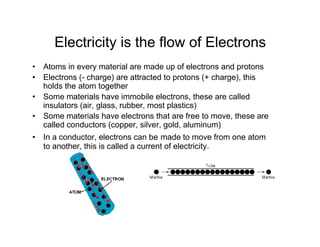
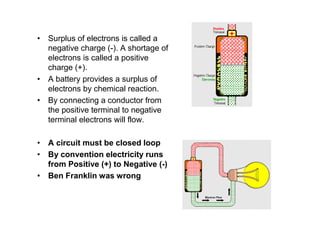
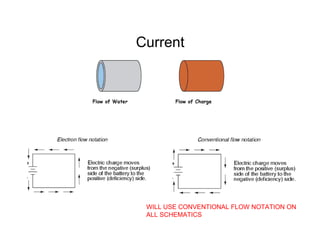
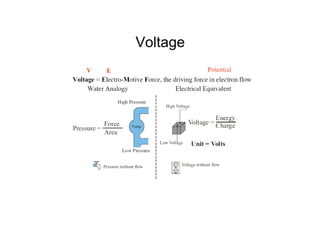
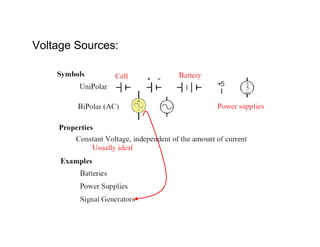
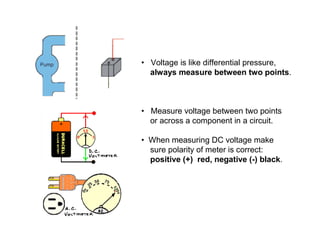
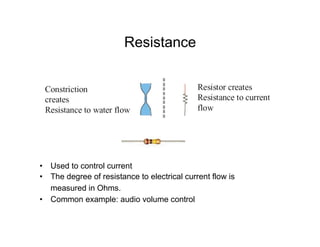
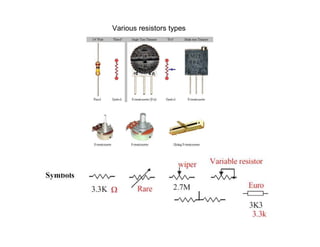
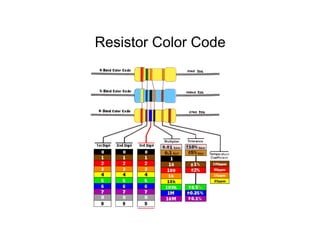
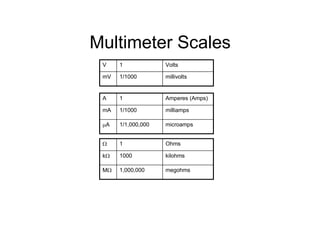
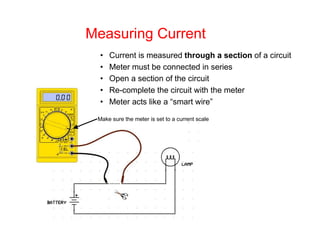
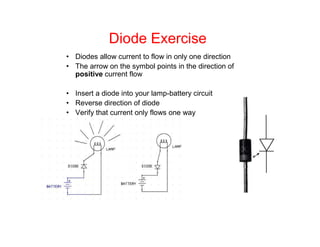
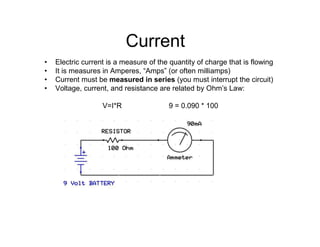
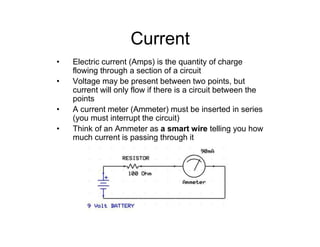
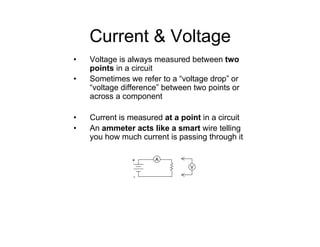
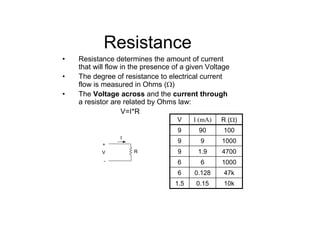
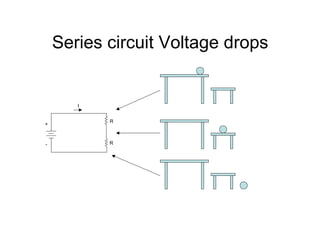
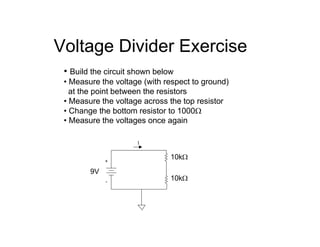
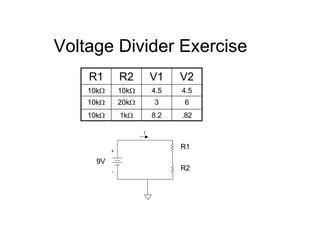
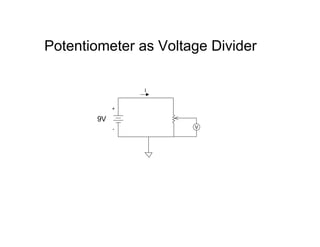
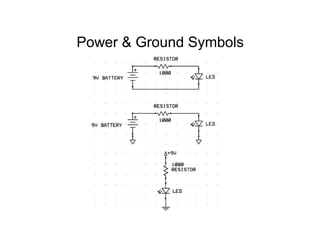
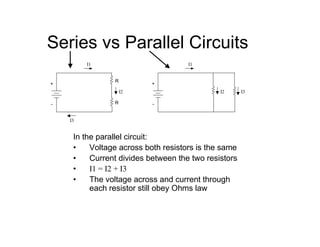
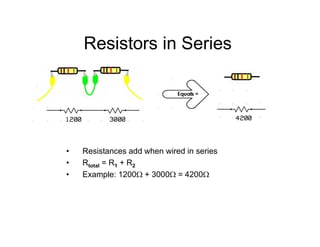
