Viruses-definition, classification, replication, cultivation of viruses
- 2. Definition:- Viruses are the infectious agent, too small to observe with light microscope and can not cultured outside the host. Viruses are the non-cellular particle made-up of genetic material & protein that can invade the living cells.
- 3. General Characteristics 1. viruses only seen by electron microscope 2. they are 10-100 times smaller than other bacteria. 3. size ranges from 20-300 nm. 4. easily filterable 5. Incapable to grow on artificial media. 6. grow only in host (animal, plant, and other microorganisms )
- 4. 7. Vital Function- depends on host. 8. only one genetic material present either DNA/RNA not both at a time. 9. Reproduction- complex process but not by binary fission. Invades a host cell and takes over the cell causing it to make copies of the viral DNA/RNA. Destroys the host cell releasing new viruses. 10. containing protein coat that surrounds nuclic acid.
- 5. 11. Lack of enzymes for protein synthesis & ATP generation. 12.Absense of ribosome's 13. Causes systemic minor(Cold fever) to Fatal(AIDS) Diseases. Most viral illnesses last 2 to 10 days. Viruses are not beneficial.
- 6. Classification: 1. Bacterial Viruses:- They have DNA and called bacteriophages. 2. Plant viruses:- They have RNA and infects Plants 3.Animal Viruses:- They may have DNA/RNA. Infects human & animals.
- 7. SIZE:- The viral size determined with the help of electron microscope. Most are smaller in size but only vaccina are larger in size. General size range 20-1000 nm in size.
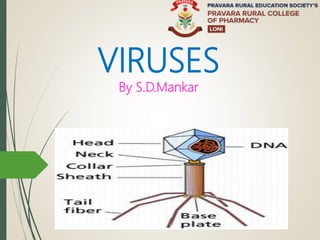
- 8. Structure A “Virion” is a complete, fully developed infectious viral particle composed of nuclic acid and surrounds by a protein coat called capsid. Capsid protect viruses from environment and serve as velicle of transmission from one host cell to another host cell. Viruses are not cellular and therefore do not have nucleus, cytoplasm, or cell membrane.
- 9. Nucleic acid:- In contrast of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells viruses can have either DNA/RNA i.e contains only single nucleic the nucleic acid of viruses only the genetic material present. It may be single or double stranded. Depending upon nucleic acid viruses linear or circular. The percentage of nucleic acid in relation to protein is about 1 % in influenza viruses & 50% in bacteriophages.
- 10. Capsid:- The Nucleic acid of viruses is surrounded by a protein coat is called capsid. The determination of structure of capsid is depends on viral nucleic acid. Each capsid is composed of protein subunits called capsomers and it may be single or multiple type. Envelope:- In some viruses the capsid is covered by envelope which mainly consist of combination of lipid, protein & carbohydrates. It is for protection purpose.
- 11. Spikes:- Depending on viruses the envelope may or may not be covred by spikes which are carbon protein complex. That projects from surface of envelope. Some viruses attach to host cell by means of spikes. This characteristics used for identification purpose. Ability to clump with RBC( Influenza) –
- 12. Spikes:- Depending on viruses the envelope may or may not be covred by spikes which are carbon protein complex. That projects from surface of envelope. Some viruses attach to host cell by means of spikes. This characteristics used for identification purpose. Ability to clump with RBC( Influenza) –
- 13. As per capsid structure viruses may be classified as 1.Helical viruses :- consist of long rods may be rigid or flexible. Viral nucleic acid found in hollow, cylindrical capsid- which is of helical in structure. 2. polyhedral viruses:- Bacterial/plant/animal viruses are many sided or poly hedral. 3.Enveloped viruses:- Capsid covered by envelope ( Influenza) 4.Complex Viruses:- Bacterial viruses have complex structure ( Bacteriophages)
- 14. Replication of viruses Replication of virus is very complicated process Viruses never reproduce by division They are replicated by a process in which all components of virus are produced separately and are assembled into intact virons. For replication of virus host is necessary Visuses are host specific Host may be a bacteria, plant or an animal
- 15. There are 2 types of life cycle commonly seen in viruses They are i] Lytic Cycle ii] Lysogenic Cycle
- 16. Key steps in the Viral Replication Cycle: 1. Attachment 2. Penetration (Entry) 3. Uncoating 4. Genome replication 5. Assembly 6. Maturation 7. Release
- 18. Lytic cycle:- When the lytic phages ( Bacteriophages) infect cells, the cell responds by producing large no few viruses i.e. at the end of incubation period the host cell burst or lysis, releasing new to infect other host cells. These is called lytic cycle.
