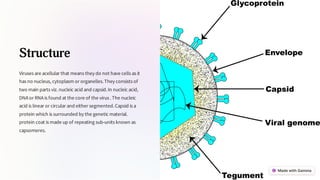
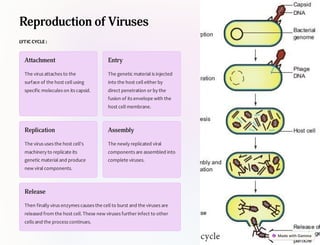
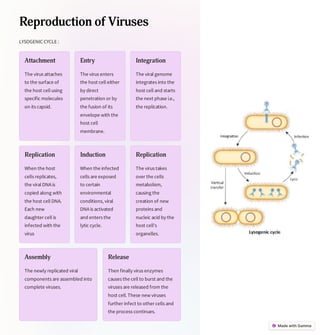
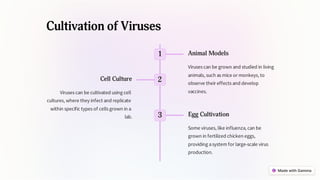
Viruses are tiny infectious agents that multiply within living cells and consist of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat. They do not have cells and can have different structures including icosahedral, helical, and complex symmetry. Viruses are classified based on their genetic material, host range, site of replication, capsid structure, and mode of transmission. Viruses reproduce through lytic and lysogenic cycles using the host cell's machinery to replicate their components and release new viruses. They can be cultivated in animal models, cell cultures, and fertilized eggs to study and mass produce viruses. Studying viruses is important for disease prevention, emerging infection monitoring, and biotechnological applications.