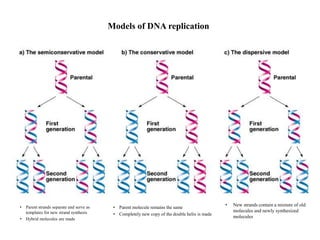
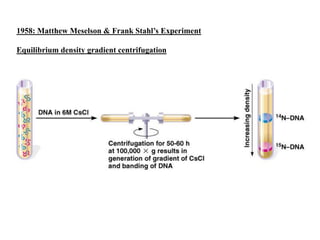
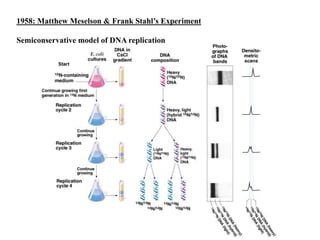
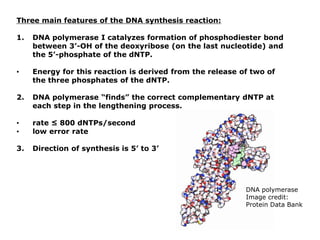
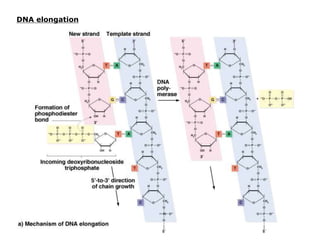
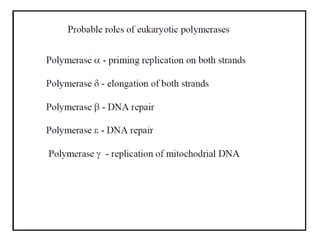
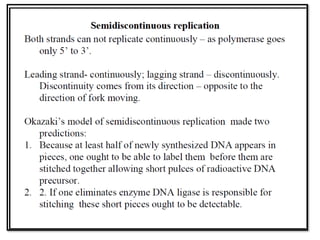
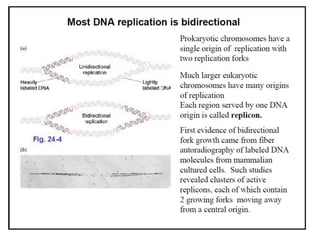
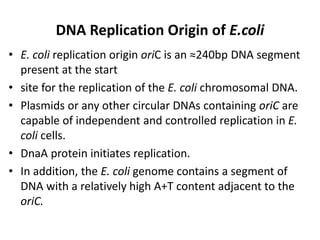
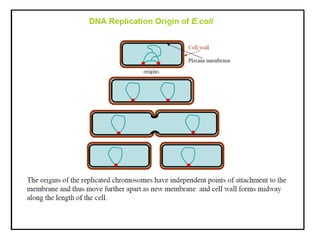
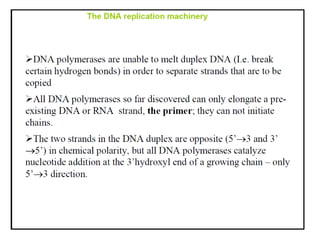
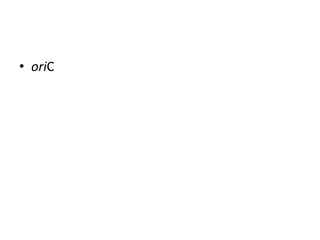DNA replication occurs through a semiconservative process where the parental DNA strands separate and act as templates for the synthesis of new complementary strands. Key experiments by Meselson and Stahl provided evidence for this semiconservative model. DNA polymerase, discovered by Arthur Kornberg in 1955, is the main enzyme that catalyzes DNA synthesis. It requires DNA templates, dNTPs, and magnesium ions to carry out the step-wise addition of nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction to form new DNA strands.