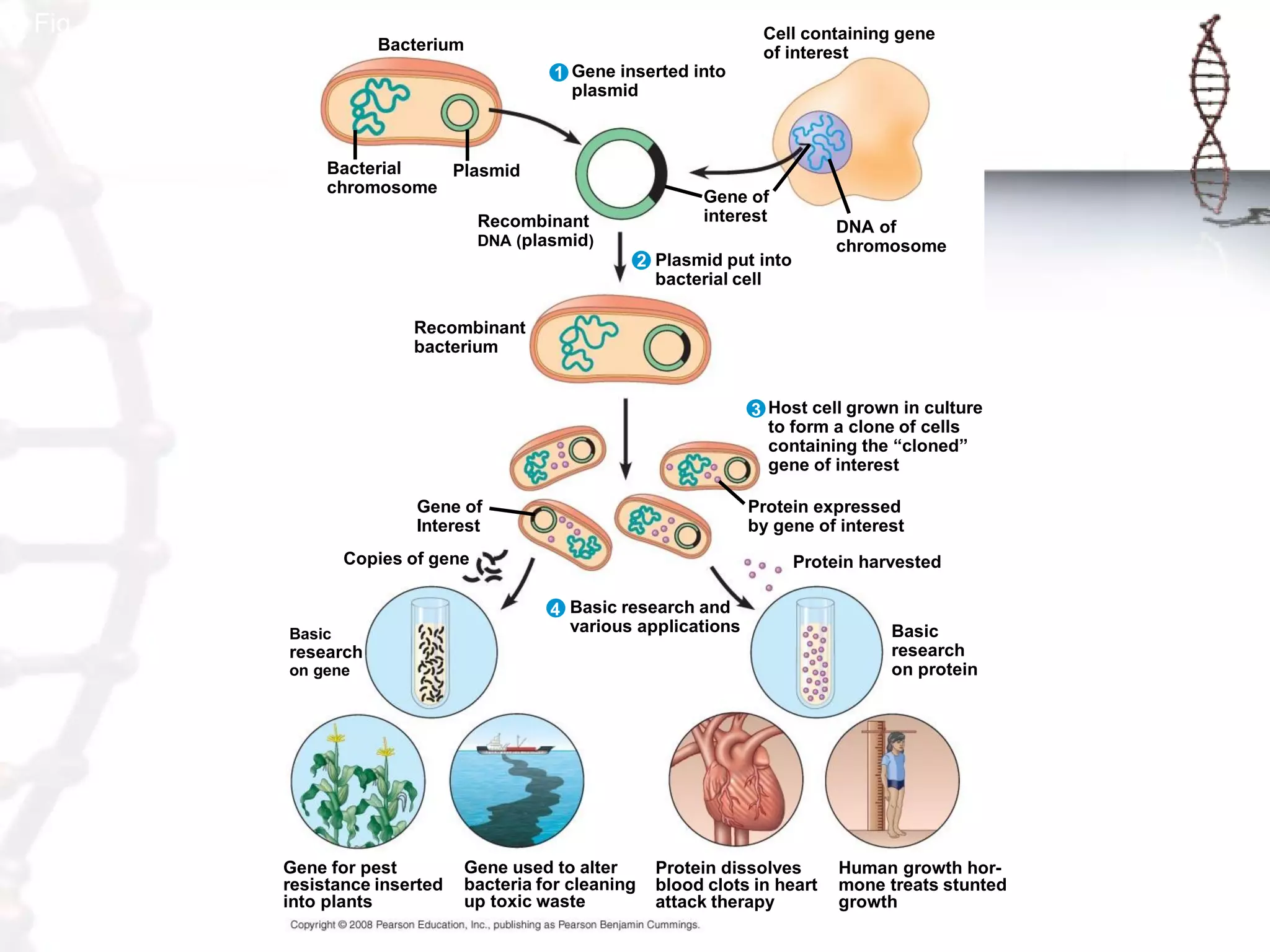
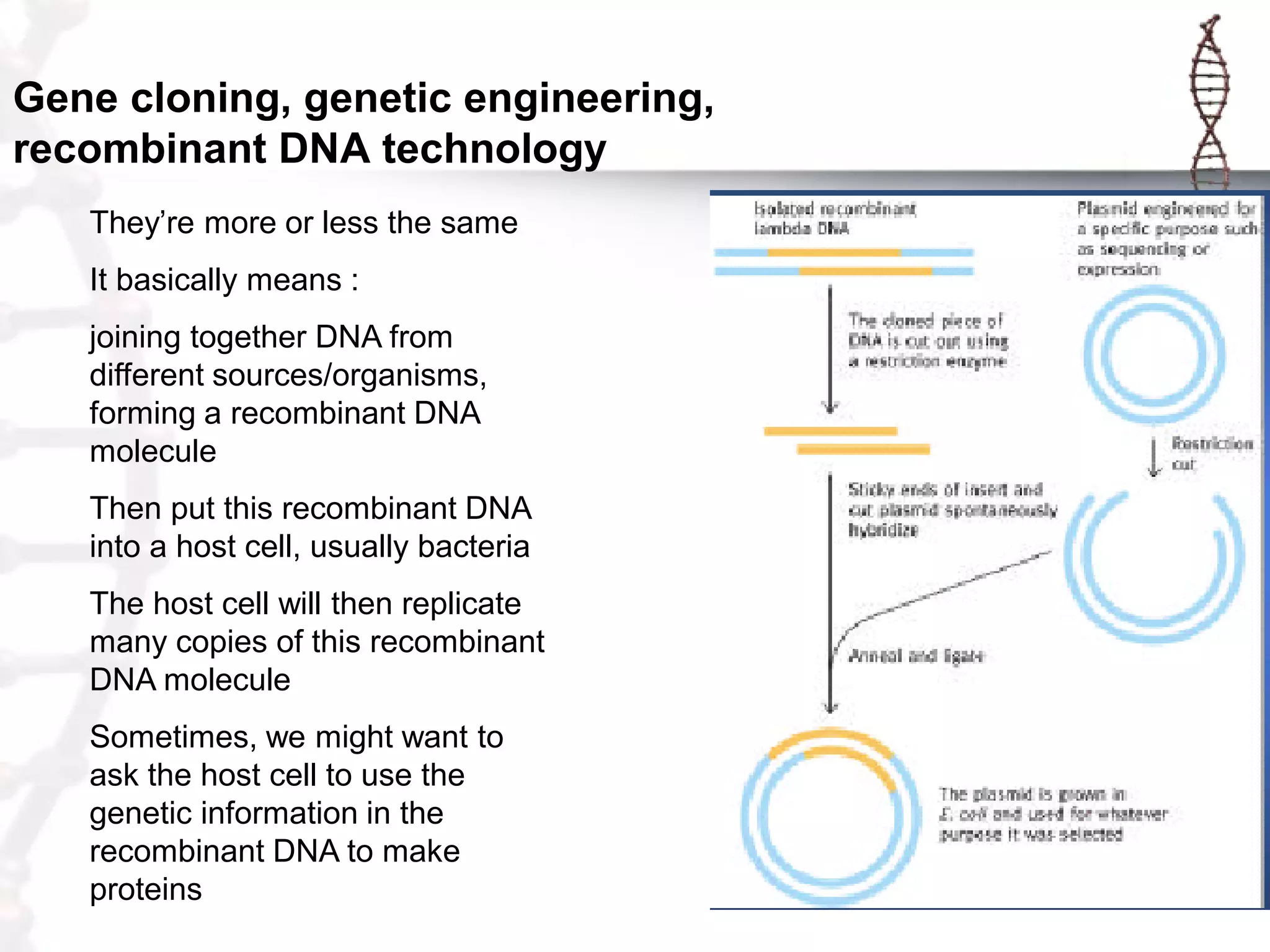
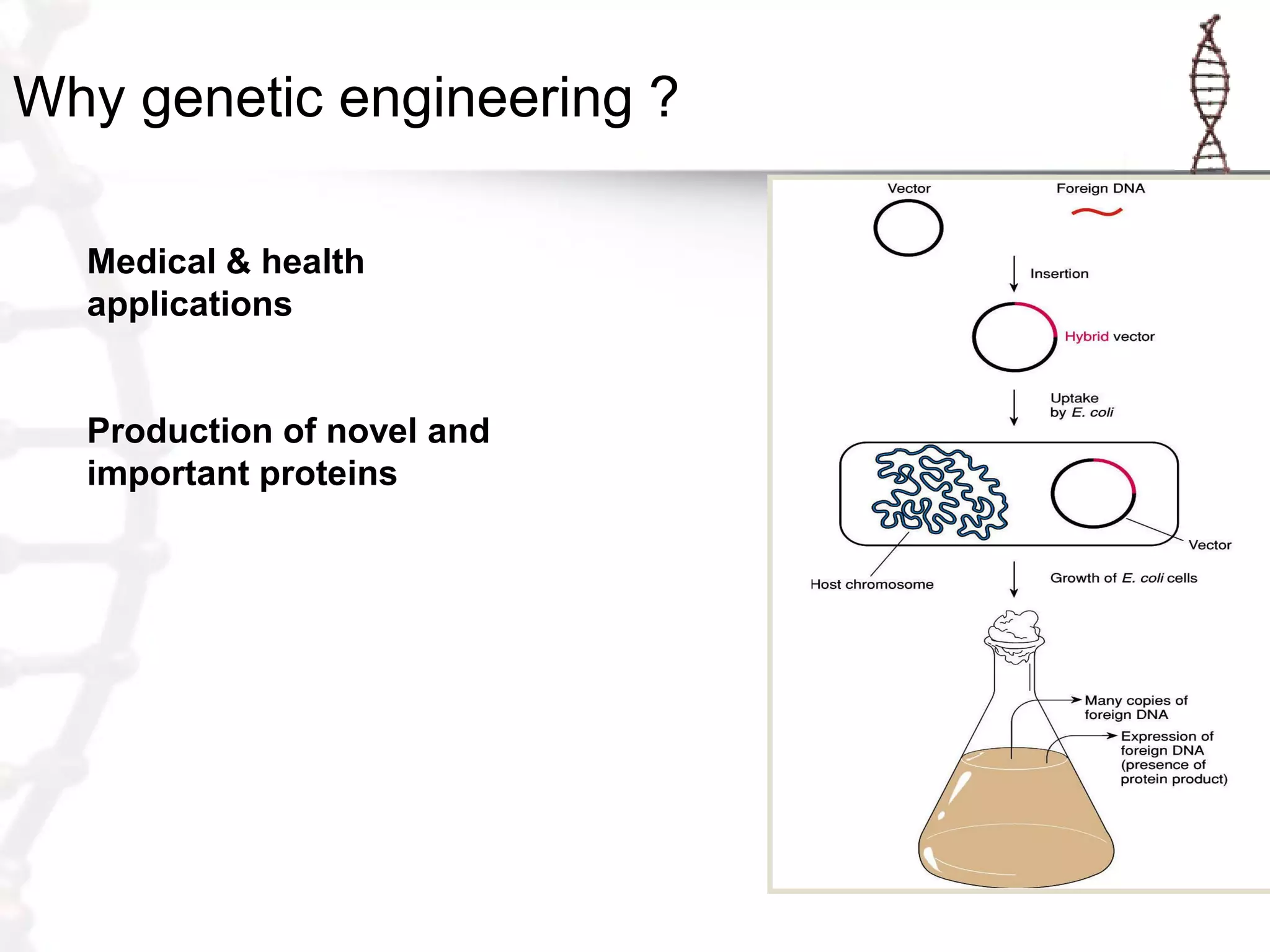
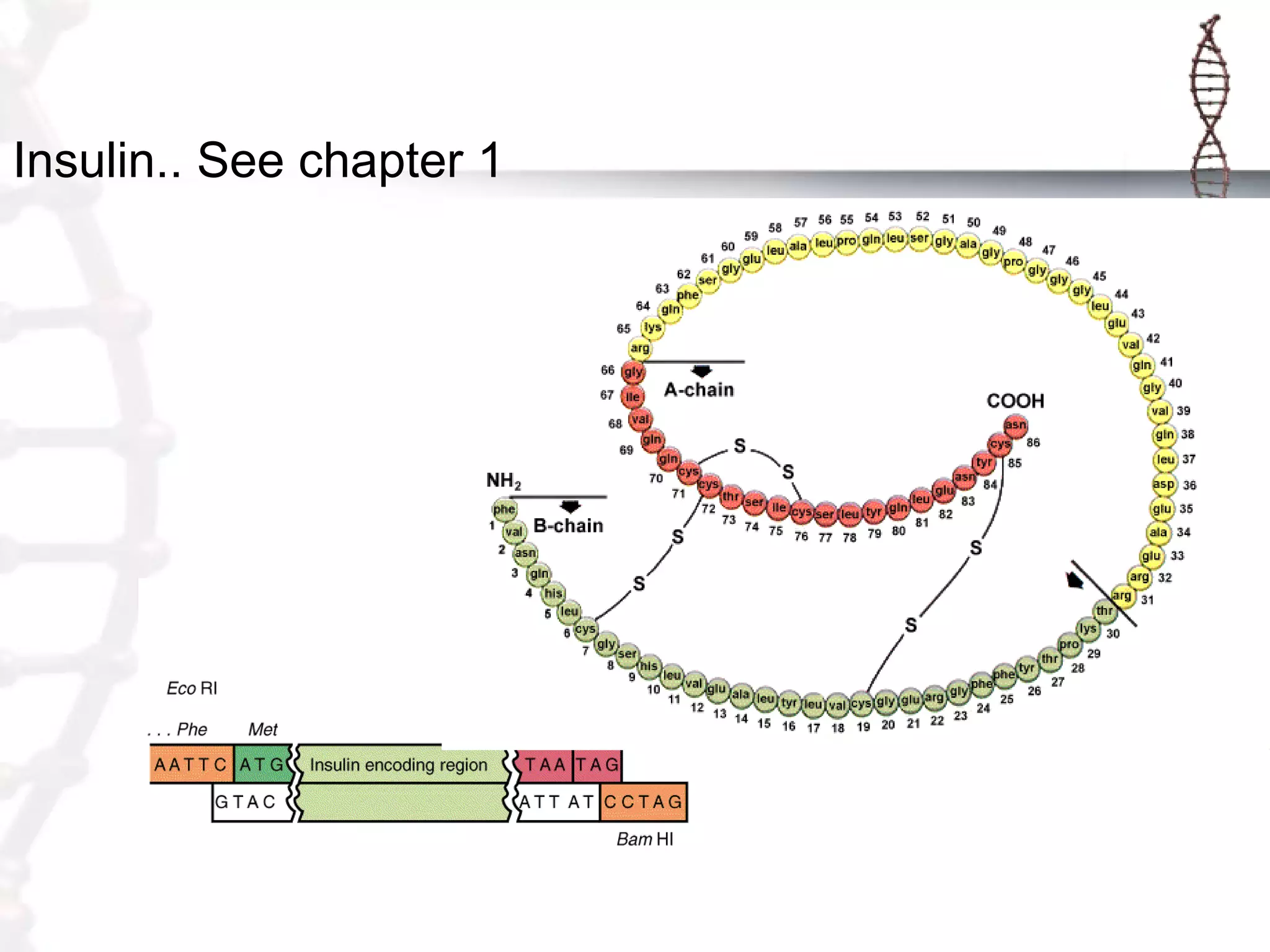
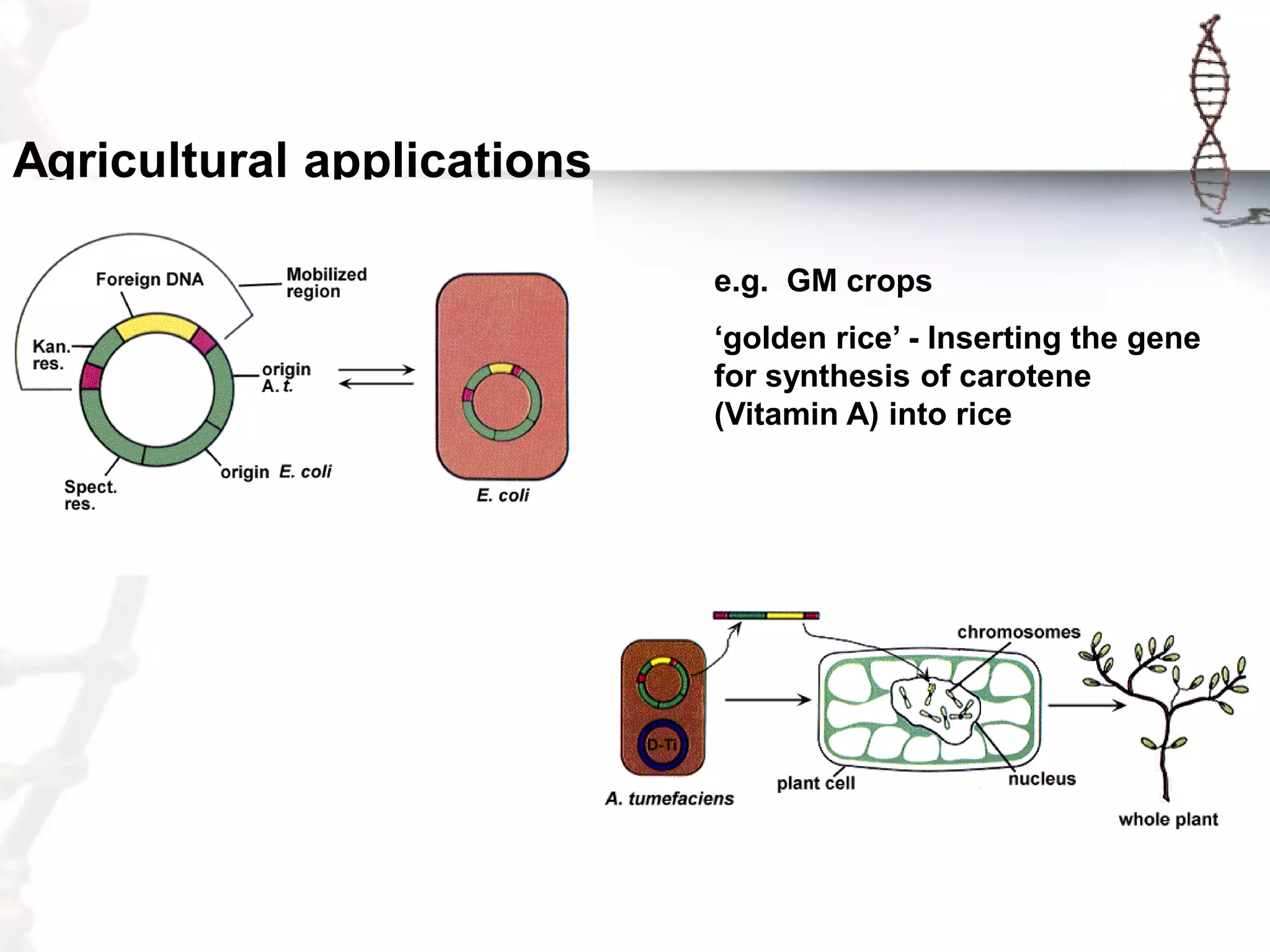
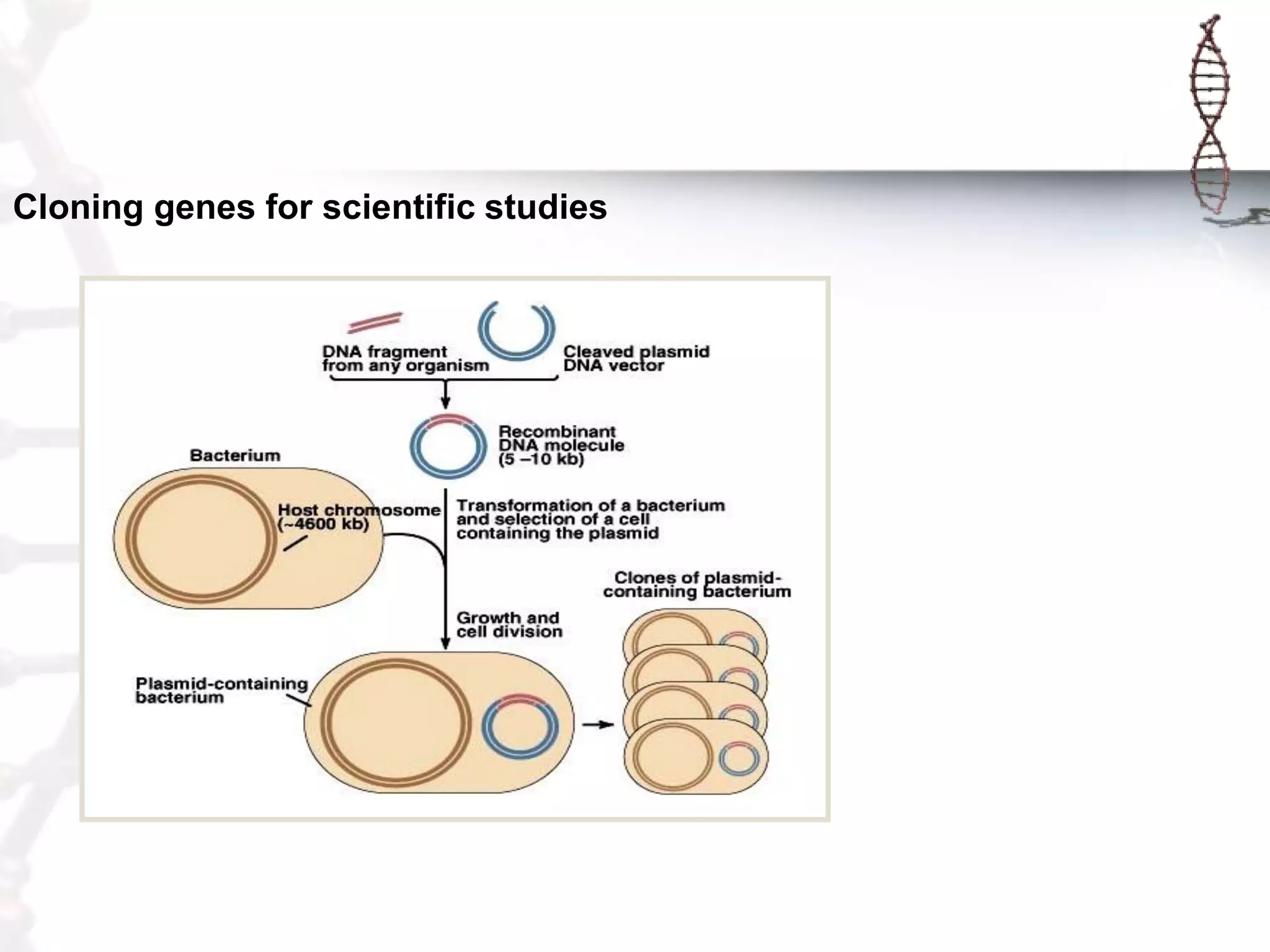
