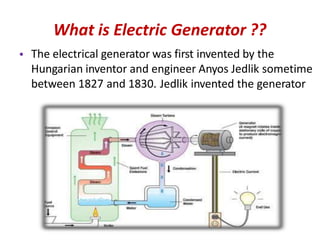
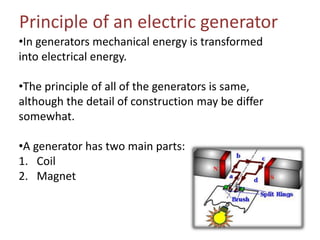
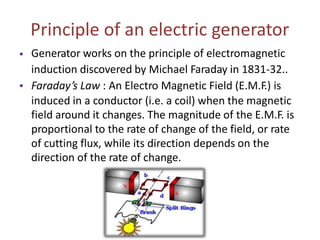
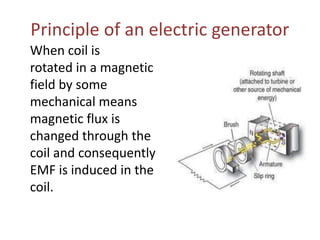
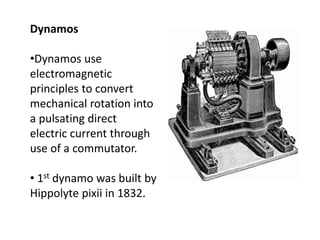
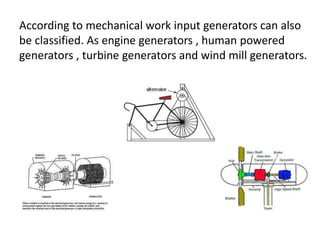
Electric generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through the process of electromagnetic induction. They have two main parts - a coil and a magnet. When the coil rotates in the magnetic field, it cuts magnetic flux and induces an electric current in the coil. Generators can produce direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) and come in various types depending on their application, such as standby, portable, or commercial generators that provide backup power. The main uses of electric generators are to provide electric power for vehicles, buildings, and power grids.