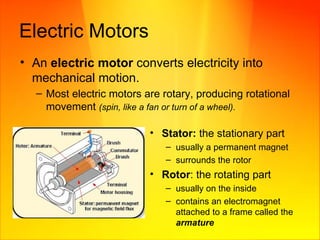
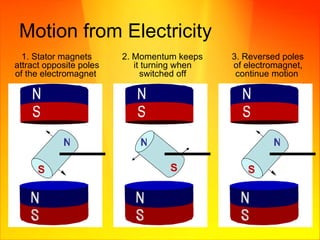
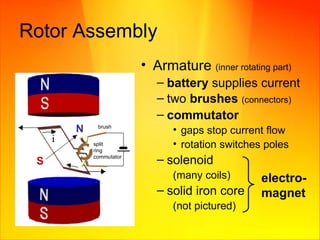
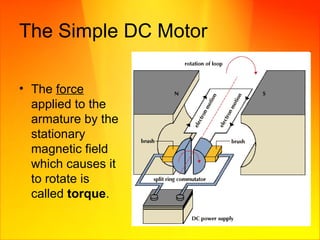
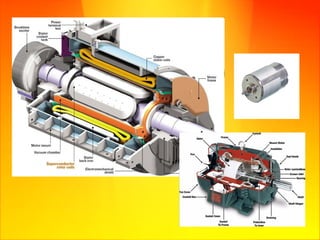
The document discusses magnetism and electricity concepts including:
- Iron, nickel, and cobalt have the greatest magnetic permeability.
- Permanent magnet examples include ceramic bars, fridge magnets, and neodymium discs.
- Temporary magnets include induced paper clips and electromagnets.
- Earth's magnetic field is generated by a dynamo effect in its solid iron inner core.
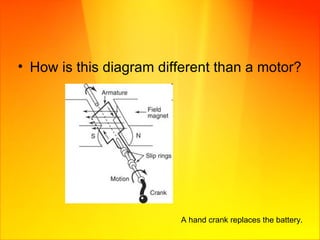
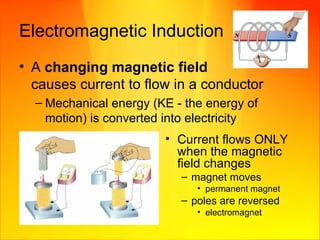
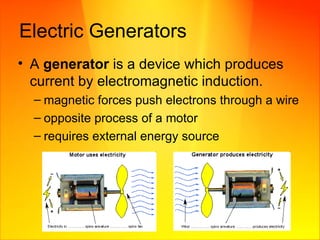
- Moving a magnet near a wire or changing the magnetic field around a wire induces electric current in the wire.