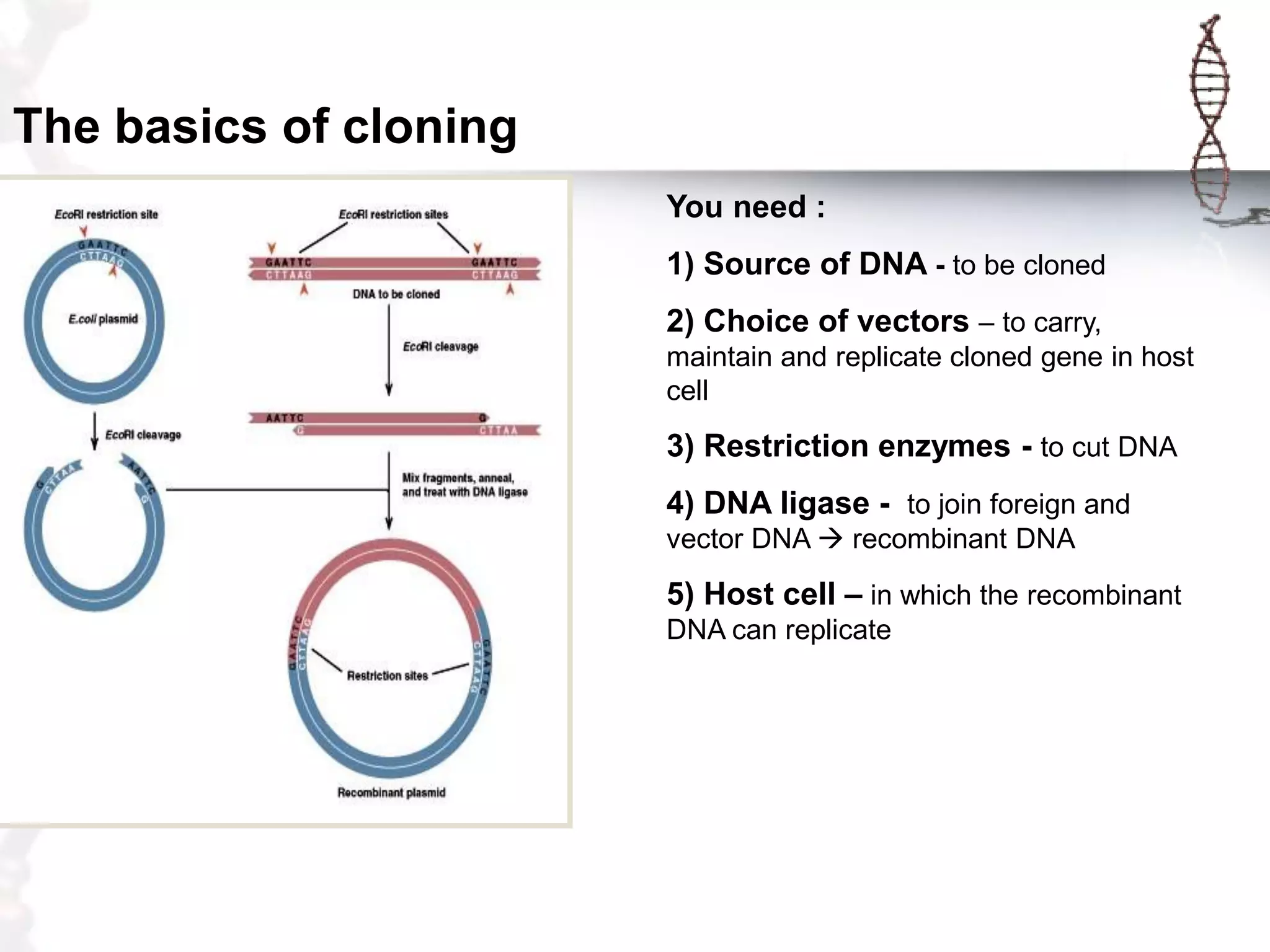
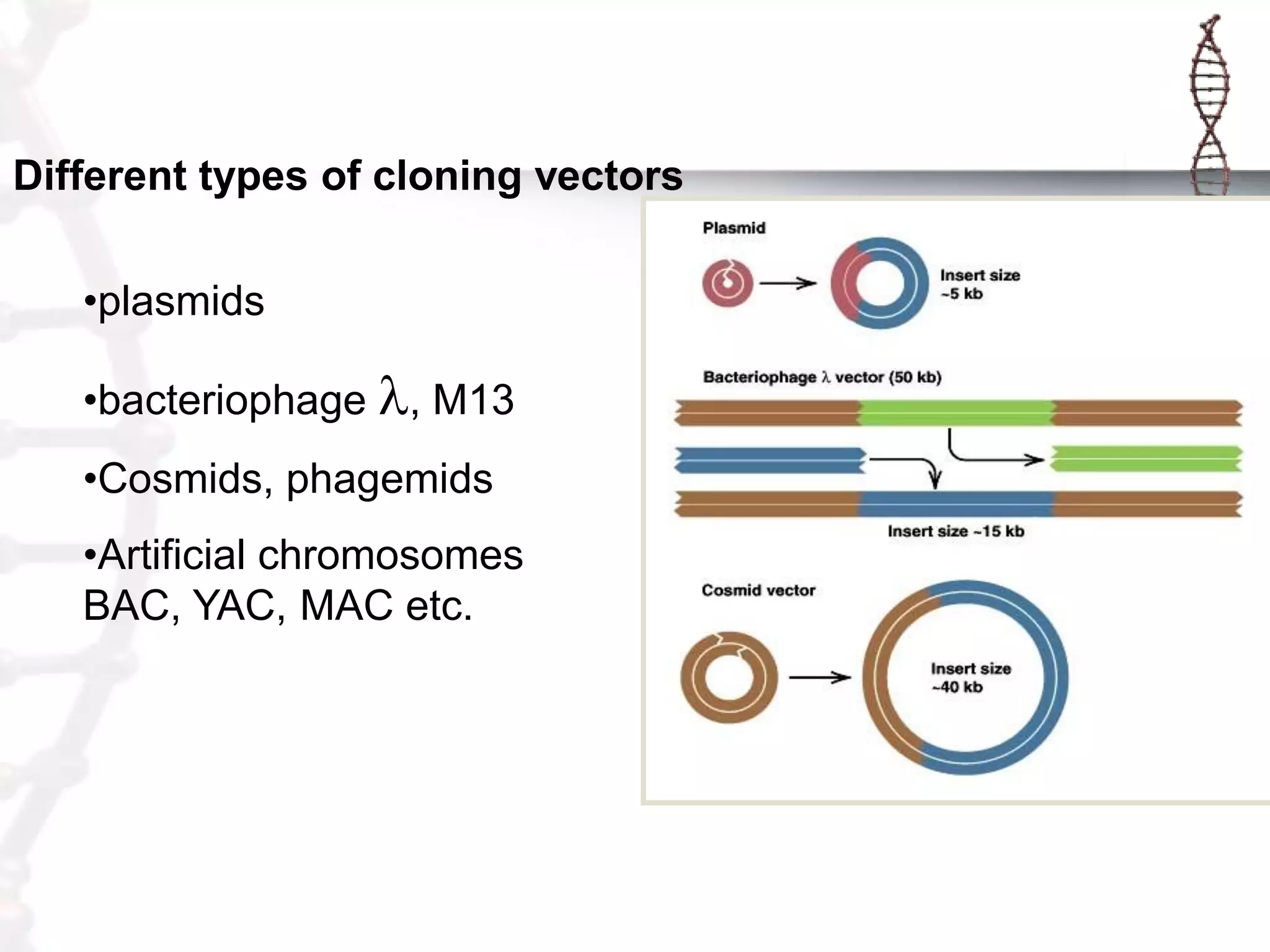
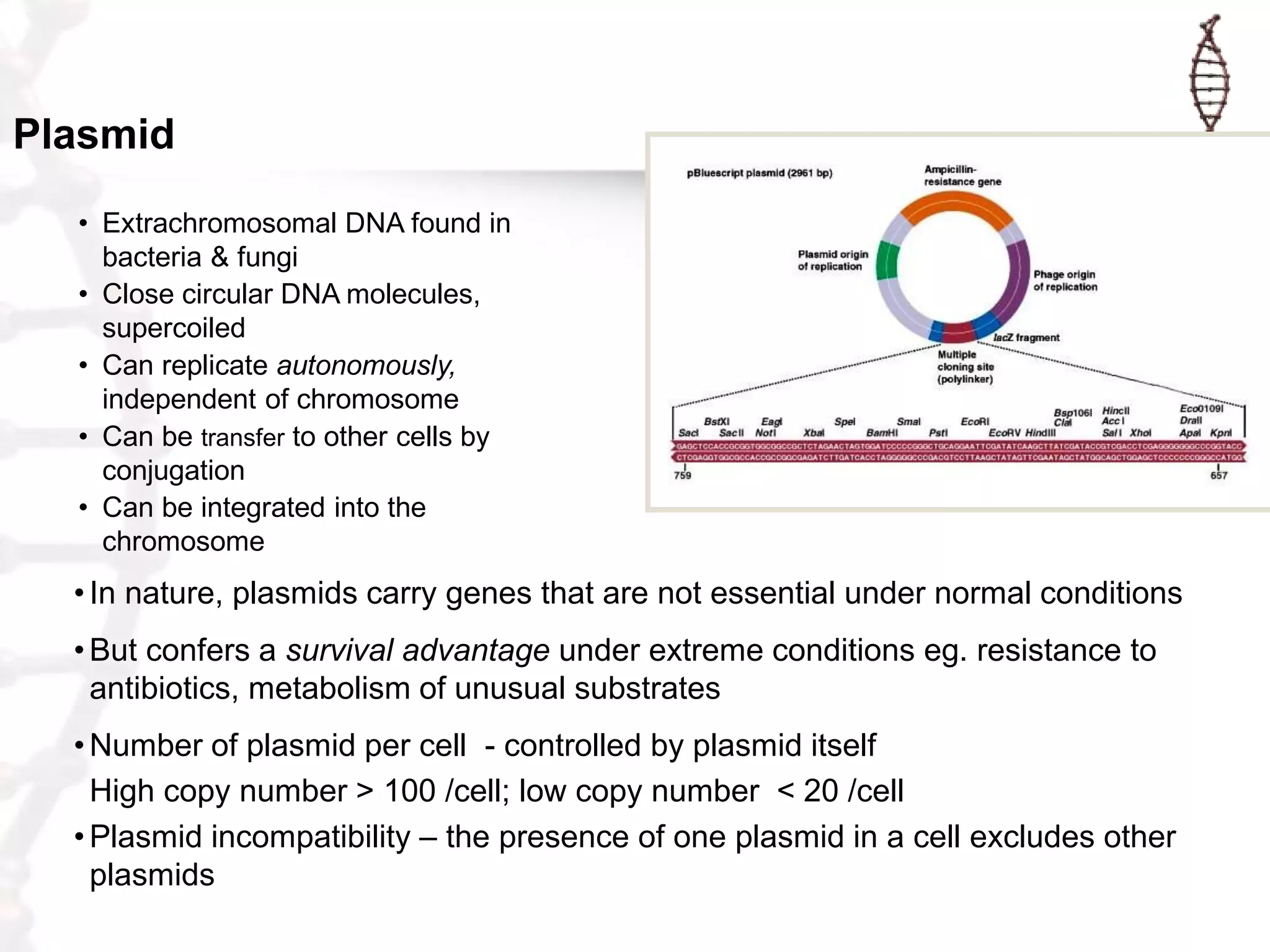
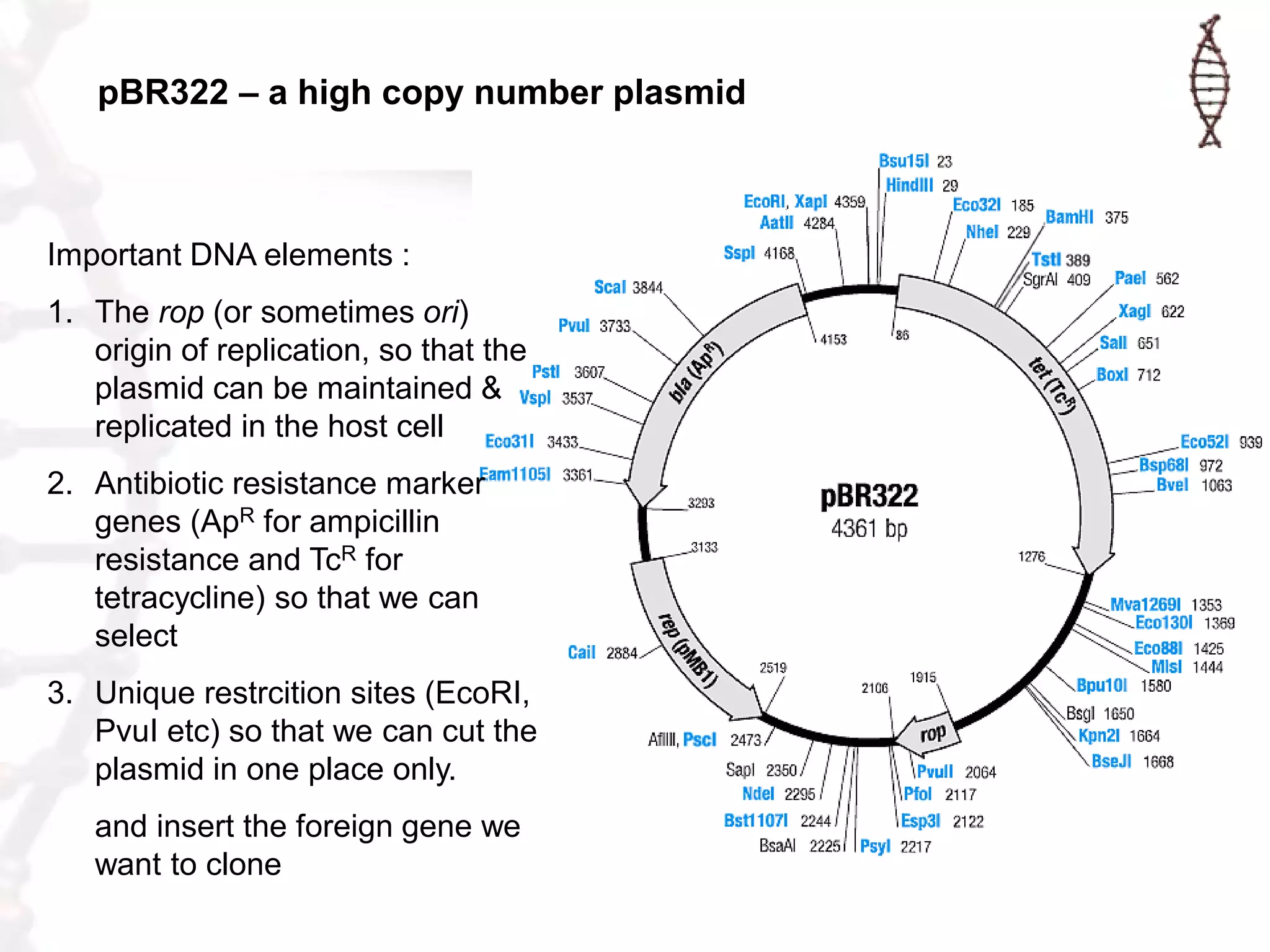
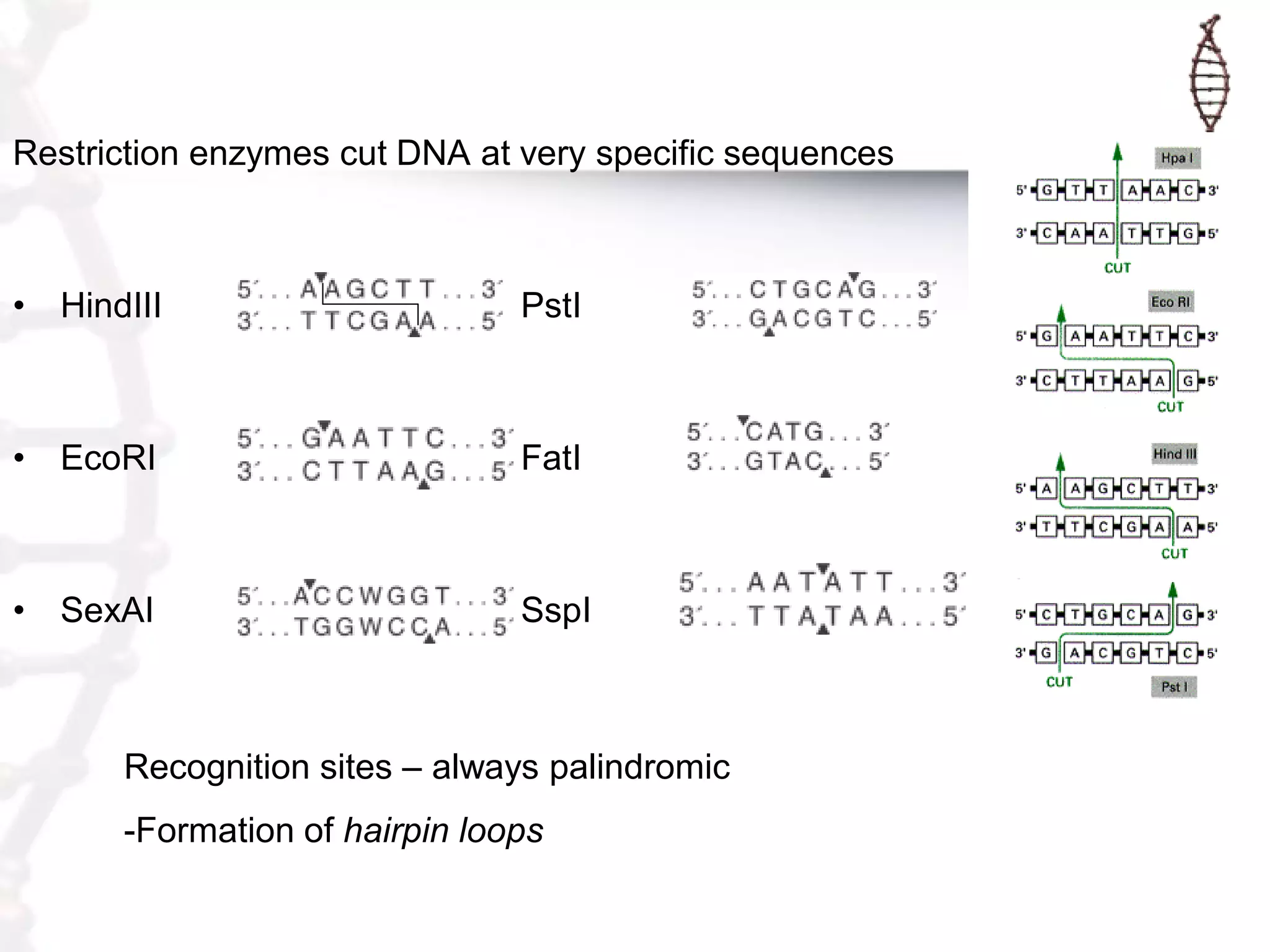
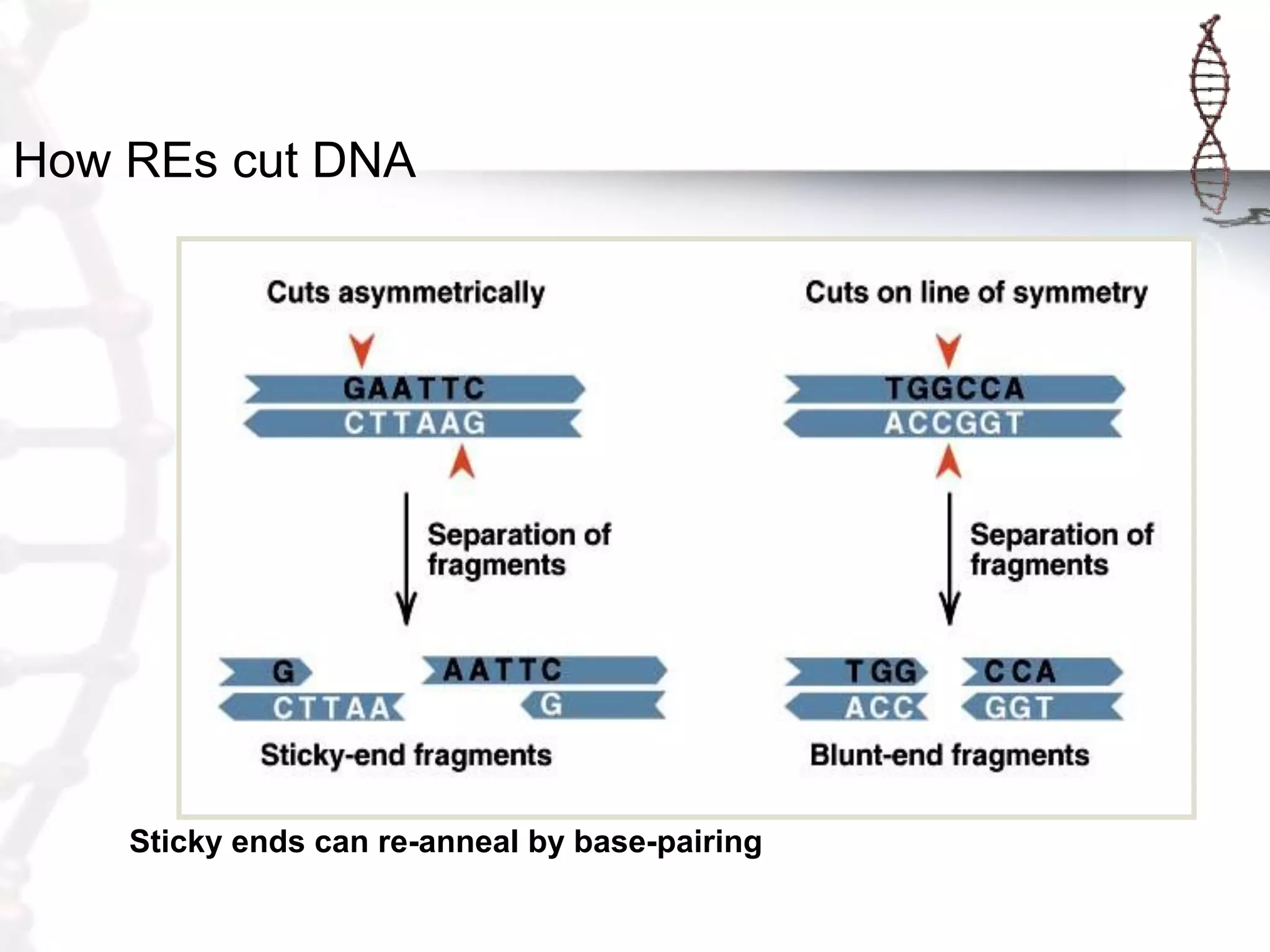
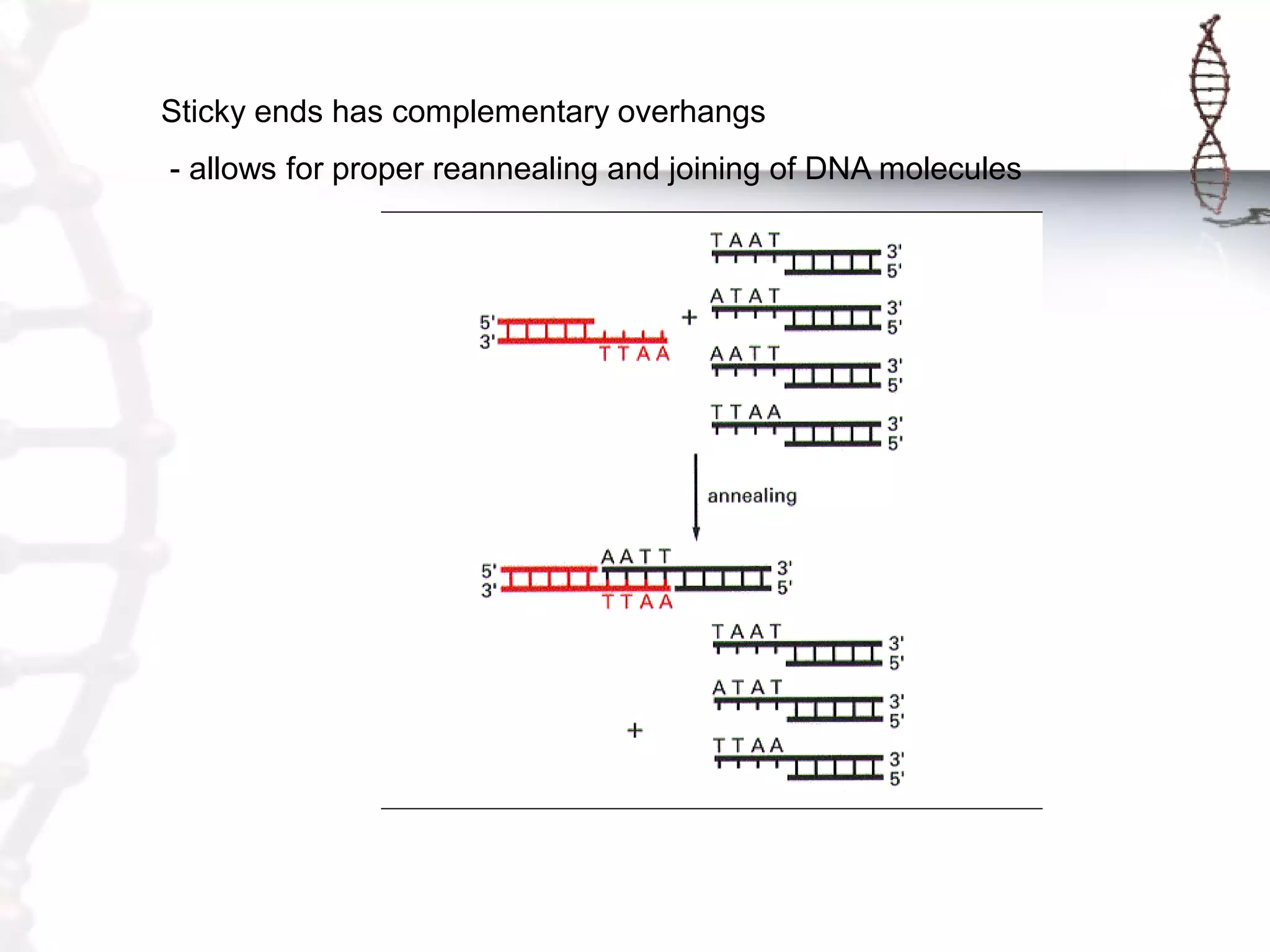
