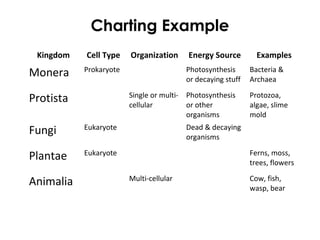
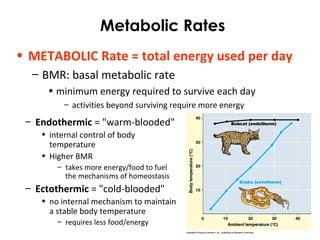
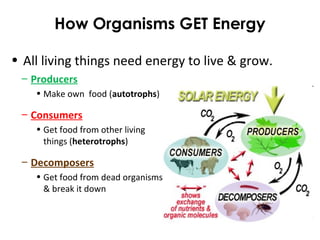
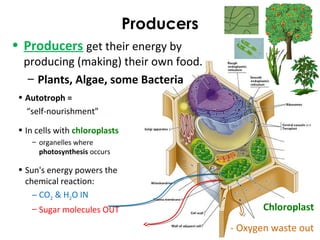
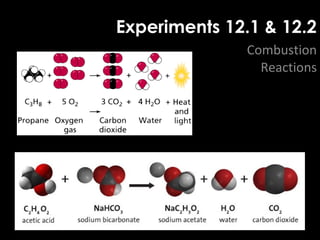
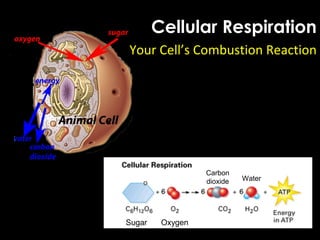
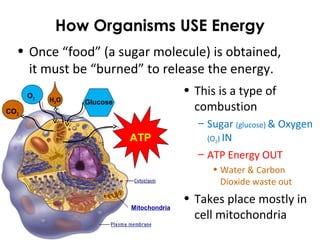
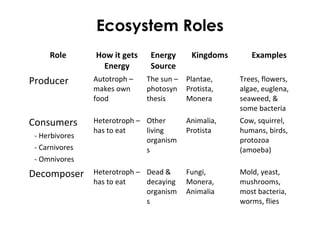
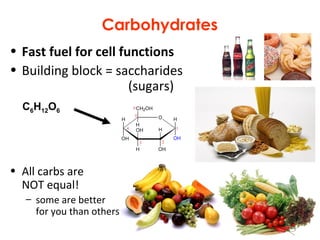
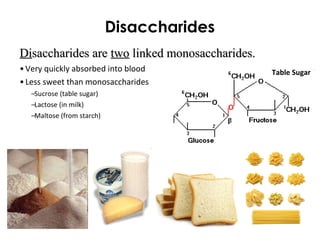
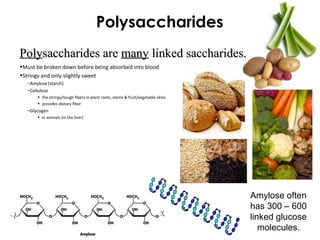
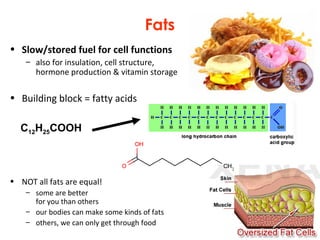
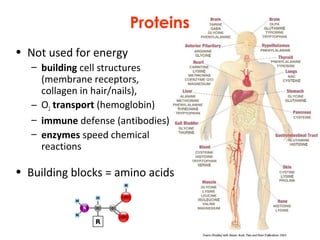
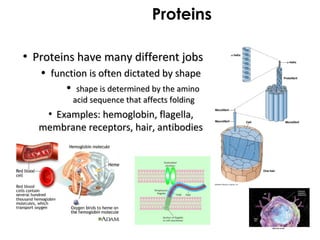
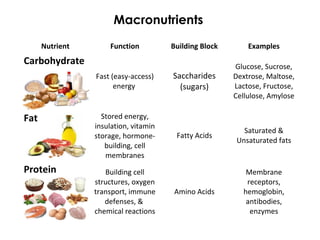
This document provides information about energy and metabolism in living things. It discusses how organisms get and use energy through photosynthesis, respiration, and the breakdown of nutrients. Producers, consumers, and decomposers are defined by how they get energy. The main macronutrients - carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins - are examined in terms of their functions, building blocks, and examples. Metabolic rates and homeostasis in endothermic and ectothermic organisms are also covered.