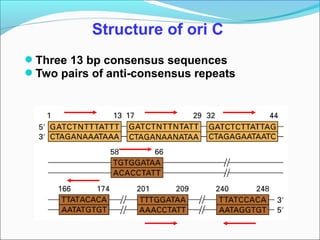
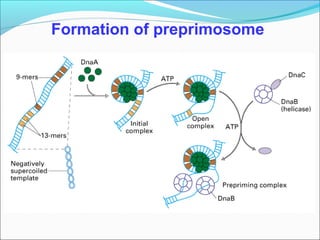
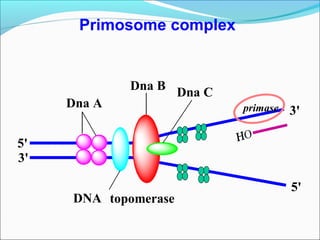
DNA replication involves the synthesis of daughter DNA strands using parental DNA as a template. It occurs through a semi-conservative process whereby each new DNA molecule contains one original and one newly synthesized strand. Replication is bidirectional, with replication forks moving in opposite directions from an origin of replication. The leading strand is synthesized continuously while the lagging strand involves the discontinuous synthesis of Okazaki fragments. DNA polymerases and other proteins such as helicases, primases, ligases and topoisomerases work together to facilitate the replication process.