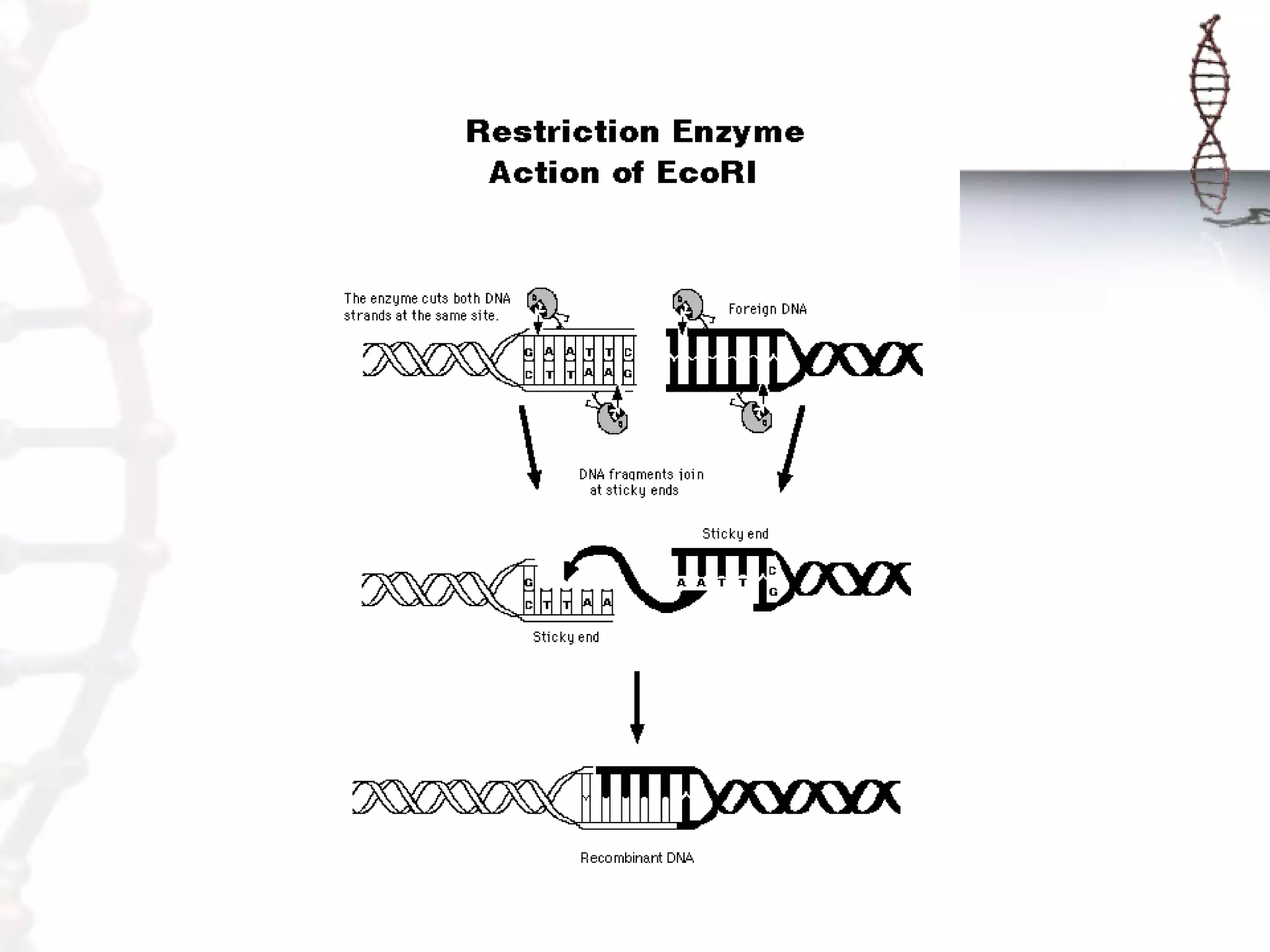
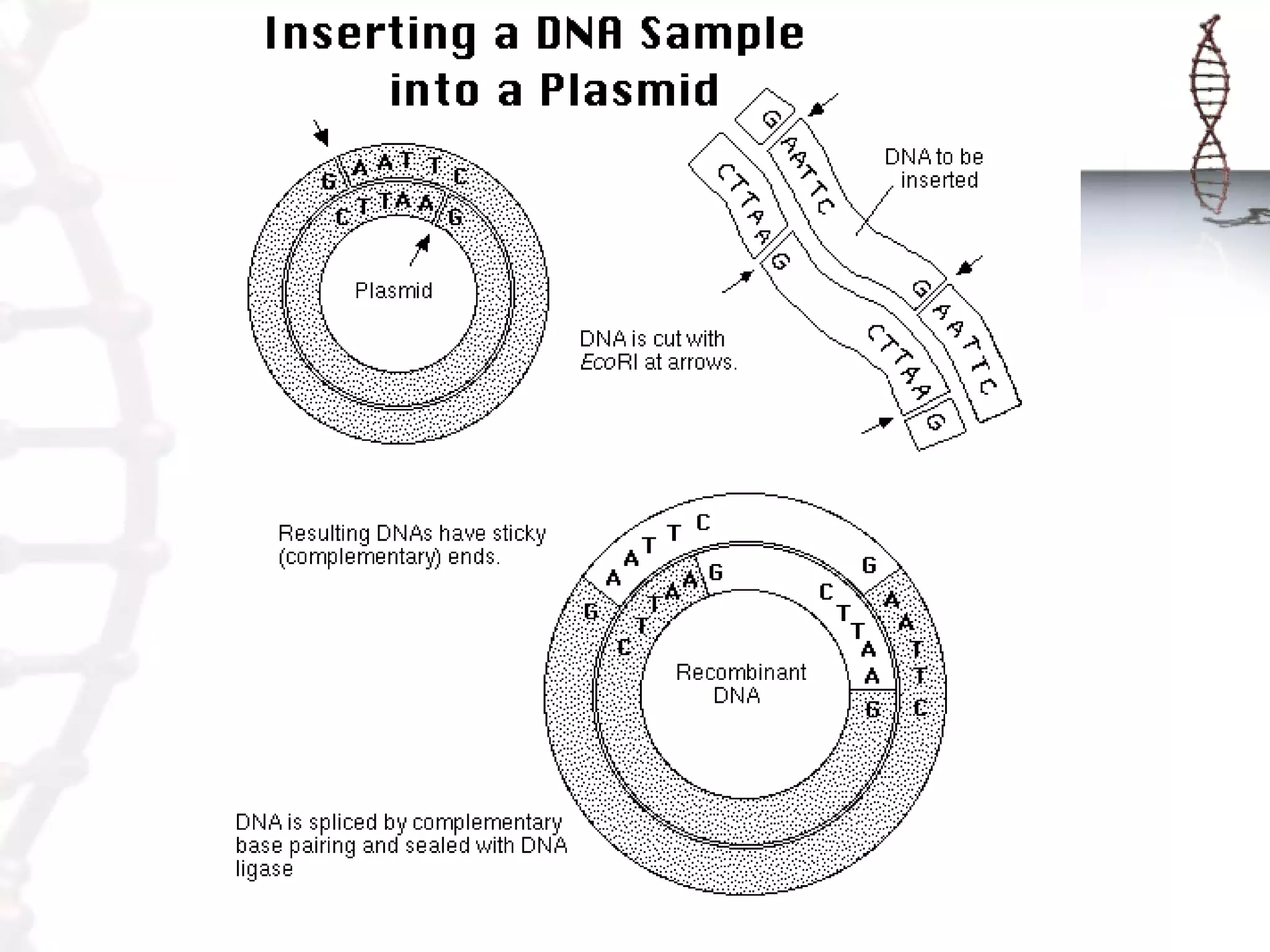
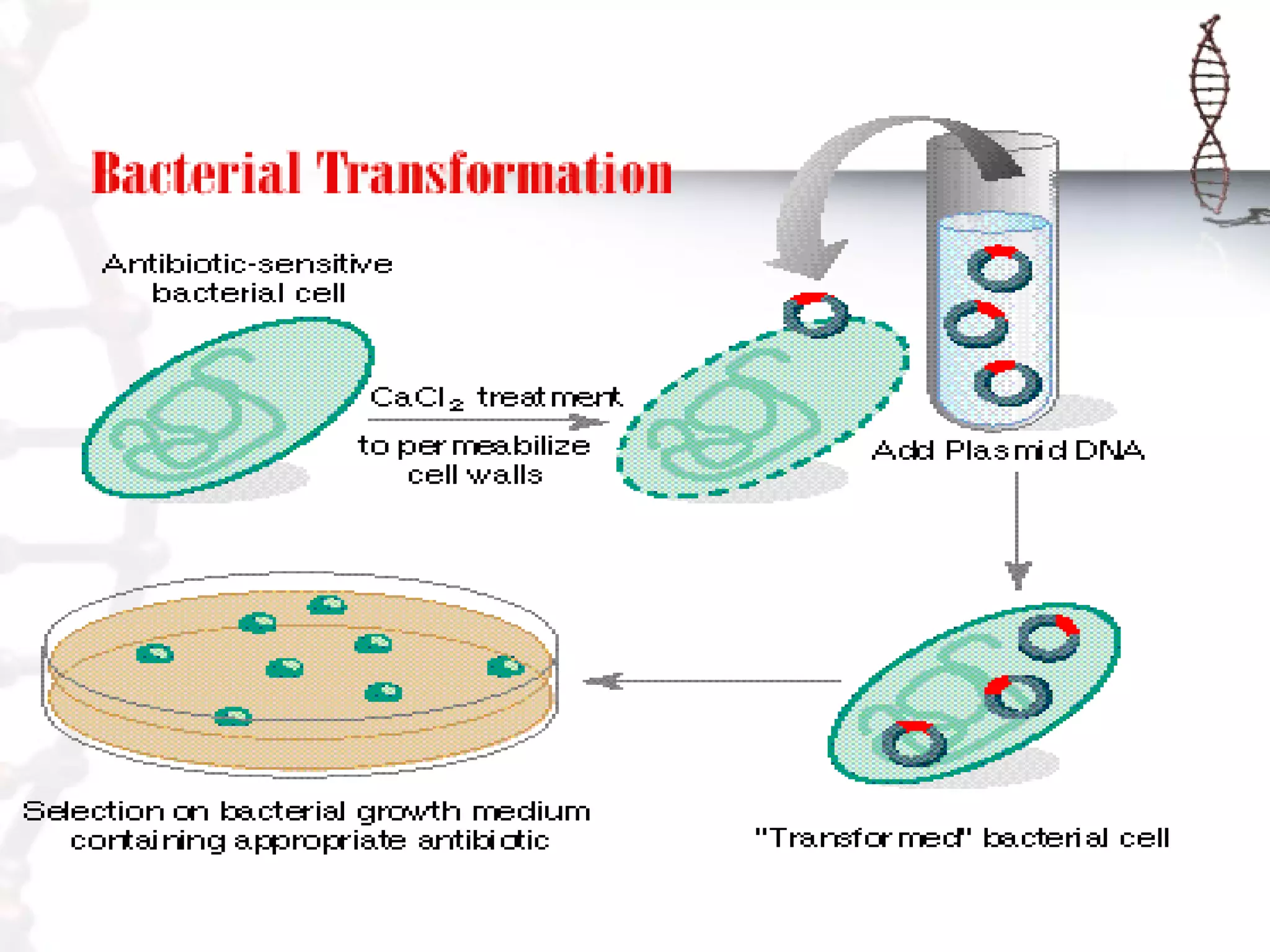
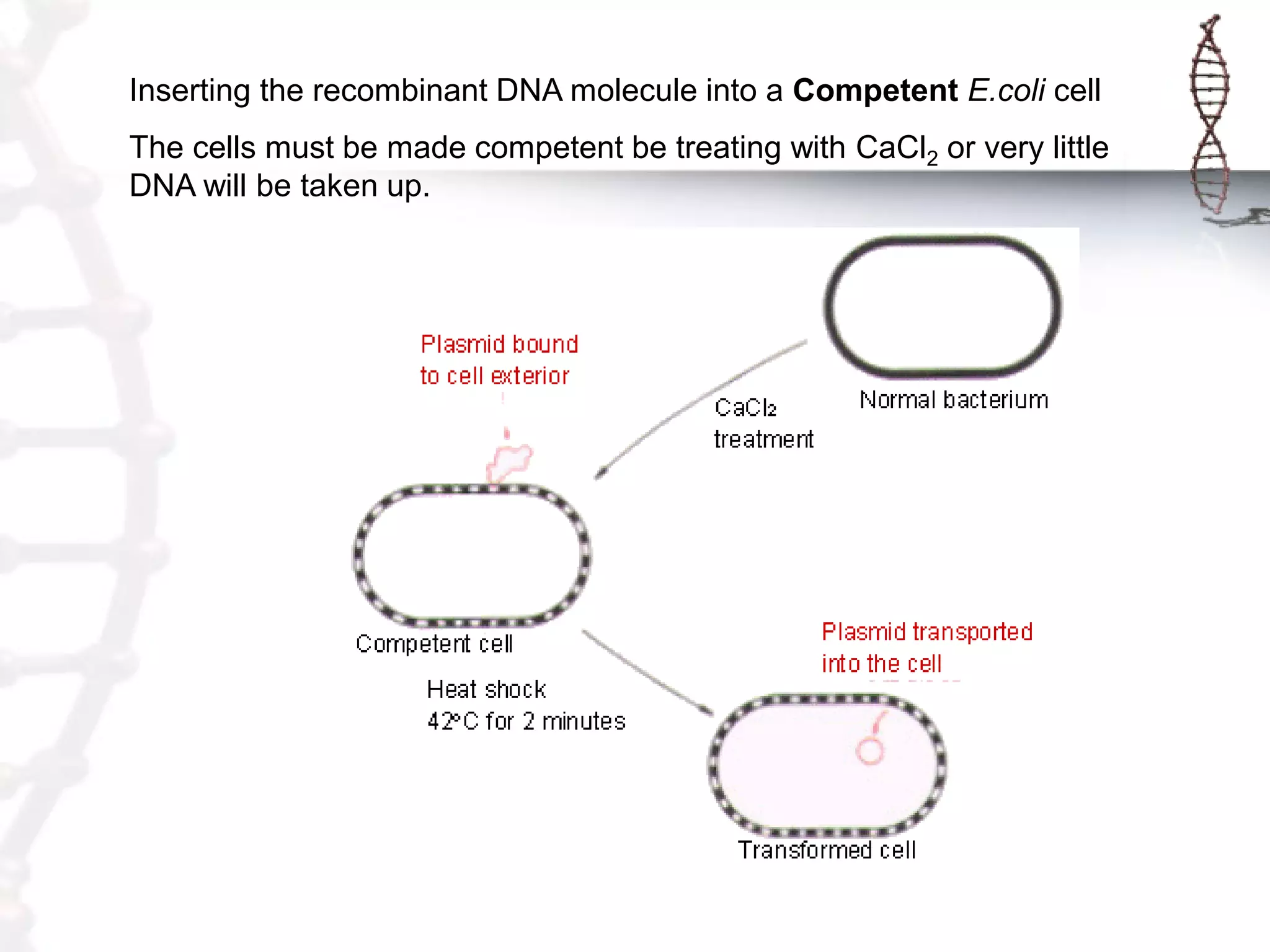
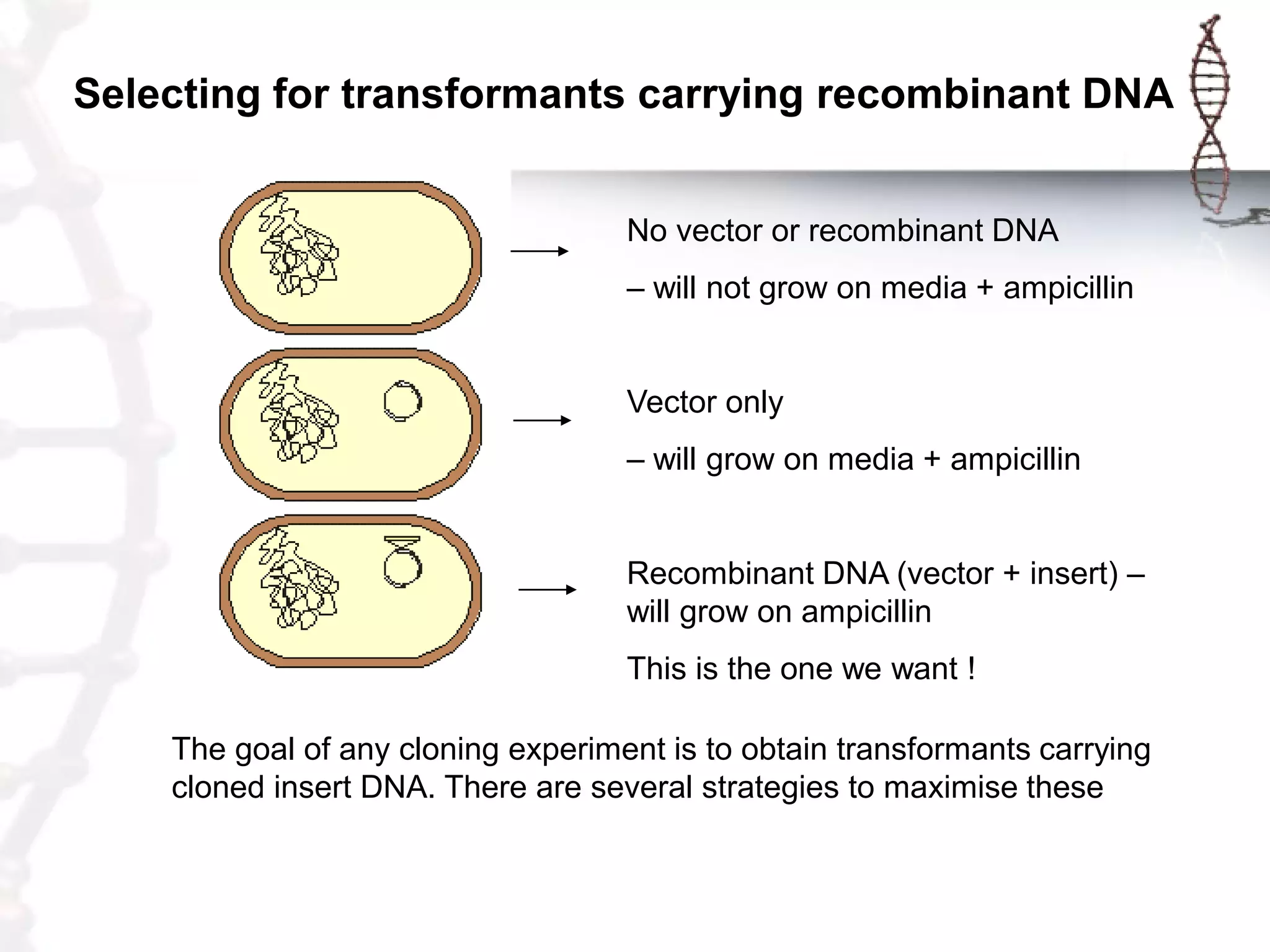
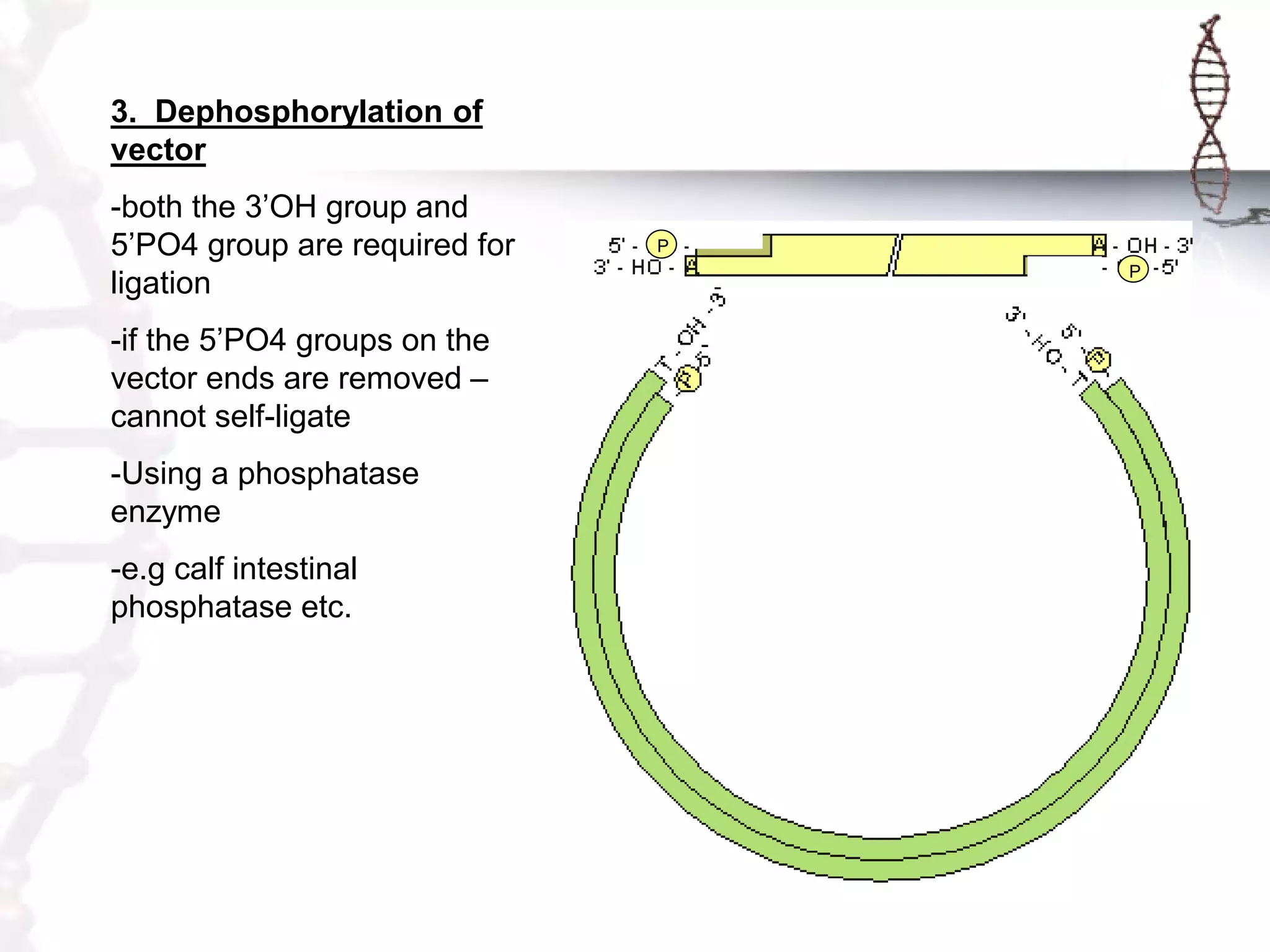