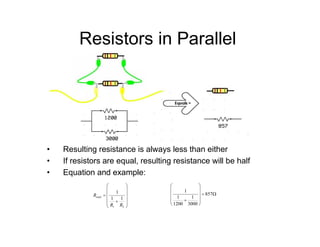
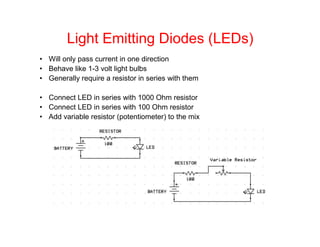
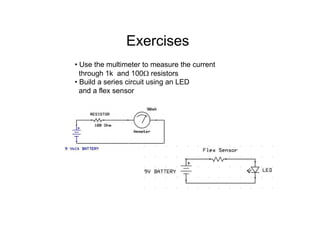
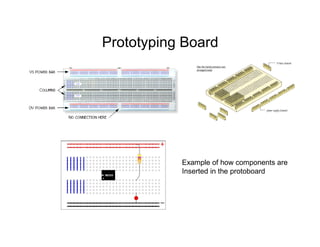
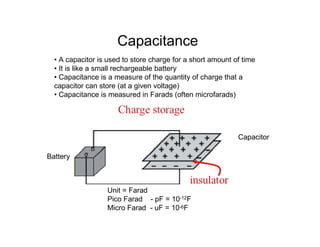
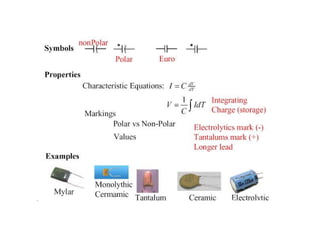
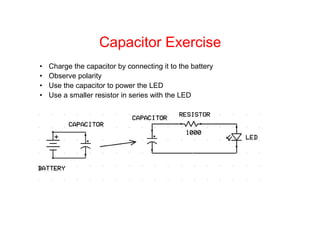
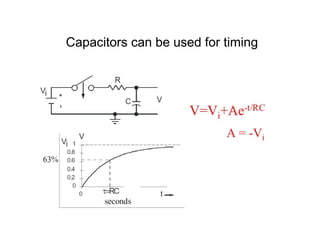
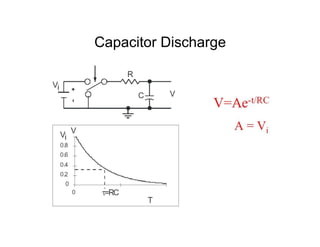
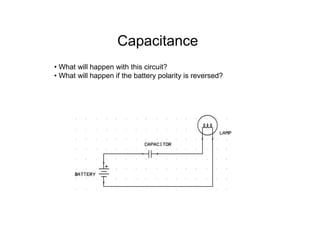
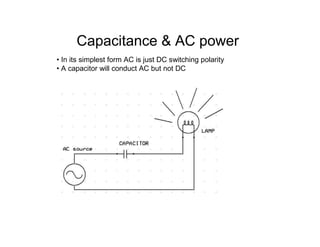
This document provides an introduction to basic electronics concepts including voltage, current, resistance, Ohm's Law, resistors, diodes, LEDs, capacitors, breadboards, and AC/DC power. Key topics covered are voltage measured in volts, current measured in amps, resistance measured in ohms, and their relationship as defined by Ohm's Law. Circuit components such as resistors, diodes, LEDs, and capacitors are explained along with their schematic symbols and uses. Breadboards and prototyping are also discussed.