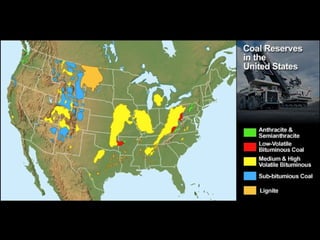
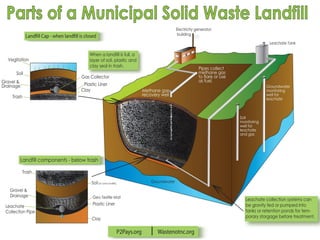
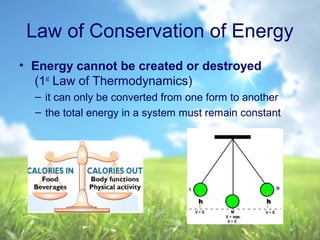
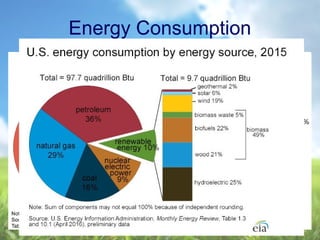
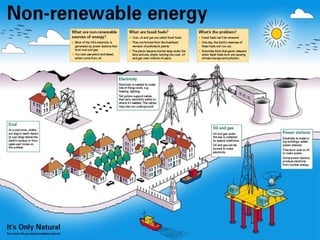
The document discusses managing natural resources and preserving Earth's cycles. It covers renewable and nonrenewable resources, describing examples of each type. Renewable resources include air, water, living things, land, sun, wind and geothermal energy. Nonrenewable resources are being used faster than they can be replenished, such as fossil fuels like coal and natural gas, minerals, and land. Air and soil pollution from human activities are also discussed.