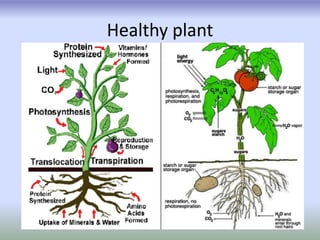
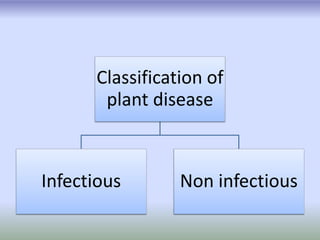
This document provides an introduction to plant pathology. It defines plant pathology as the study of plant diseases caused by pathogens and environmental conditions. Plant disease is defined as a malfunctioning process caused by continuous irritation that produces symptoms, impairing the plant's quality and value. Plant diseases are classified as either infectious, caused by living pathogens that can spread, or non-infectious, caused by non-living factors like temperature, moisture, pollution or nutrient issues.