This document provides an overview of current electricity, including:
- Current electricity involves a continuous flow of charged particles through a conductor, measured in amperes.
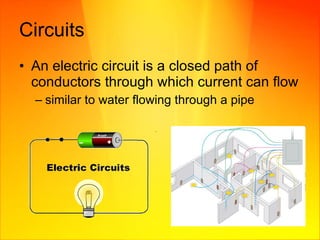
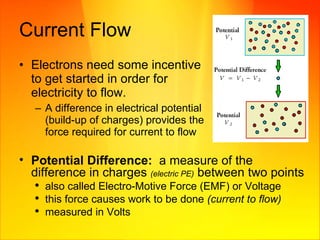
- Electric circuits form a closed loop through which current can flow. A difference in electric potential provides the incentive for current to flow.
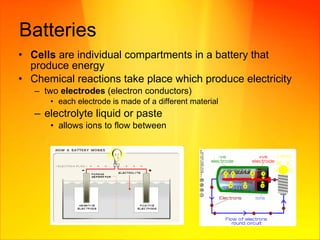
- Voltage is a measure of the difference in electric potential and provides the force for current to flow. Batteries use chemical reactions to produce electricity between two electrodes.
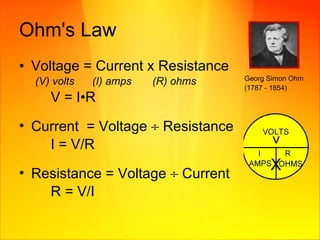
- Resistance opposes the flow of current and is affected by the material, length, and diameter of a conductor. Ohm's law describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit.