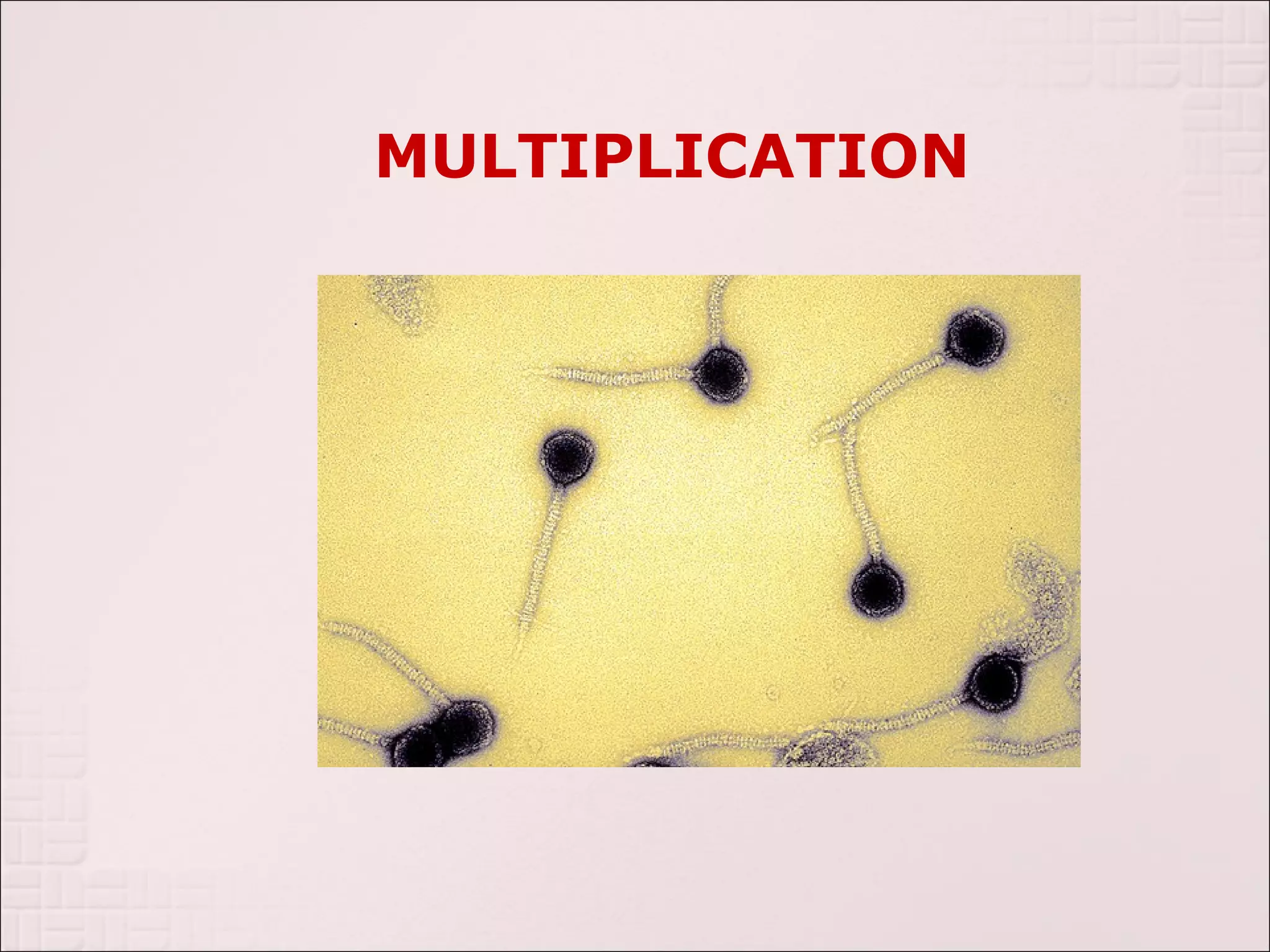
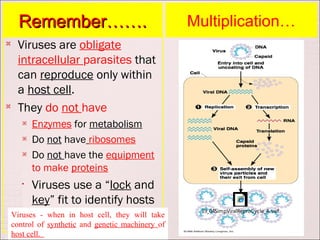
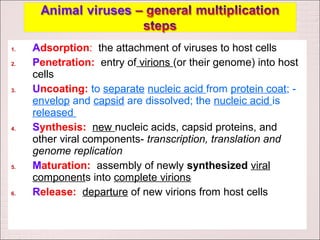
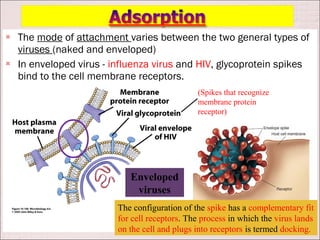
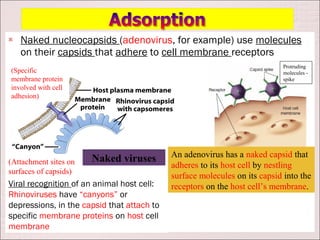
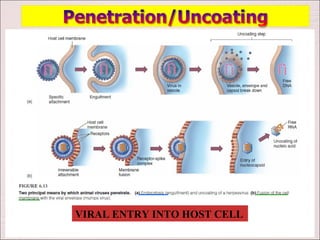
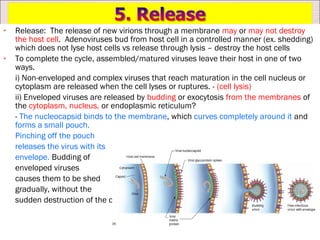
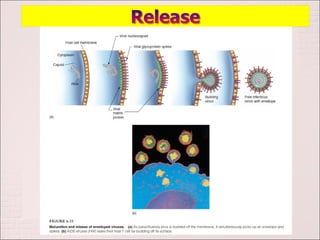
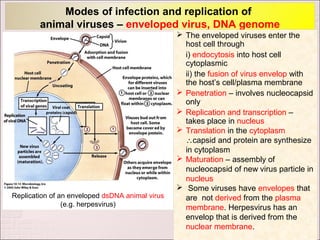
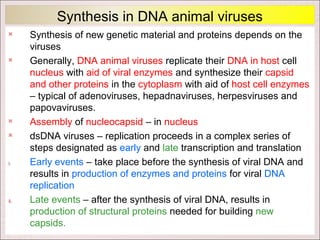
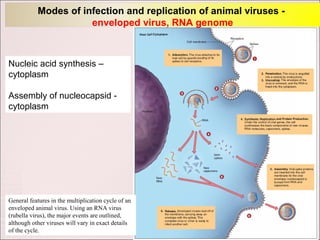
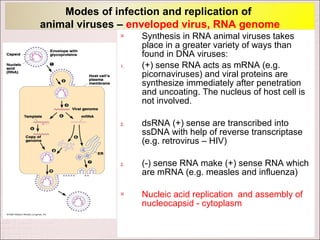
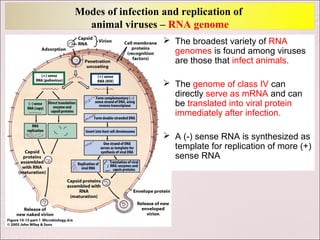
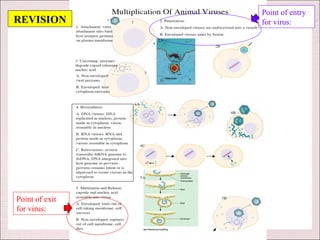
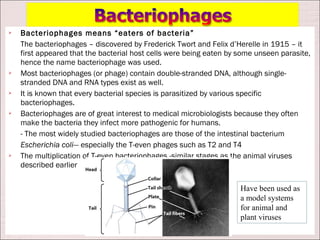
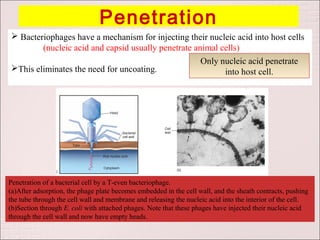
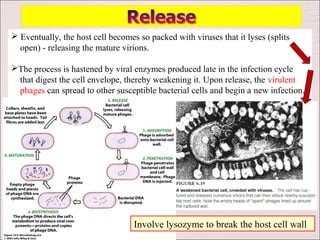
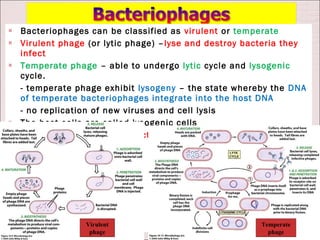
