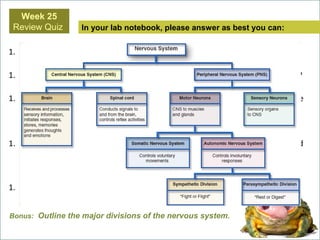
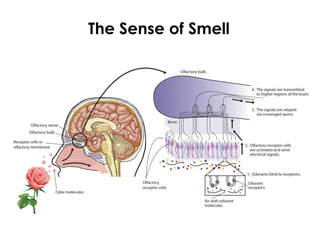
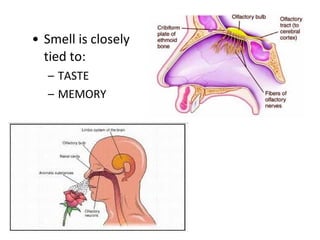
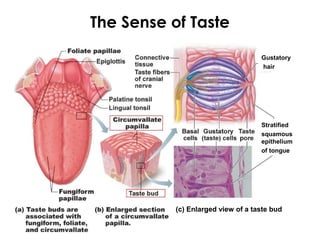
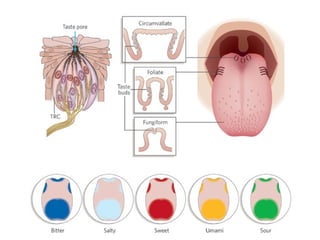
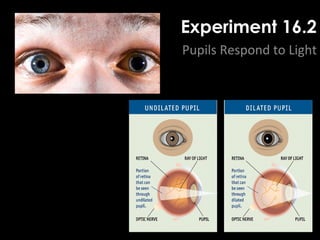
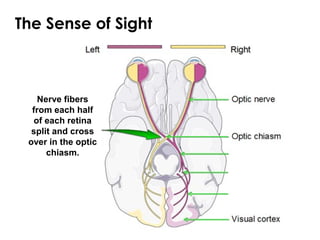
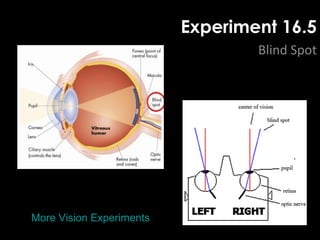
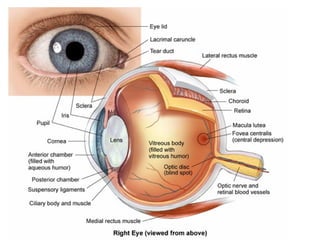
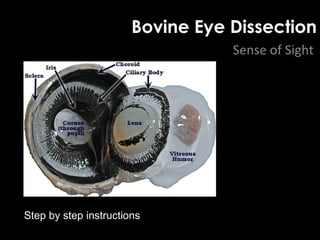
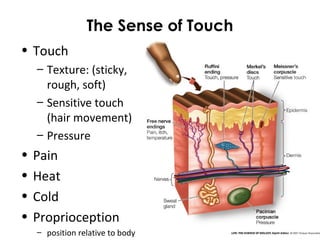
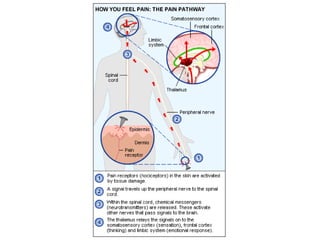
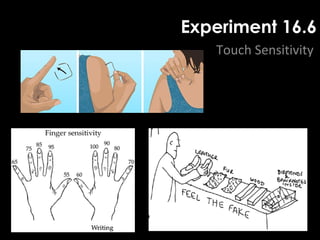
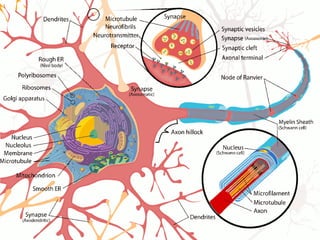
The document summarizes several key human body systems and the five senses. It includes review questions about the nervous system and its major divisions of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Experiments are described to test sight, smell, taste, touch and reflexes. Step-by-step instructions for a bovine eye dissection are provided to examine the anatomy of vision.