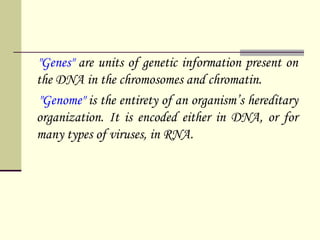
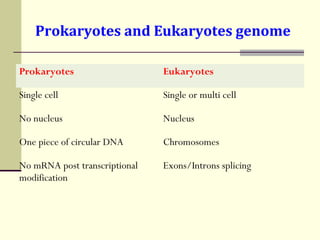
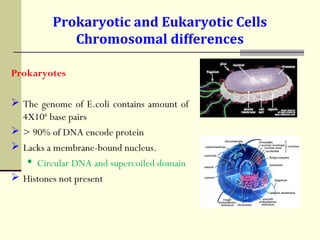
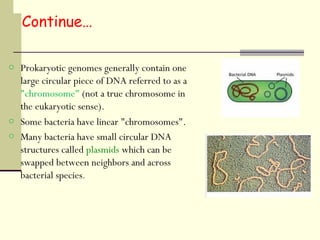
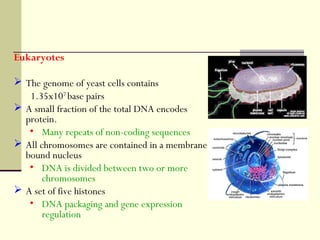
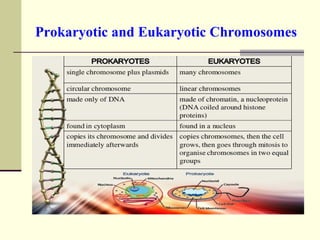
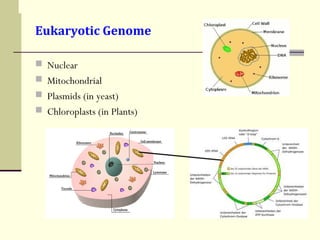
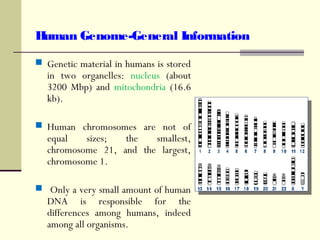
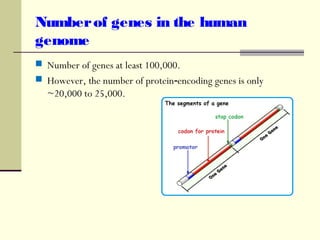
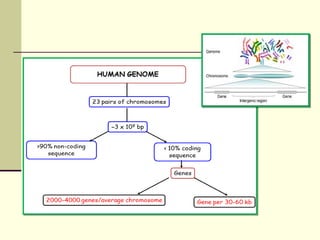
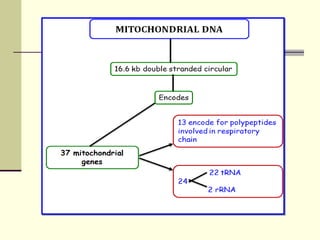
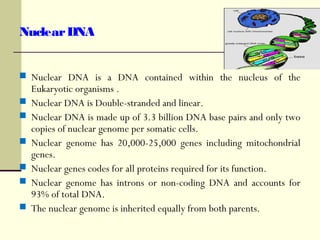
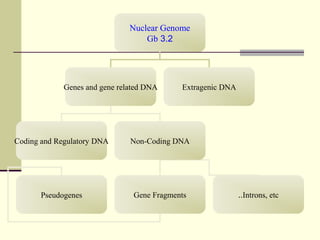
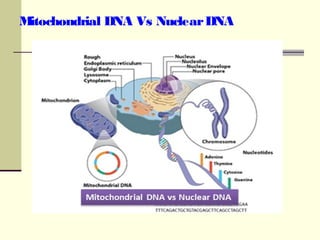
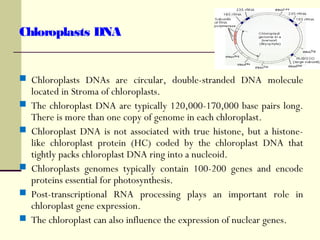
The document discusses the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. Prokaryotes generally have a single, circular chromosome while eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes within a membrane-bound nucleus. The human genome contains around 3 billion base pairs divided between nuclear and mitochondrial DNA. The nuclear genome encodes around 20,000-25,000 protein-coding genes and is inherited equally from both parents, while mitochondrial DNA is maternally inherited.