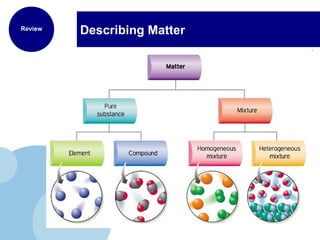
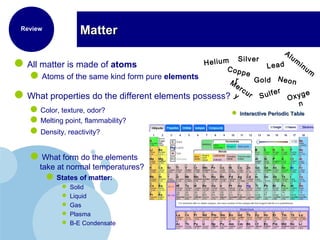
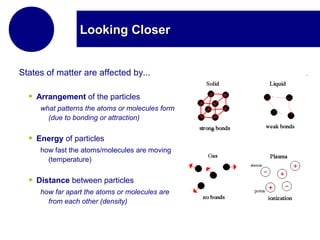
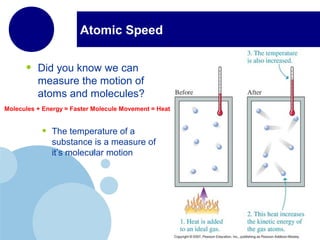
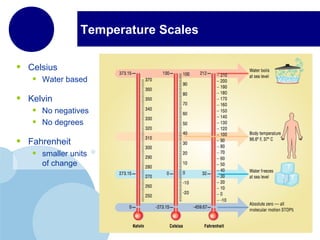
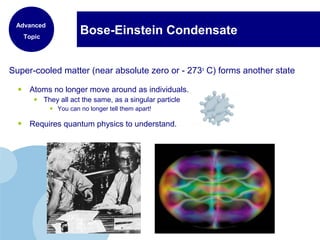
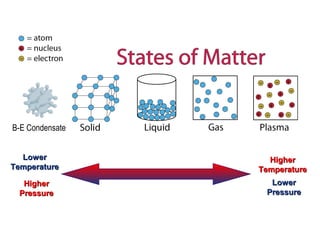
This document discusses the properties and states of matter. It defines matter as anything that has mass and takes up space, and explains that matter is made up of atoms. It then describes the three main states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases - and how their properties differ based on factors like the arrangement and movement of particles. The document also briefly introduces plasma and Bose-Einstein condensates as more advanced states of matter. It concludes by contrasting physical and chemical properties and changes in matter.