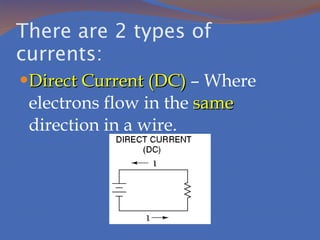
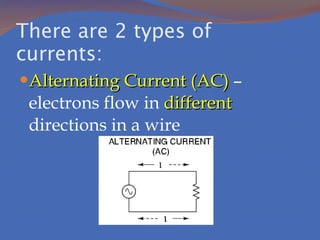
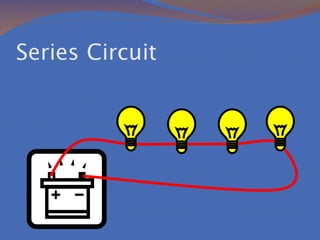
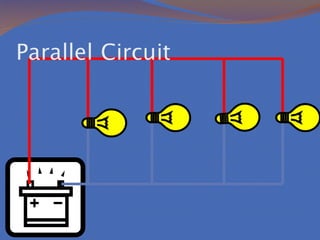
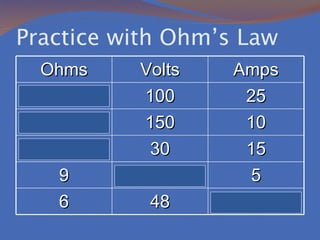
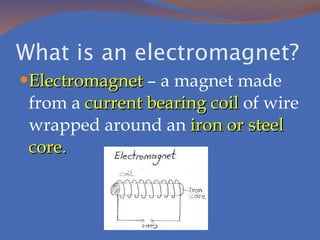
Static electricity refers to the buildup of electric charge on the surface of an object without flowing. It is potential energy that does not move and is stored. Electricity that moves is called current, which is the flow of electrons measured in amperes. There are two types of currents: direct current where electrons flow in one direction and alternating current where electrons flow in both directions. There are also two types of circuits: series circuits where all components are on one path and parallel circuits with multiple branching paths. Conductors allow electric current to flow easily while insulators do not allow current to pass through. Resistance opposes current flow and produces heat, with better conductors having lower resistance. Voltage measures the energy driving current flow with higher