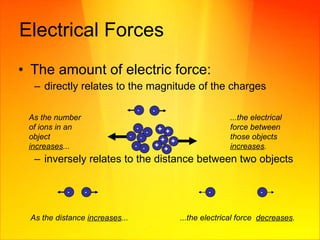
Electrical energy is the movement of charged particles called ions. There are two types of ions: cations with positive charges that have missing electrons, and anions with negative charges that have extra electrons. Ions exert forces on one another, with opposite charges attracting and like charges repelling. The electrical force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charges and inversely proportional to the distance between objects. Static electricity occurs when electrons are transferred between materials that touch, resulting in an accumulation of charges and forces on nearby objects. Electrical conduction allows the movement of electrons along conductors like metals, while insulators tightly hold electrons in place.