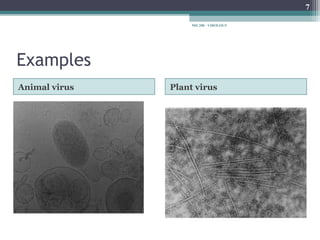
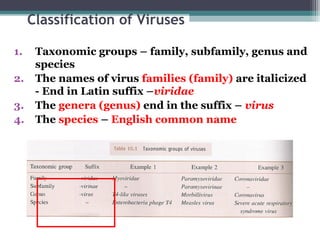
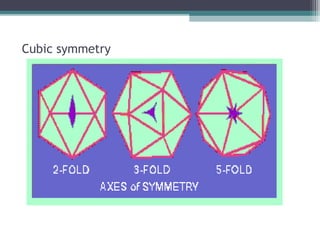
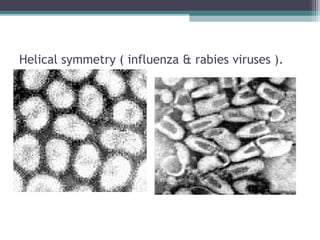
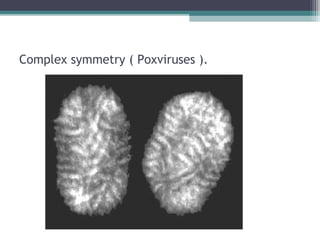
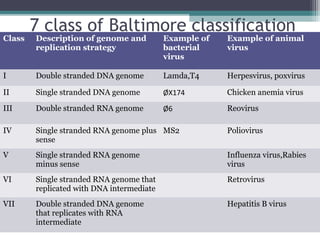
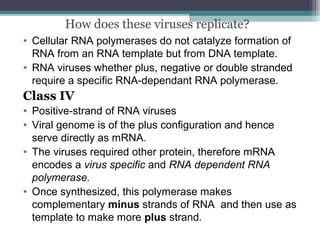
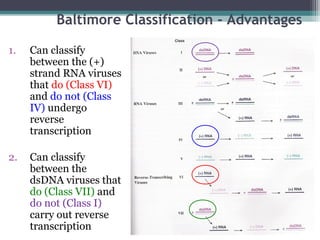
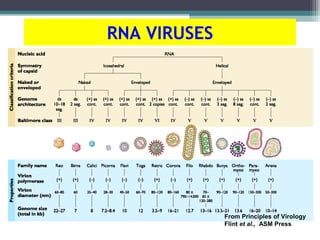
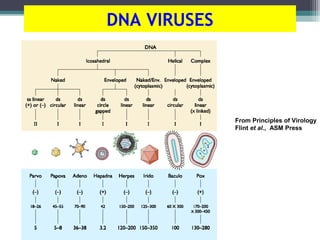
This document provides an overview of virus classification and the Baltimore classification system. It begins with an introduction to naming conventions for viruses and general approaches to classification. It then describes the Baltimore classification in detail, which divides viruses into 7 classes based on their genome type and replication strategy. The classification focuses on whether the viral nucleic acids are DNA or RNA, and if they are single- or double-stranded. Key viral families are listed as examples for each class.