Embed presentation
Downloaded 378 times






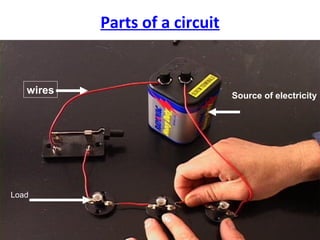

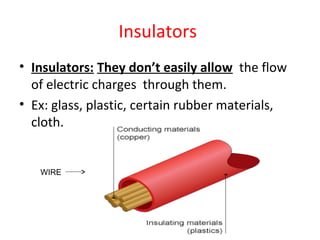

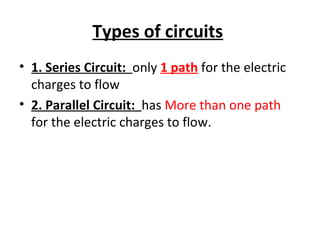
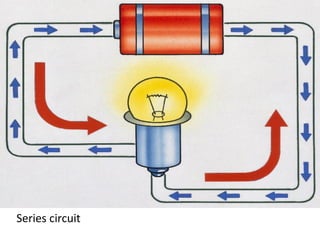
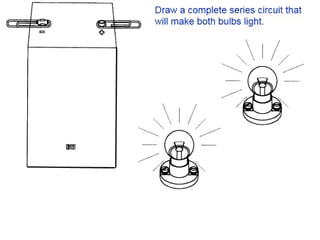

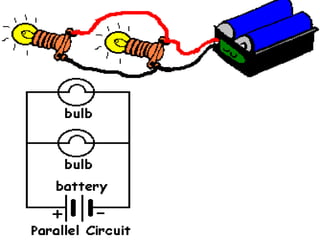
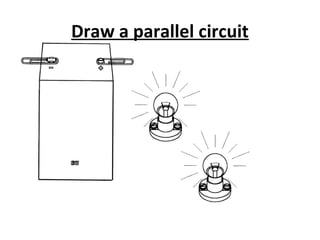

Electricity is the flow of electrons. Static electricity occurs when there is a buildup of electrons on an object without a discharge path, such as through friction. Current electricity requires a closed circuit or conductive path for electrons to flow from a power source through a load. Circuits can be in series, with one conductive path, or parallel with multiple paths. Conductors allow electron flow while insulators do not. Switches open or close circuits to control electron flow.
















