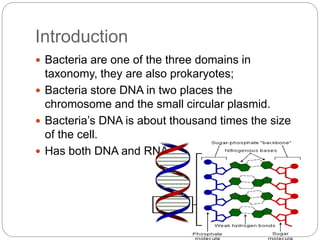
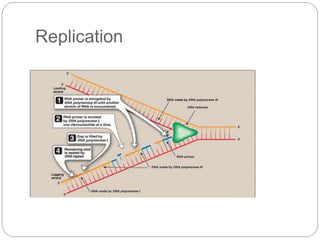
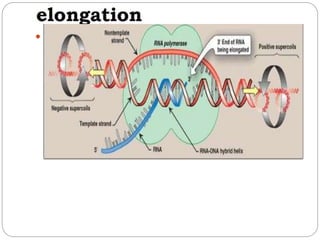
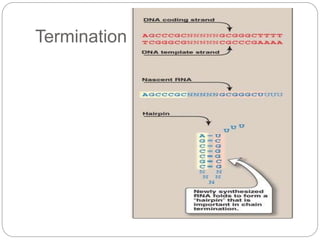
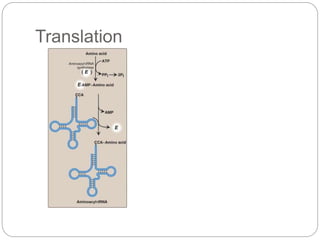
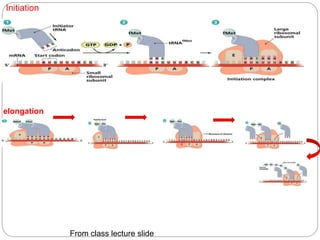
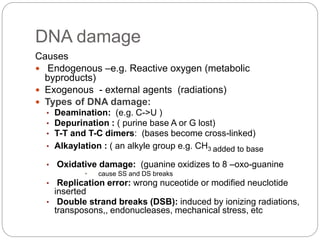
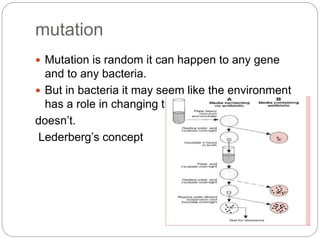
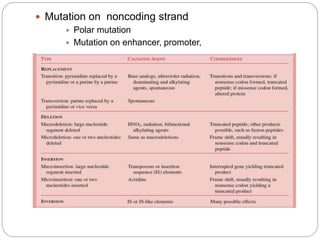
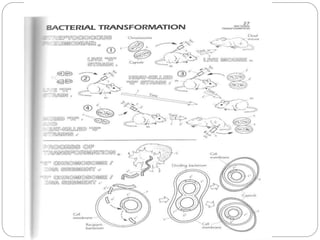
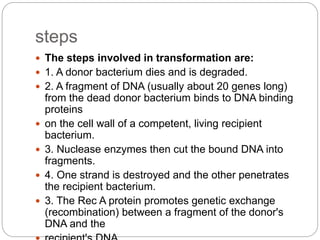
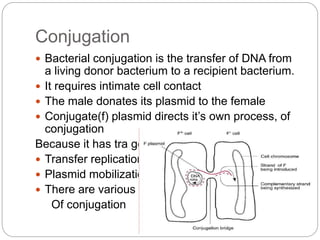
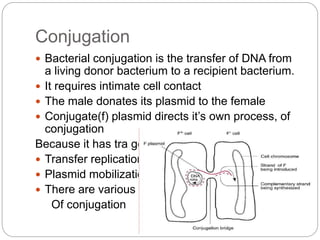
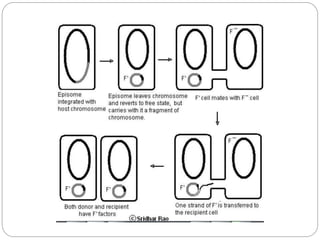
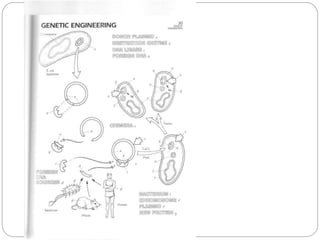
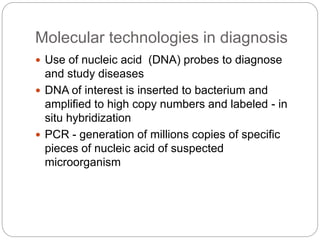
Bacterial genetics involves the study of bacterial chromosomes, plasmids, transcription, translation, replication, and genetic variation. Bacteria store DNA in circular chromosomes and small plasmids. Transcription and translation allow genes to be expressed. Replication duplicates genetic material. Bacteria undergo genetic variation through mutation, transformation, conjugation, and transduction, allowing them to adapt. Genetic engineering uses bacteria to produce recombinant proteins for research and medical purposes like vaccines.