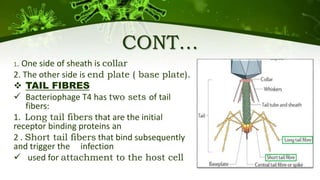
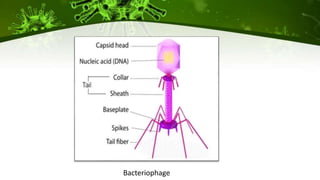
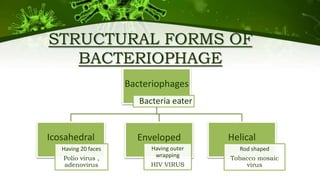
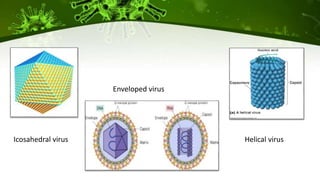
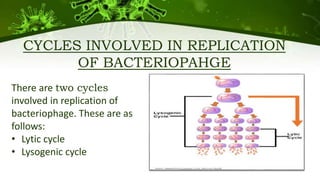
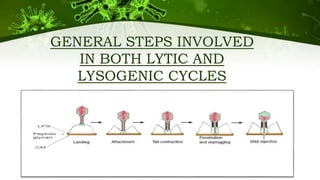
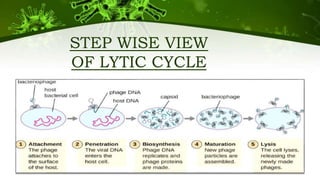
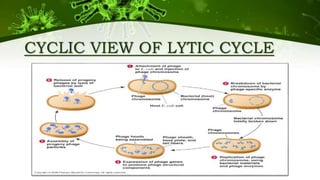
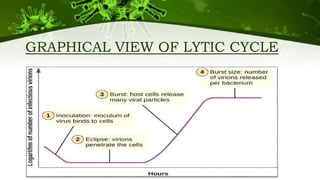
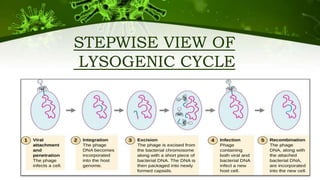
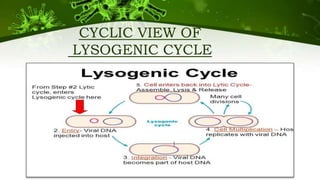
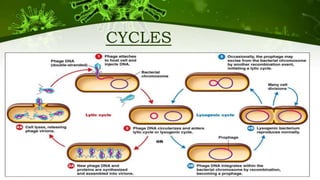
The document discusses the life cycle of viruses, specifically bacteriophages. It describes two main cycles - the lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle. The lytic cycle involves the viral DNA replicating separately from the host cell and ultimately causing the cell to burst. The lysogenic cycle involves the viral DNA integrating into the host cell's genome where it can remain dormant for generations before entering the lytic cycle. The key difference between the cycles is that the lytic cycle results in host cell death while the lysogenic cycle allows the host cell to survive and replicate normally.