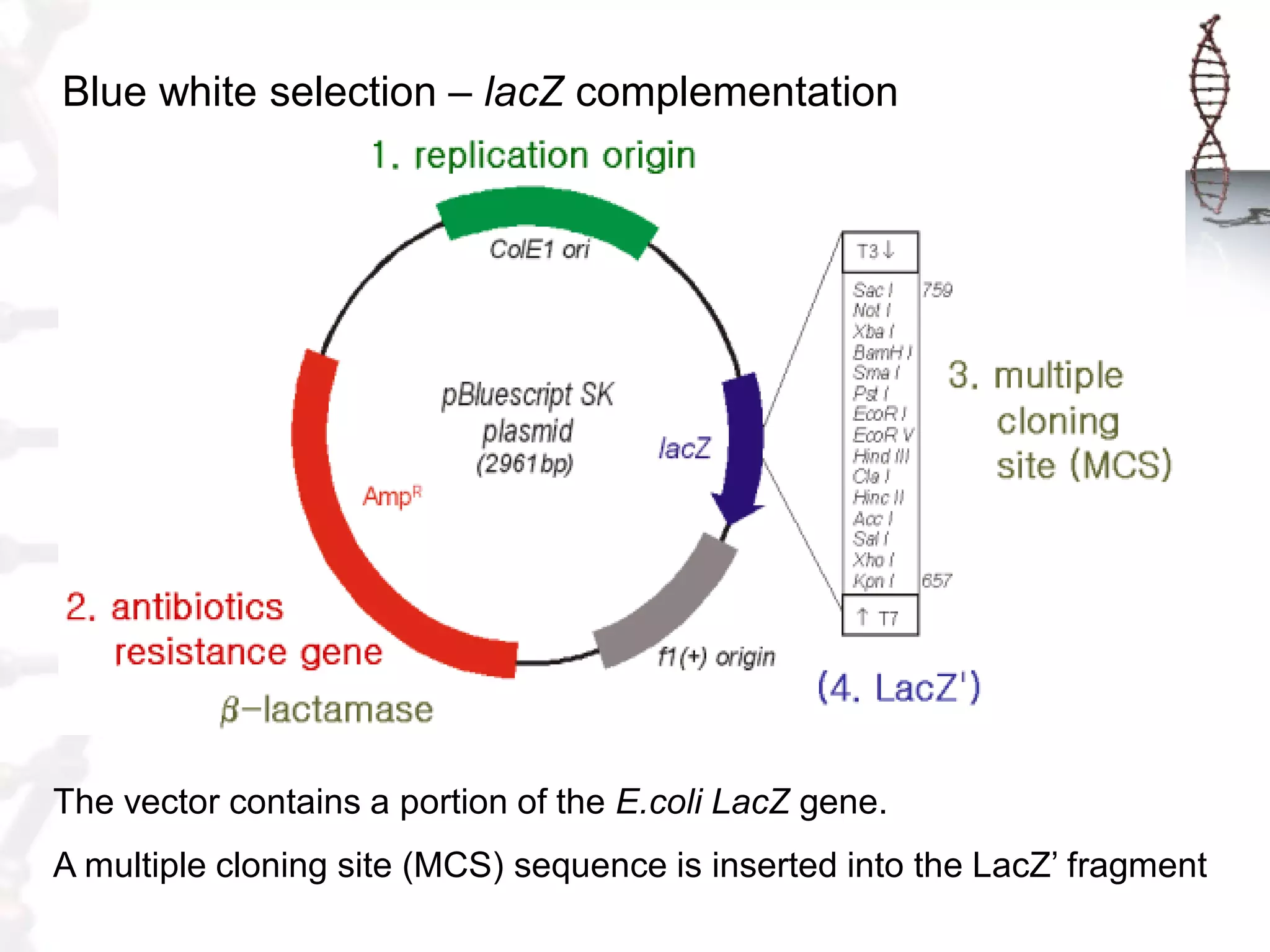
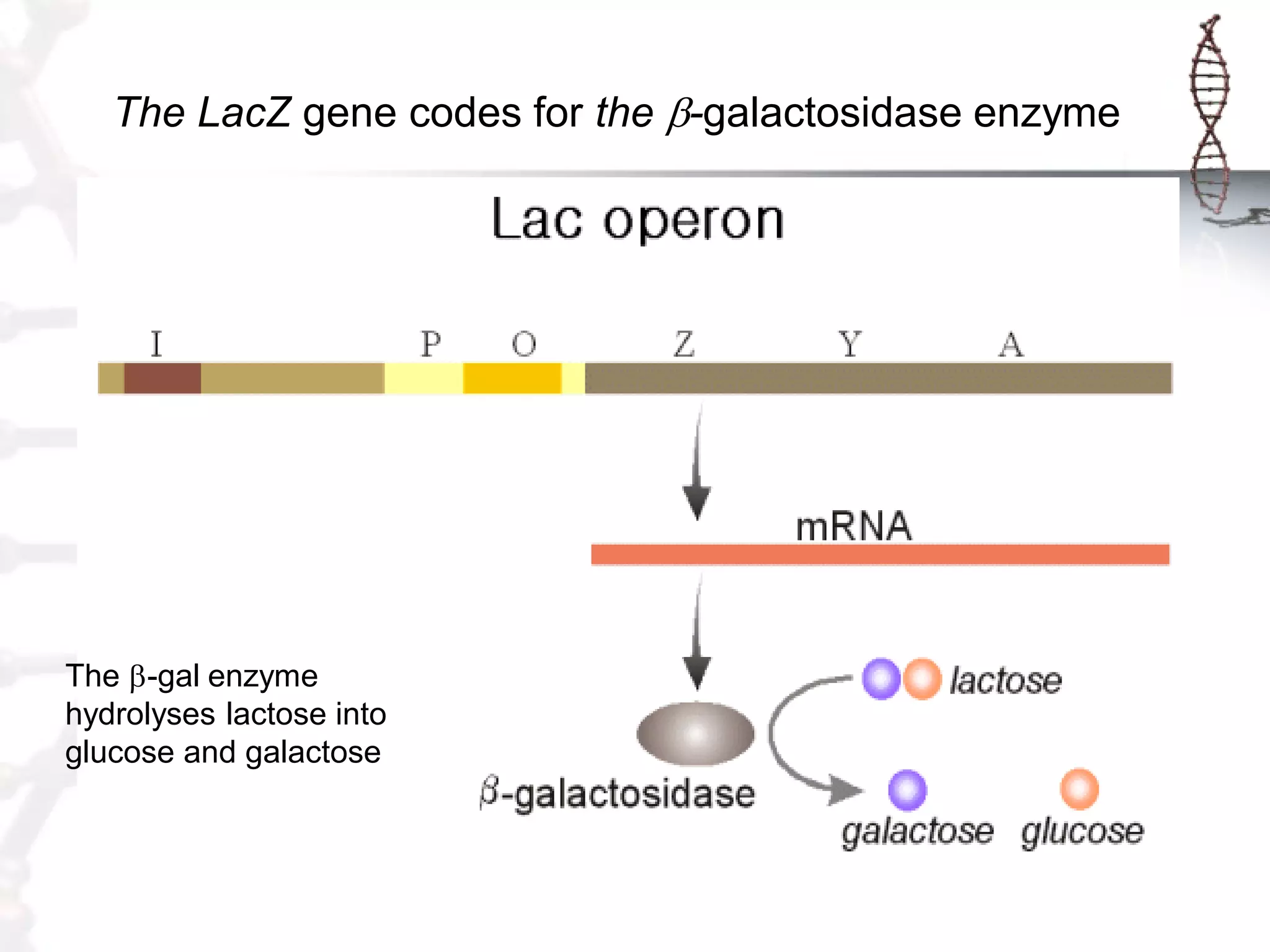
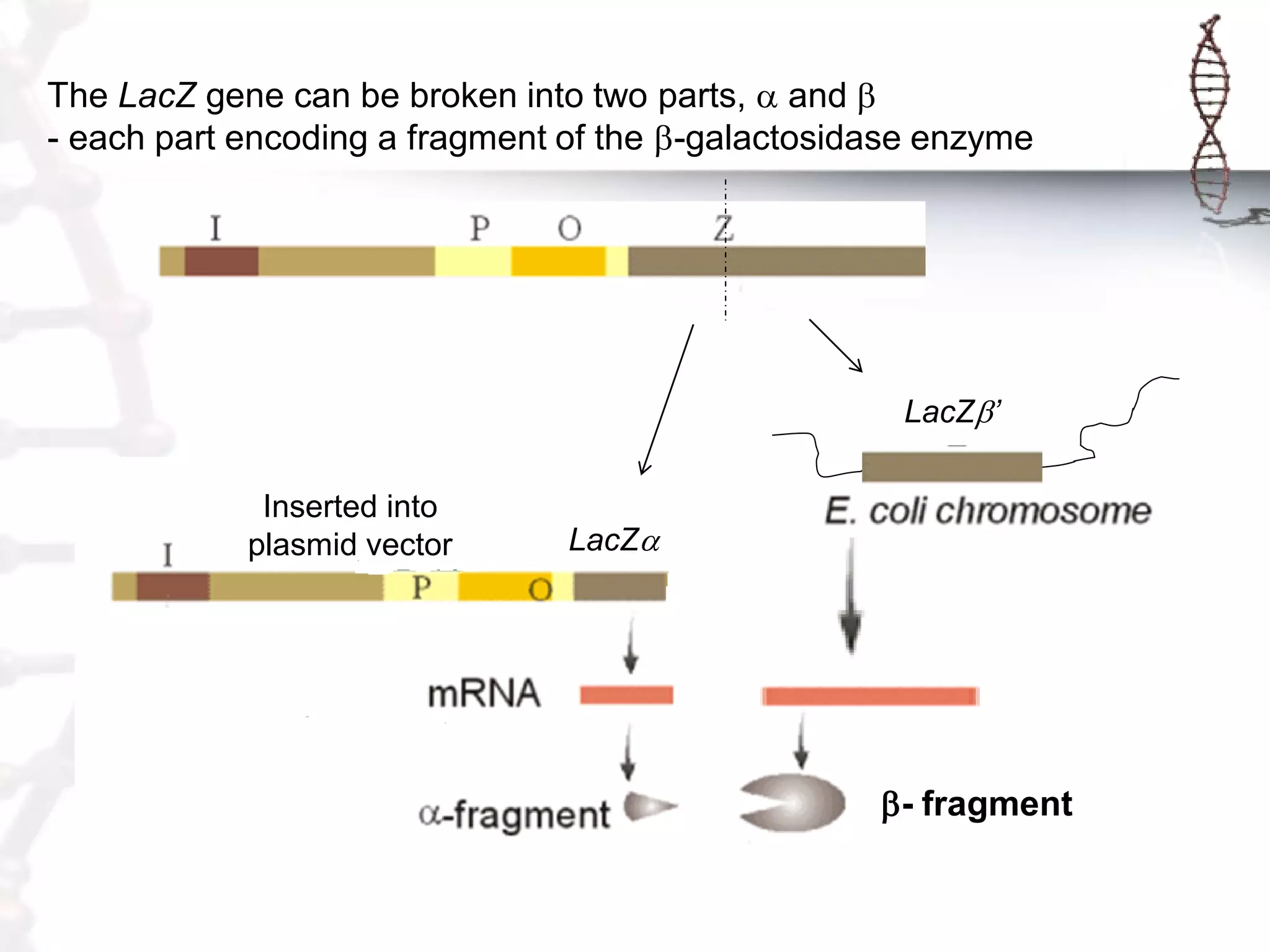
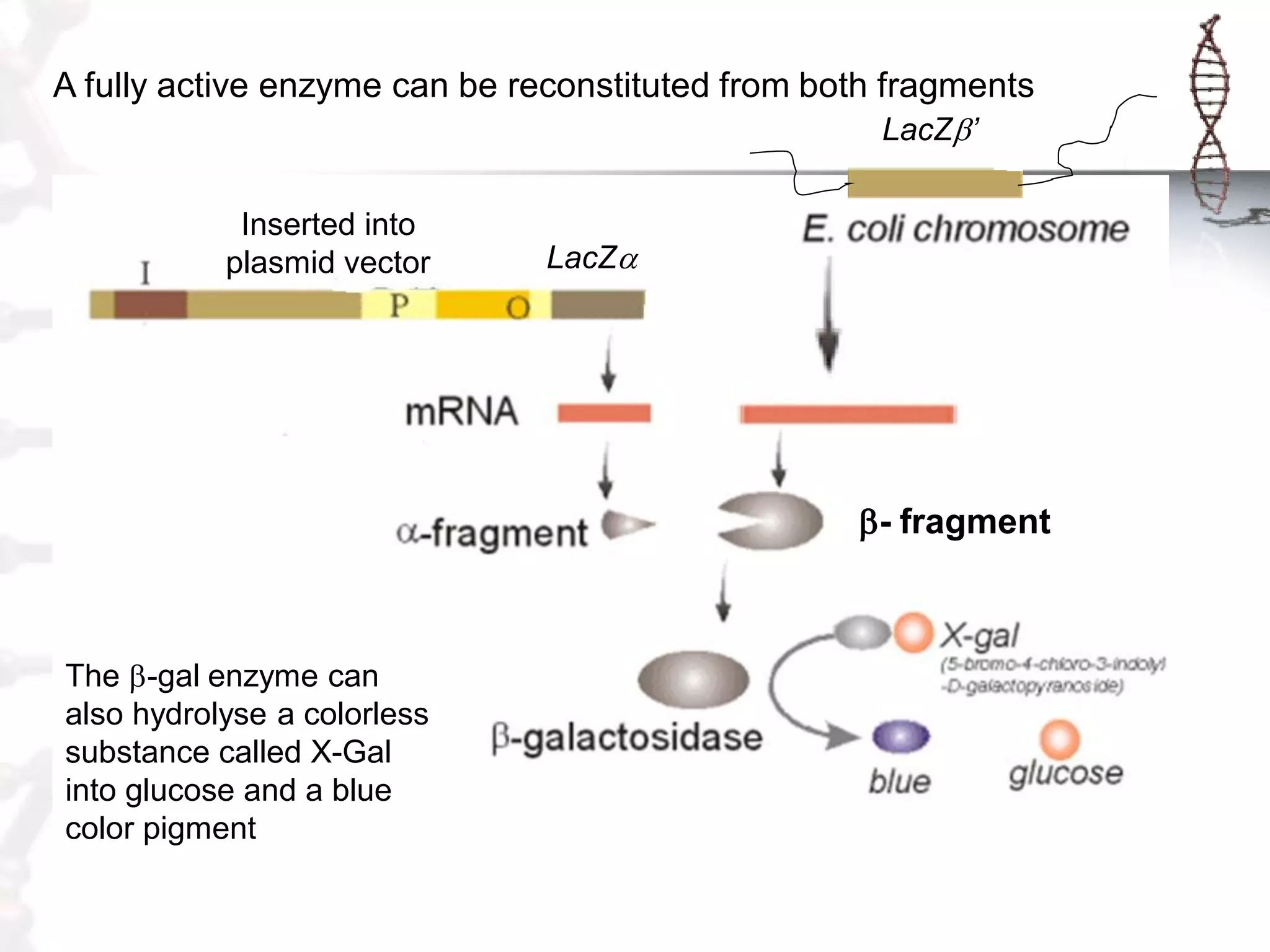
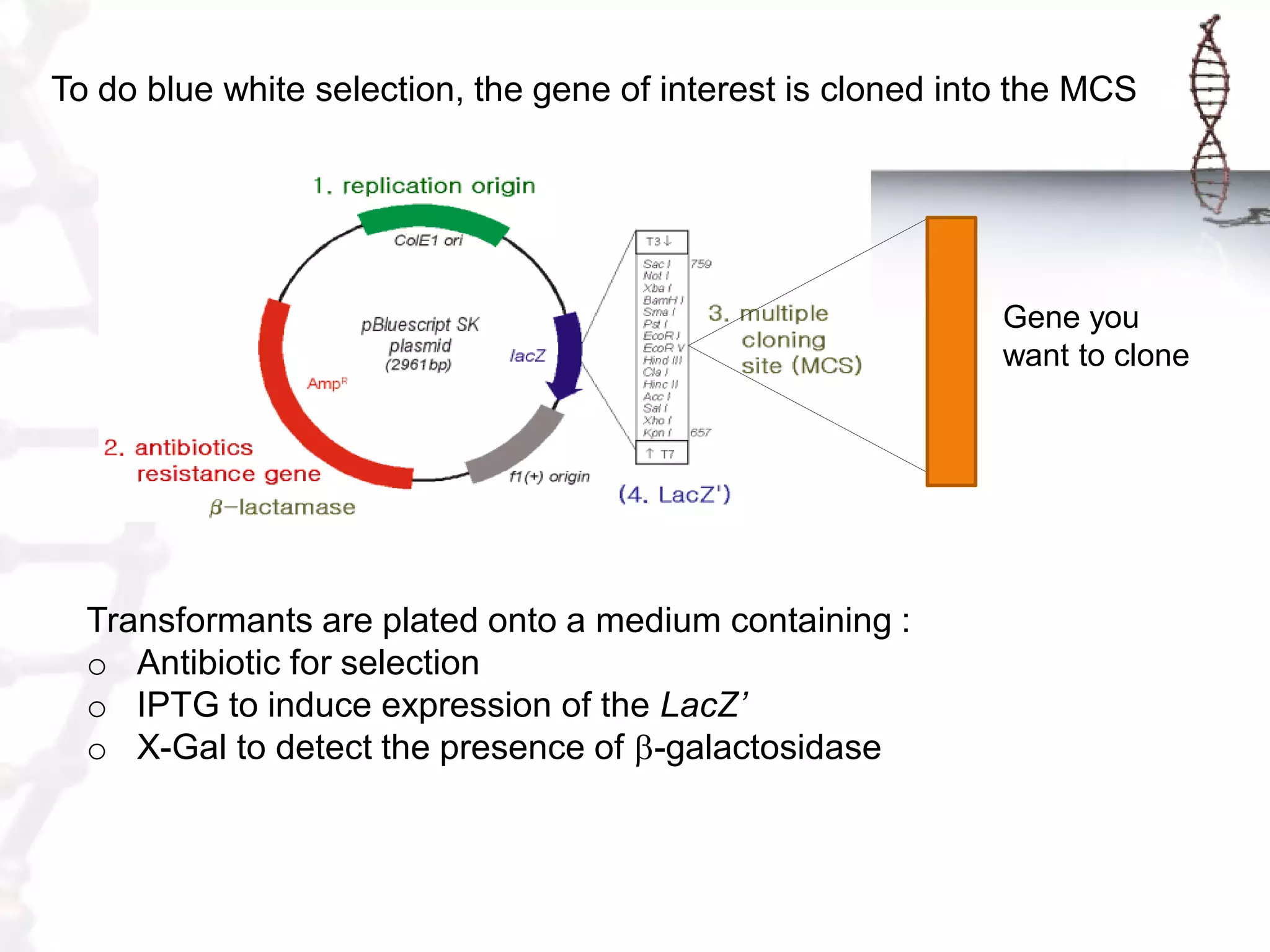
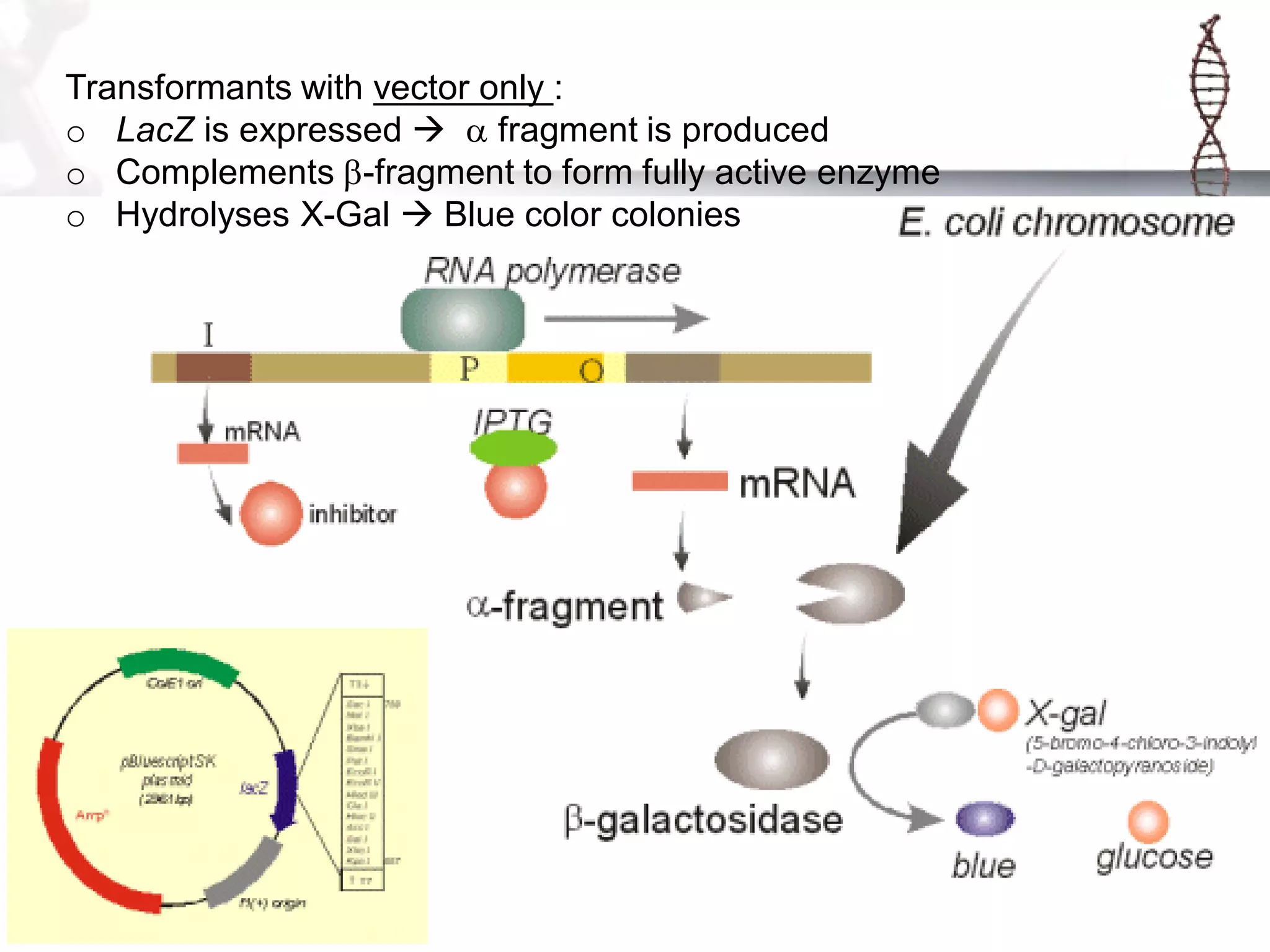
