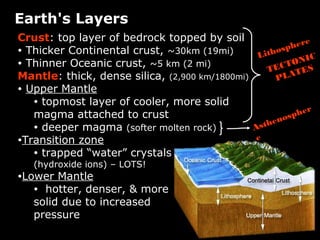
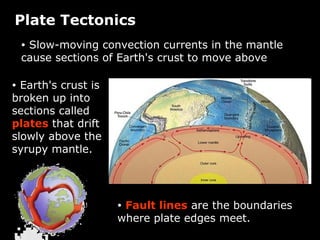
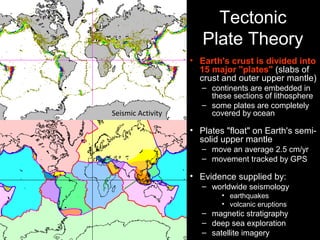
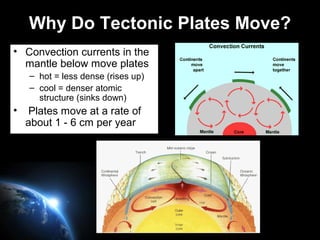
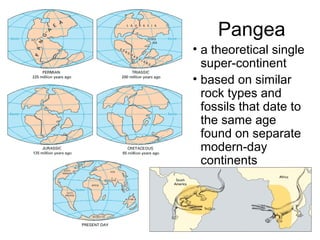
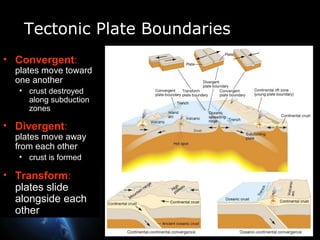
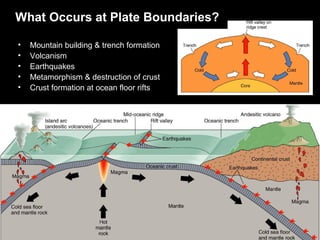
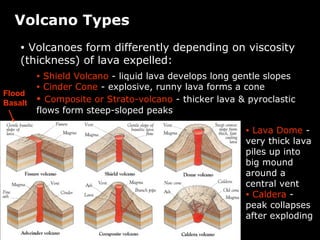
Plate tectonics involves the slow movement of sections of Earth's crust called tectonic plates. Plates move due to convection currents in the underlying mantle. Where plates meet, they can cause earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains as the plates push together, slide past each other, or move apart. The movement of plates over time has resulted in continents joining together in a supercontinent called Pangea and breaking apart again.