Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times
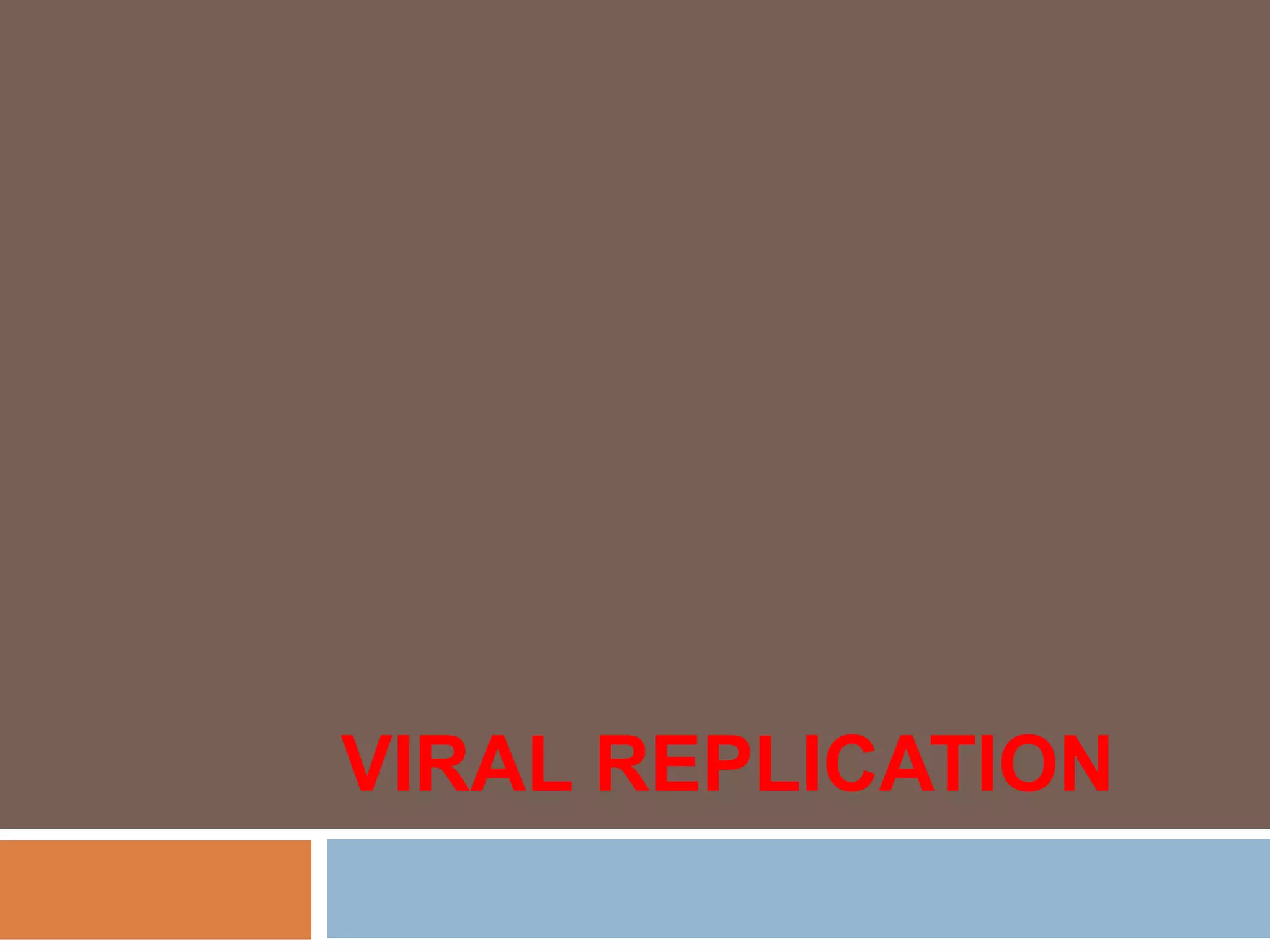

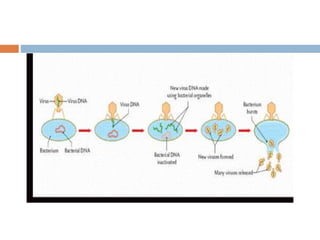






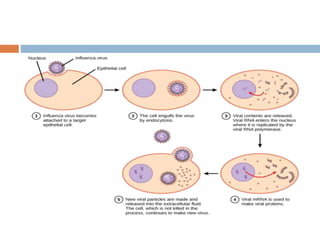

Viral replication occurs in six sequential phases: (1) attachment to host cell receptors, (2) penetration via endocytosis or membrane fusion, (3) uncoating of the viral capsid and release of genetic material, (4) biosynthesis of viral mRNA, proteins, and new genomes using host cell machinery, (5) assembly of new virus particles, and (6) release through cell lysis or budding. The host cell provides energy and materials for the virus to replicate its proteins and nucleic acids.