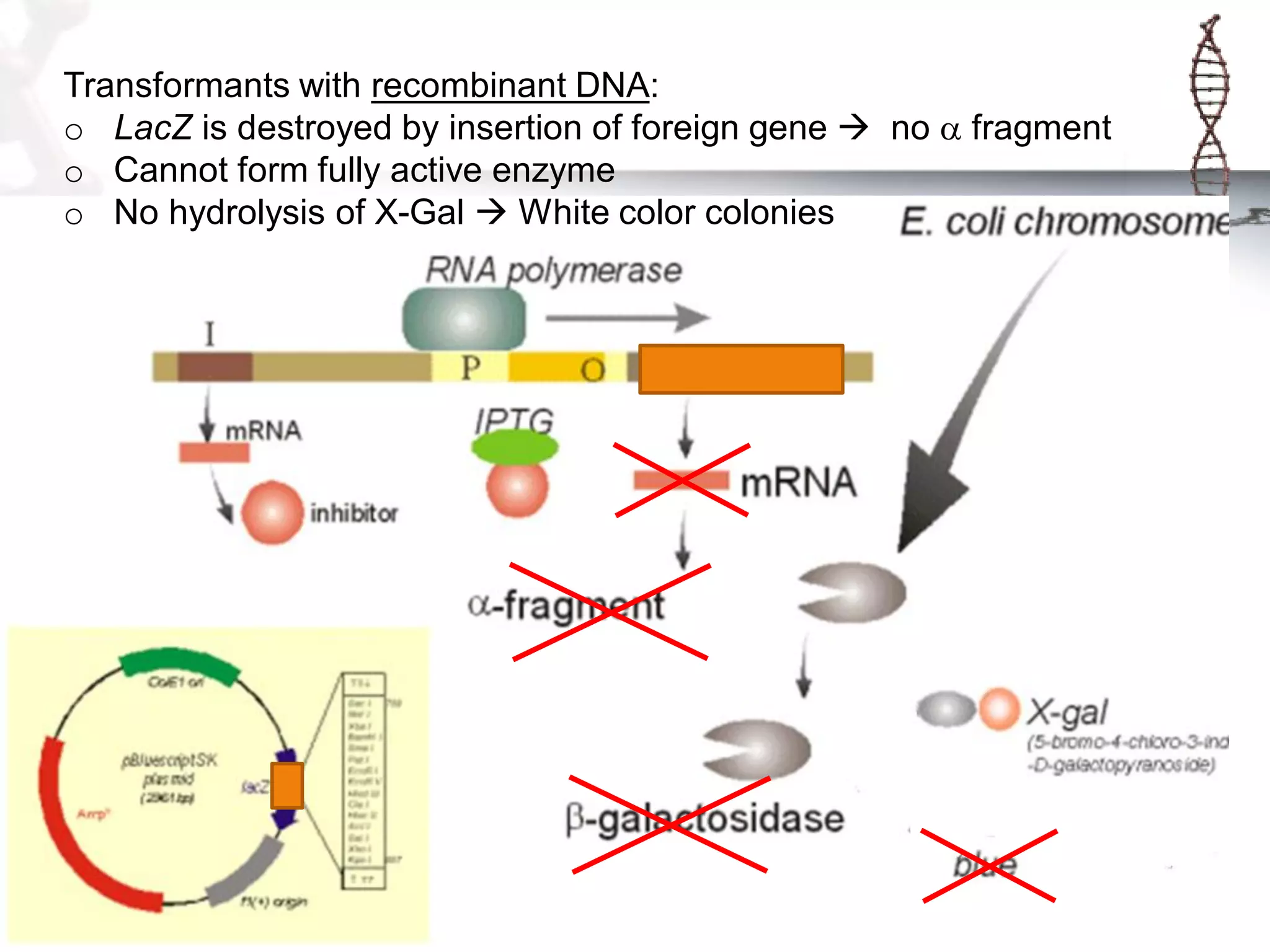
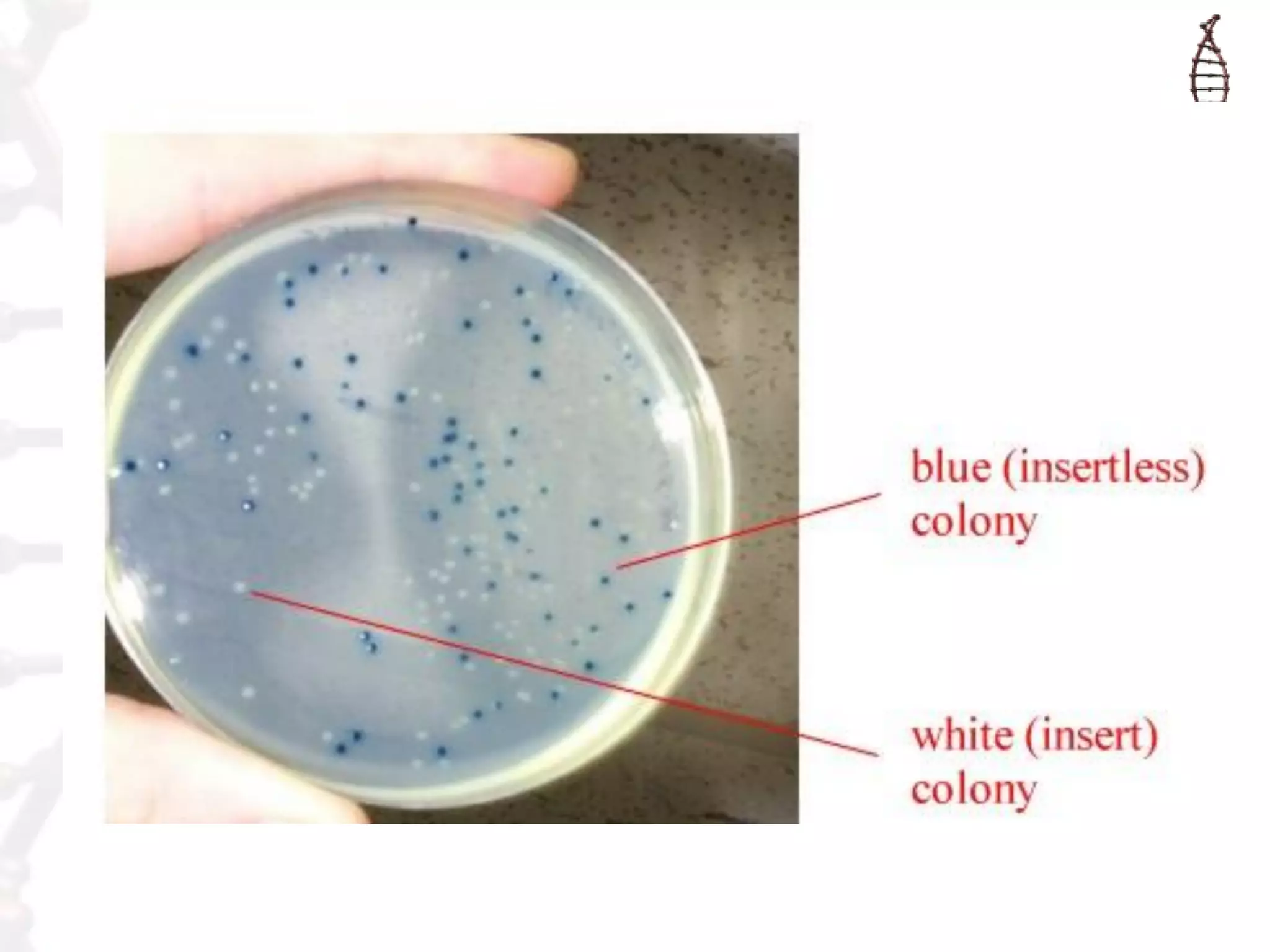
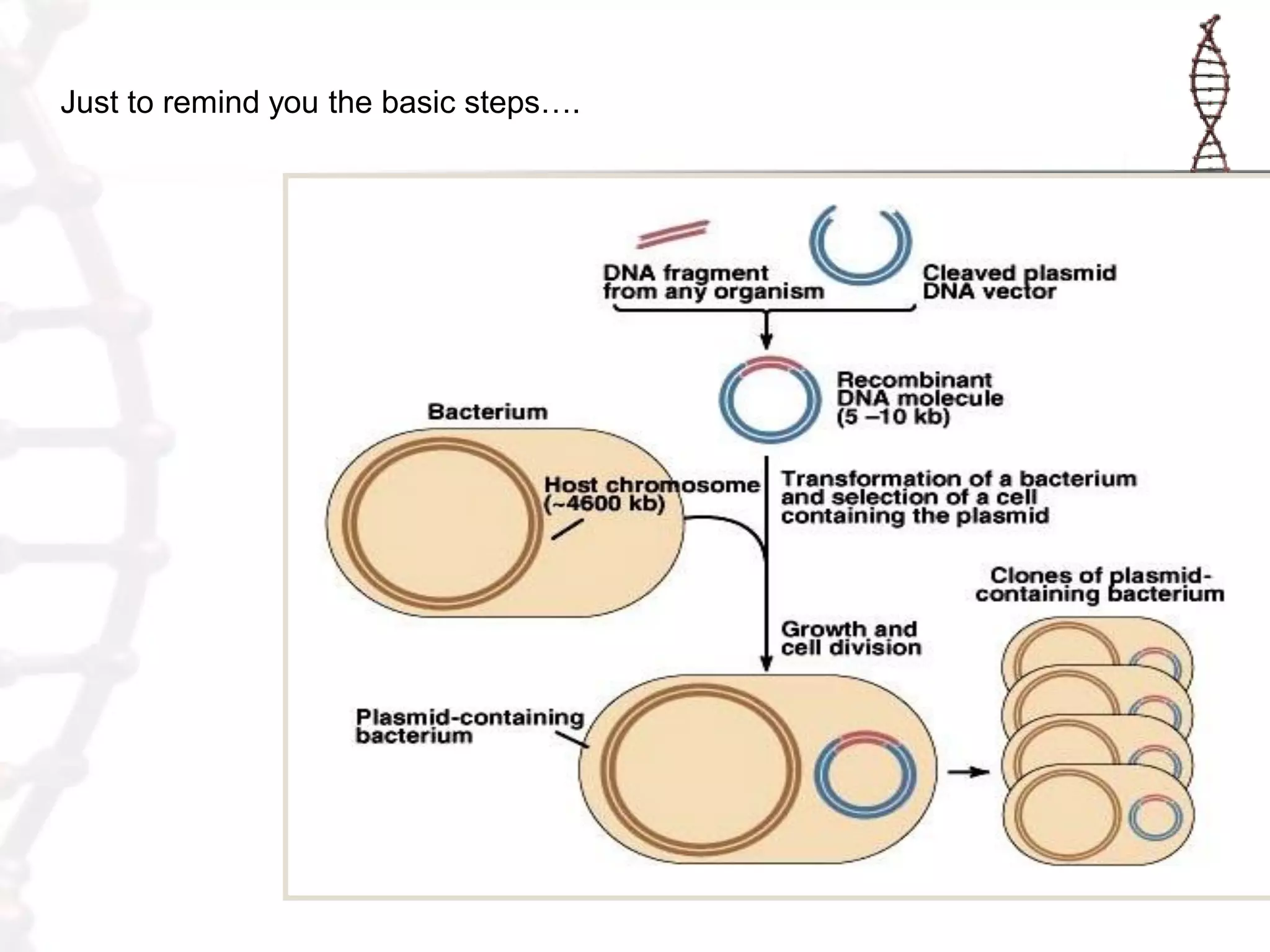
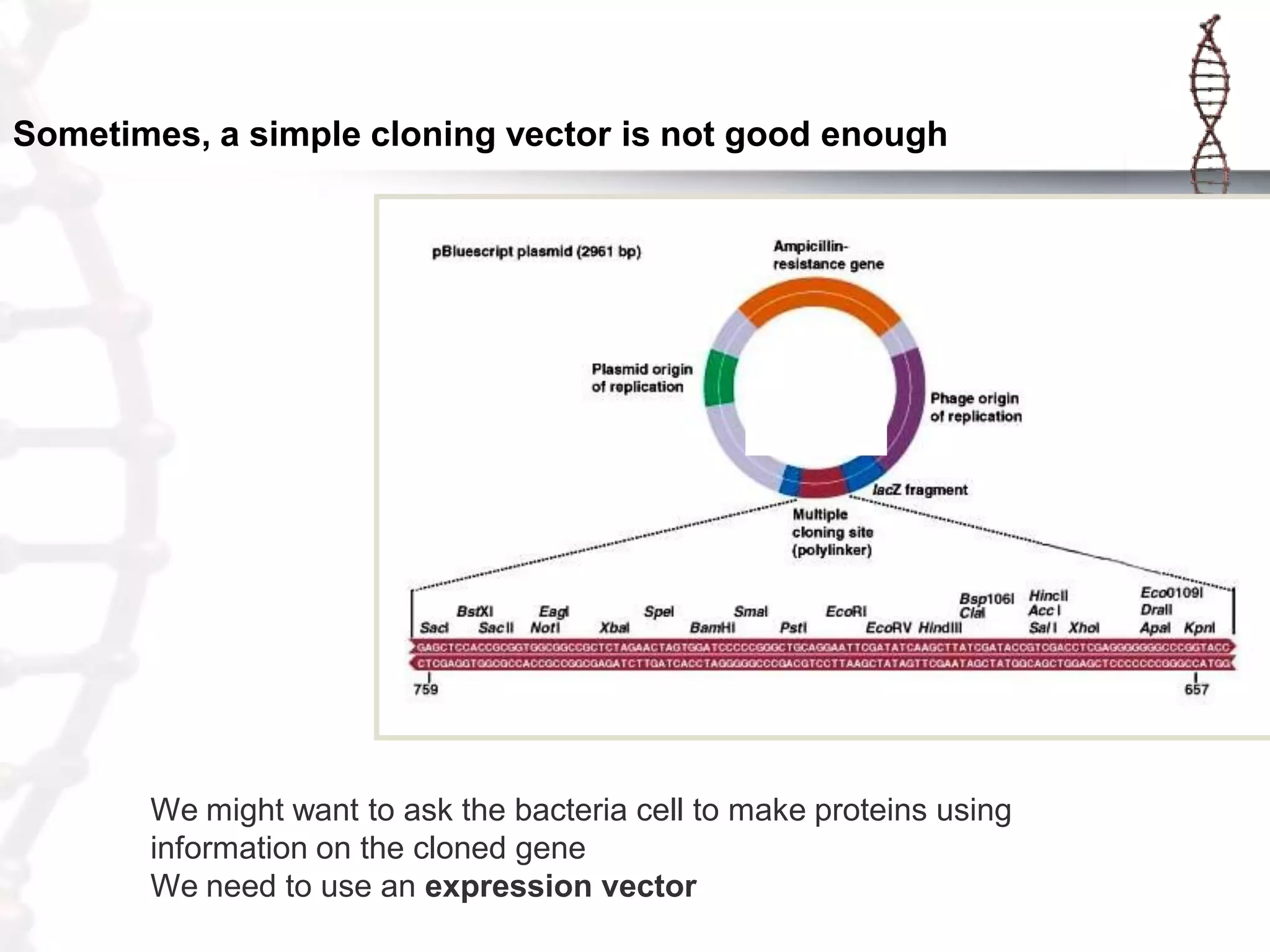
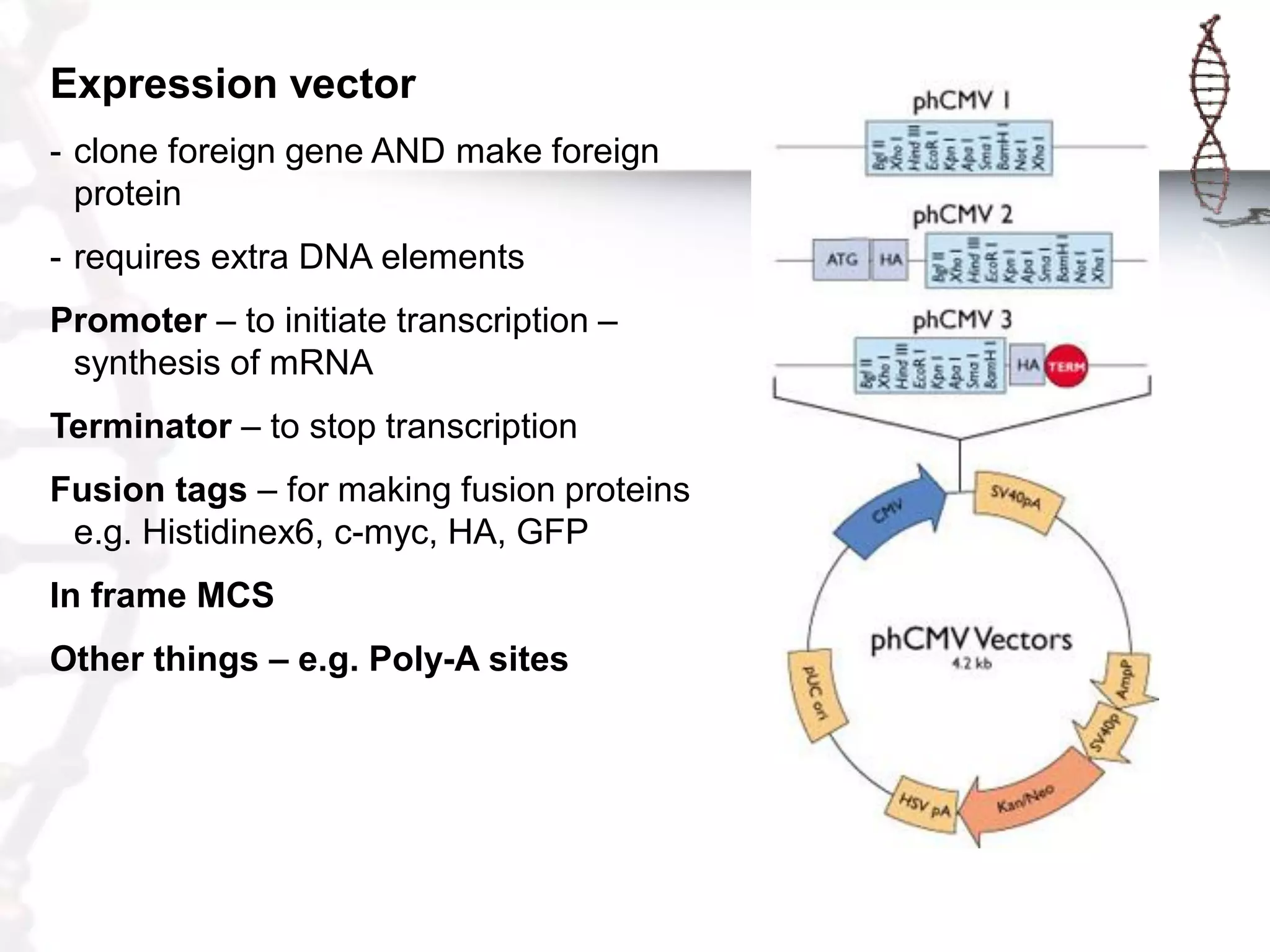
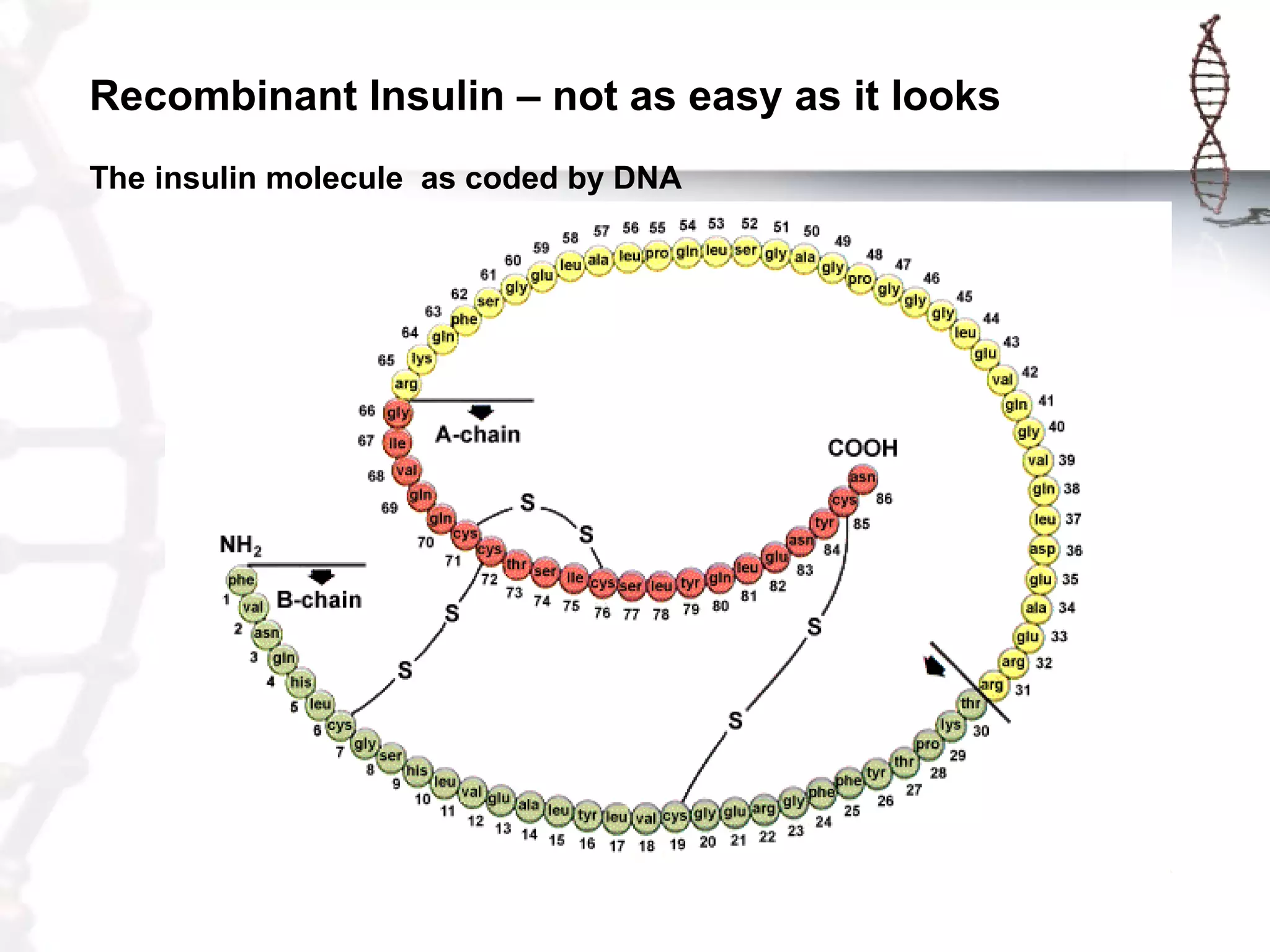
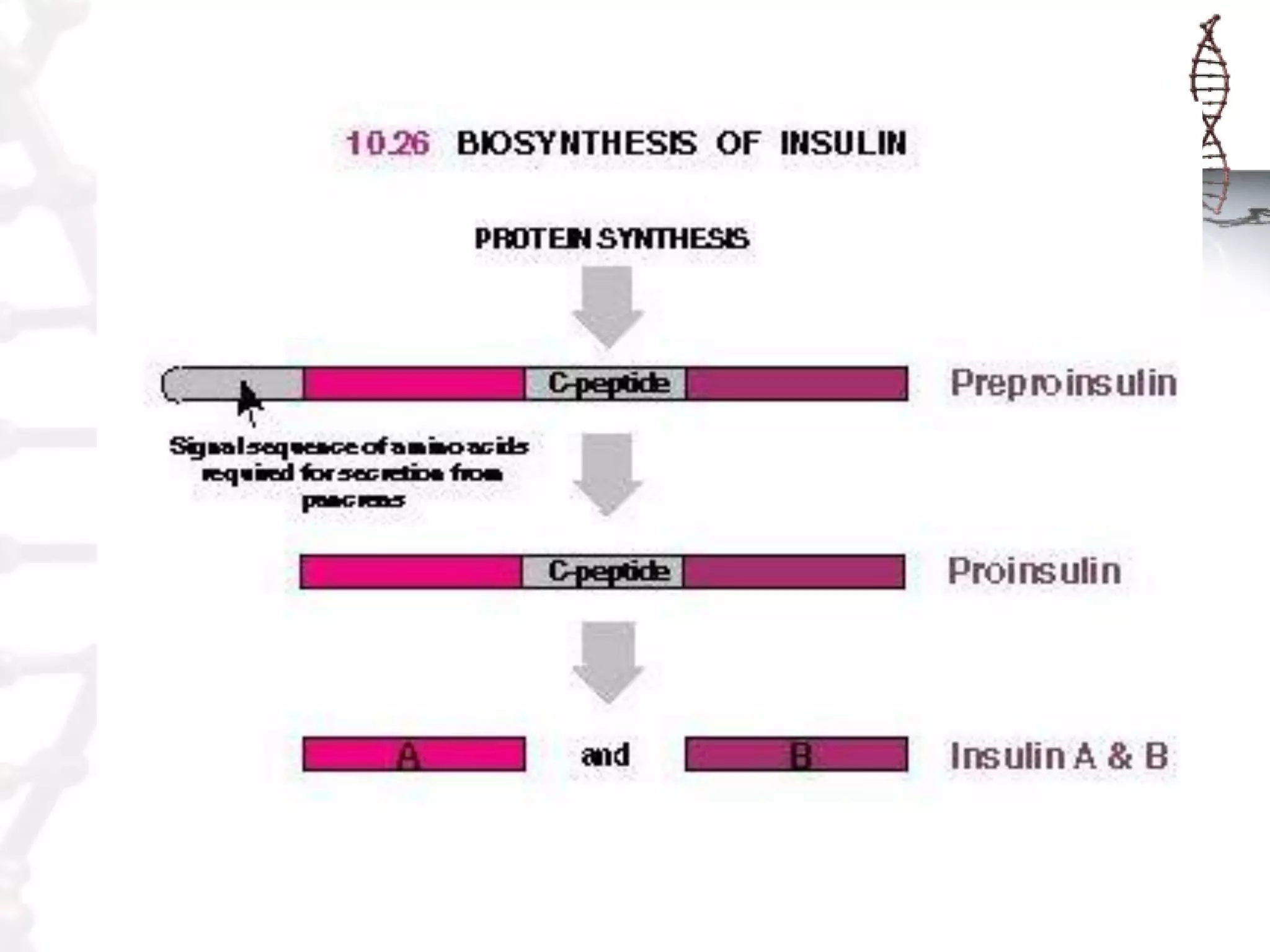
