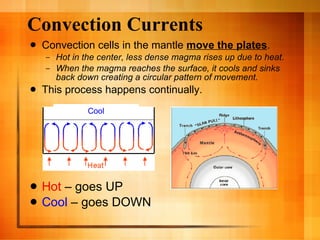
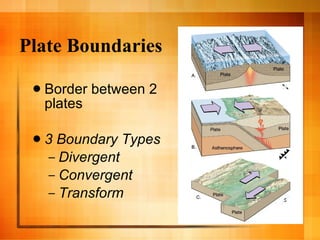
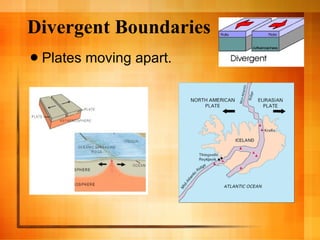
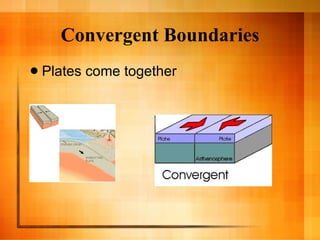
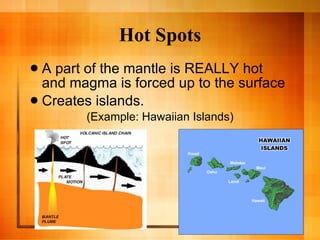
The document discusses plate tectonics and the structure and dynamics of the Earth's interior. It describes how the crust is broken into plates that move atop the mantle due to convection currents, and the three types of plate boundaries: divergent where plates move apart, convergent where they move together, and transform where they slide past each other. It provides examples of associated geological features like mid-ocean ridges, subduction zones, volcanoes, and earthquakes.