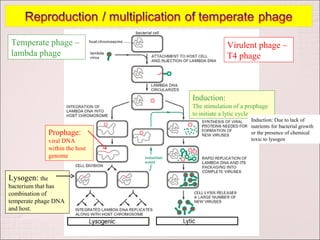
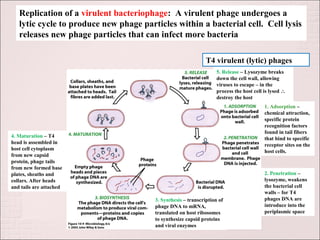
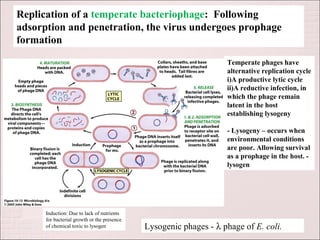
Viruses can only reproduce inside host cells. They hijack the host cell's synthetic machinery to produce new viral components. The viral replication cycle involves 5 main steps: [1] Adsorption where the virus attaches to the host cell, [2] Penetration where the viral genome enters the host cell, [3] Synthesis of new viral components using the host cell, [4] Assembly of new viral particles, and [5] Release of progeny virus from the host cell. Bacteriophages infect bacteria and have a similar replication cycle except they can directly inject their genome into bacteria without uncoating.