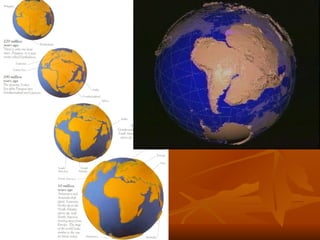
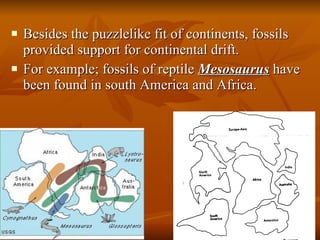
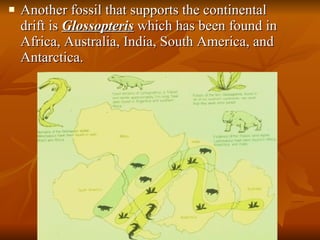
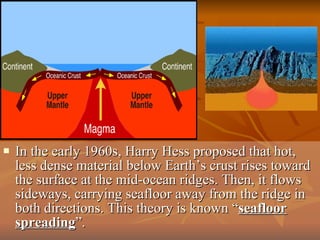
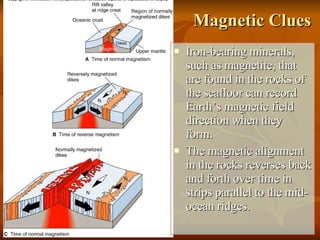
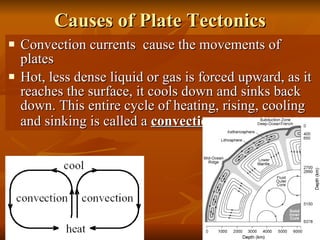
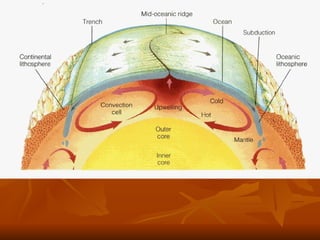
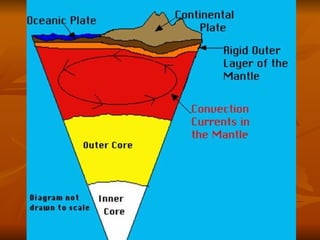
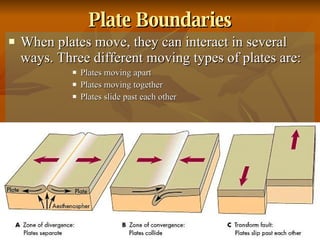
The document outlines the theory of continental drift proposed by Alfred Wegener, suggesting that all continents were once a single landmass called Pangea and have since moved to their current positions, supported by fossil and geological evidence. It then discusses Harry Hess's theory of seafloor spreading, which explains how oceanic plates move away from mid-ocean ridges due to rising molten material, leading to the formation of new crust. Finally, the text introduces the combined theory of plate tectonics, detailing how Earth's lithosphere is divided into plates that move on the asthenosphere due to convection currents, with various interactions occurring at plate boundaries.