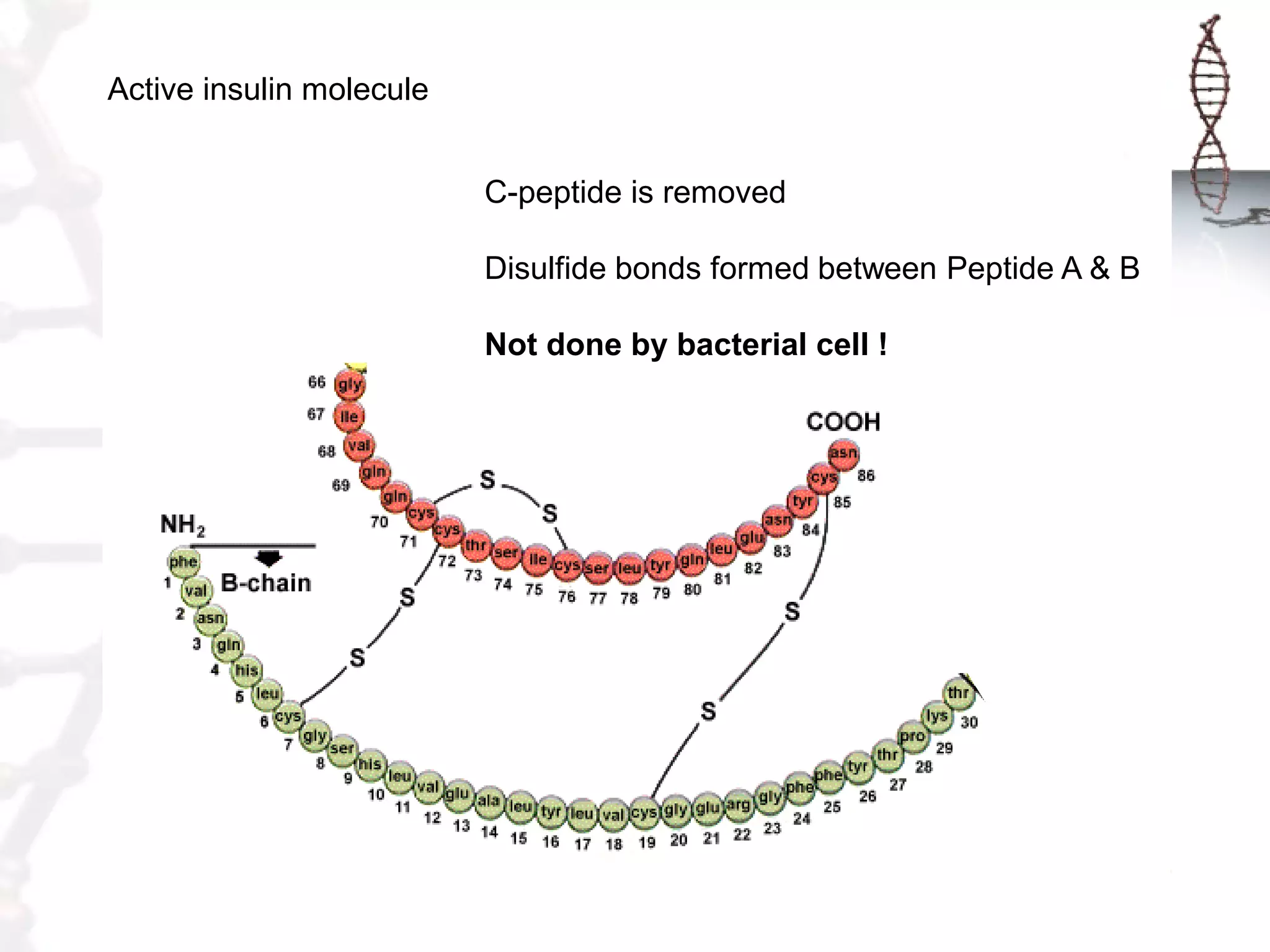
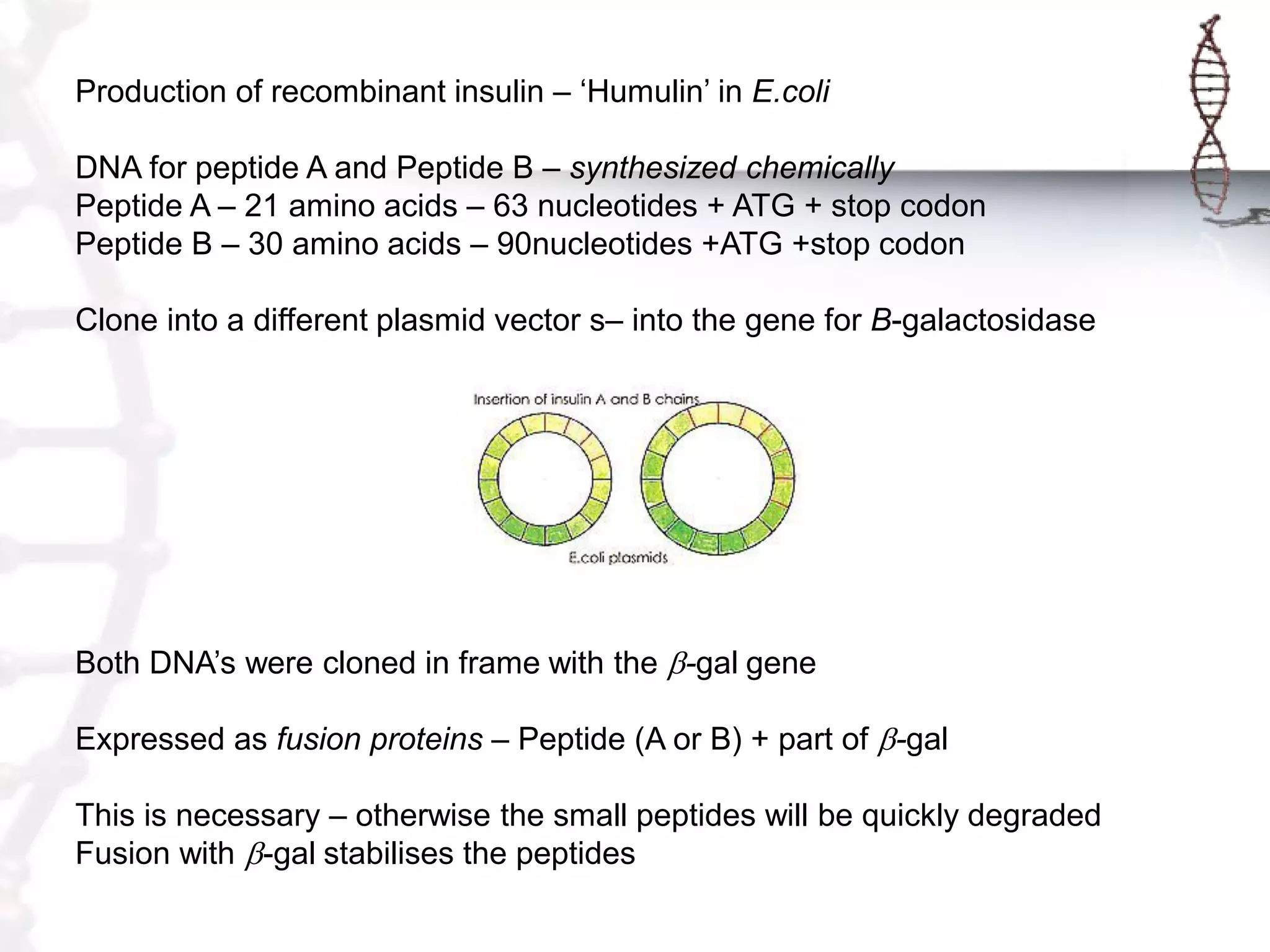
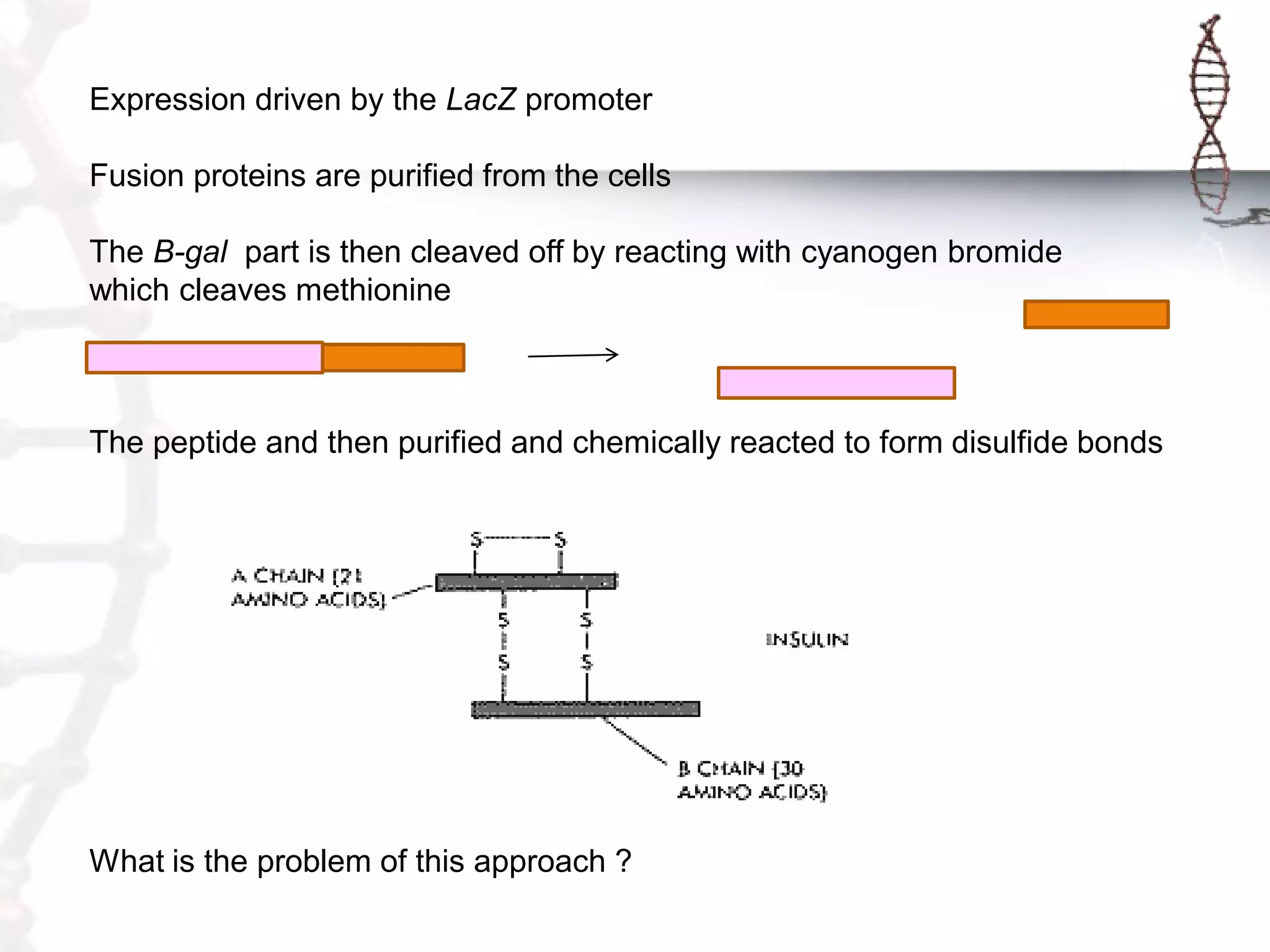
This document provides an overview of DNA cloning. It begins by defining cloning as making identical copies of DNA, genes, or cells. The basic steps of DNA cloning are described, including using a source DNA, vector, restriction enzymes to cut DNA, ligation to join DNA fragments, transformation of host bacteria, and selection of recombinant clones. Common vectors like plasmids are discussed along with selection techniques like blue-white screening. The document emphasizes that the goal is to generate multiple copies of the cloned insert DNA. Examples are given of important medical and agricultural applications of cloning genes.