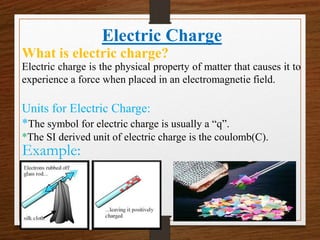
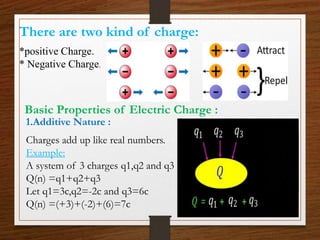
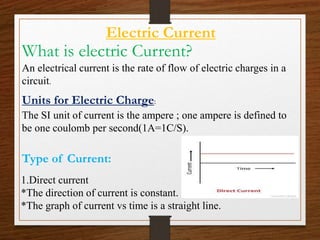
This presentation provides an overview of physics topics related to electricity, including electric charge, current, and circuits. It introduces key historical figures like Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Edison, defines electricity and discusses its importance. It explains what electric charge is, the types of charges, and basic charge properties. It then defines electric current, discusses types like direct and alternating current. The presentation also covers electric resistance, resistivity, conductivity, and the different types of electric circuits like series and parallel.