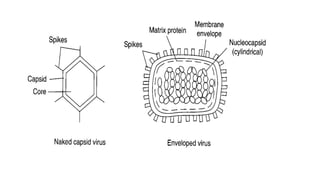
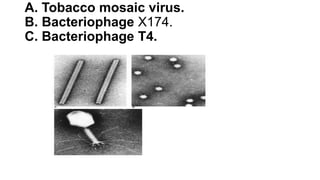
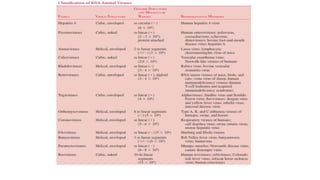
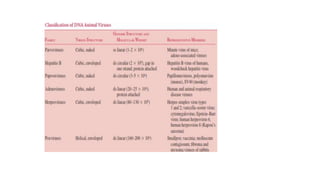
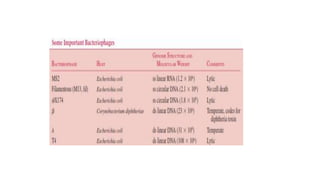
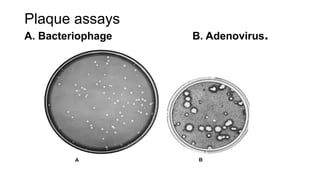
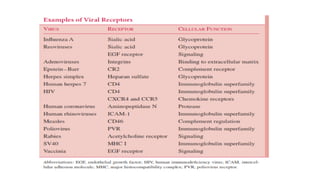
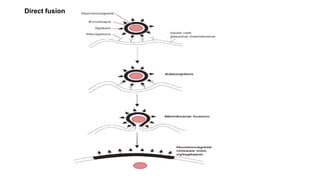
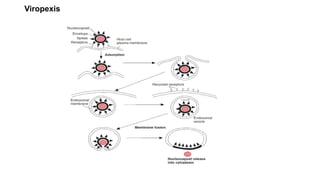
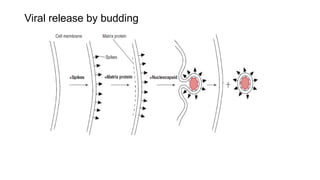
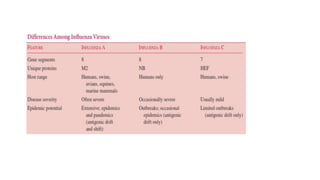
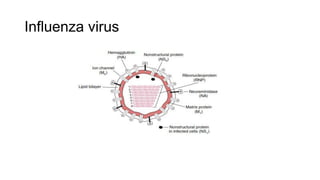
Viruses infect host cells and use the host's cellular machinery to replicate themselves. This involves the virus attaching and entering the host cell, releasing its genome, producing new viral components, assembling new virus particles, and causing the host cell to burst and release the new virus particles to infect other cells. Viruses can spread systemically throughout the host's body or remain localized to sites of infection. The replication cycle allows viruses to efficiently propagate and spread infection.