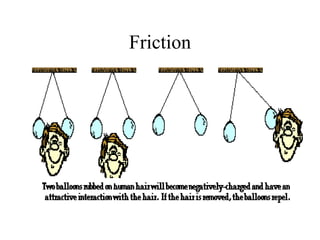
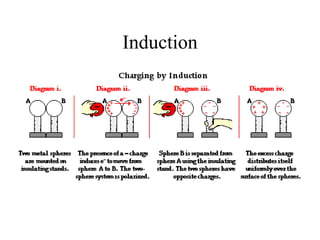
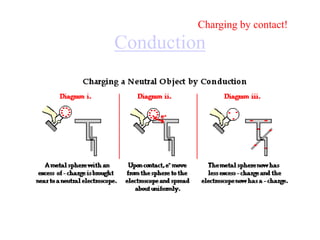
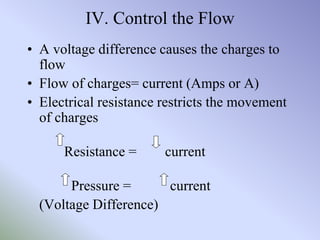
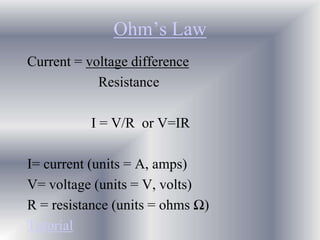
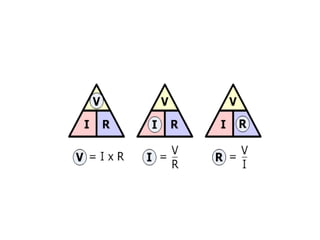
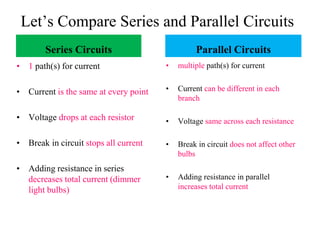
This document discusses electrical circuits and their components. It begins by defining key terms like voltage, current, and resistance. Voltage is generated by batteries, generators, or solar cells and creates a difference in electric potential that causes electric current to flow. Current is the flow of electric charge, specifically electrons, measured in amps. Resistance opposes the flow of current and converts electrical energy to heat. Ohm's Law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. The document then explains series and parallel circuits. In a series circuit there is only one path for current, while in parallel circuits there are multiple branches. It concludes by comparing the key differences between series and parallel circuits.