- 19. 1. Attachment:- After a chance of collagen between phages and bacteria attachment or absorption occurs. This attachment is chemical interaction in which weak bonds are formed between attachment and receptor 2. Penetration:- After attachment the bacteriophages injects its DNA into bacterial cell.
- 20. To do this bacteriophages tail release an enzyme lysozyme which breaks down portion of bacterial cell wall. During process of penetration, the tail sheath of the phages contracts and tail pore is driven through cell wall. When tip of core reaches the plasma membrane the DNA from bacteriophages head passes through tail core, through plasma membrane and enters the bacterial cell.
- 21. 3.Biosynthesis:- once the bacteriophages DNA has reached the cytoplasm of host cell the bacteriophages of viral nucleic acid & protein occurs. Host protein synthesis is stopped by viruses induced degradation of DNA. 4. Maturation:- In the next sequence of events maturation occurs. In this process bacteriophages DNA and capsid in to complete virions.
- 22. The phages head and tail are separately assembled from protein subunits and the head is filled DNA and attach to the tail. 5) Release:- This is the final stage of viral multiplication. The term lysis generally used for the stage bcz in this case plasma membrane actually breaks down. Lysozyme causes the breakdown of bacterial cell and newly produced bacteriophages are released from the host cell.
- 23. Released bacteriophages infects other host cells and viral multiplication cycle is repeated with those cells.
- 24. Lysogenic cycle: In contrast to lytic cycle some viruses do not cause lysis and death of host cell when they multiply.
- 25. Cultivation Of Human Viruses there are three methods used for the cultivation of human viruses. 1) In laboratory animals:- These is the oldest method for cultivation of viruses. Some human viruses can be cultured in livening animals such as mice, rabbits, guneia pig. To study the immune system response to viral infection. Some of viruses not grow in animal and due to lack of animal model for AIDS.
- 26. Chipanzees if infected with HIV but not shows symptoms of AIDS. So now AIDS vaccine tested in humans but it is very slow and take several years to determine the effectiveness. Monkey- cost and handling less application in virology. E.g.poliomyletius virus after inoculation in monkey causes paralysis. The growth of viruses in inoculated animals may be indicated by death, disease or visible lesions.
- 27. 2) In Embryonated eggs:- A hole is drilled in the shell of embroynated eggs and a viral suspension is injected into the fluid of the egg. There are several membrane in an egg and the viruses is injected near the most appropriate layer for its growth. Viral growth is signed by death of embryo by embryo cell damage or by formation of pox.or lesions on egg membrane.
- 28. Application: 1. More convinent- most widely used. 2. Less expensive 3. Easy to handle.
- 29. 3. Tissue Culture:- cell culture are started by treating a slice of animal tissue with enzyme that separates from individual cell, These cells are suspended in solution that provide osmotic pressure, nutrients and growth factors needed to cell to grow. Normal cell tend to adhere to glass or plastic container and reproduce to form a monolayer. Viruses infecting such monolayer and it detoriate when viruses multiply.
- 30. Types of Tissue Culture:-
- 33. ORGAN CULTURE
- 34. EXPLANT CULTURE
- 36. CELL CULTURE
