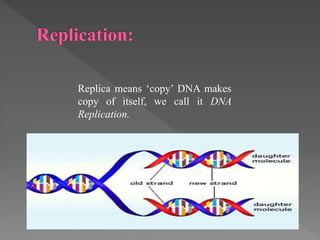
In the 1950s, the structure of DNA was identified as a double helix composed of deoxyribose sugar and four nitrogen bases. DNA replication is a complex process involving various enzymes that ensure accurate copying and repair of genetic material, with mechanisms distinguishing between leading and lagging strands. The process culminates in the formation of new DNA strands, with the removal of RNA primers and the joining of DNA fragments by ligase, while telomeres protect the ends of chromosomes.