand and one newly synthesized strand. It is also bidirectional and semi-discontinuous. The leading strand is copied continuously while the lagging strand is copied discontinuously in fragments that are later joined.