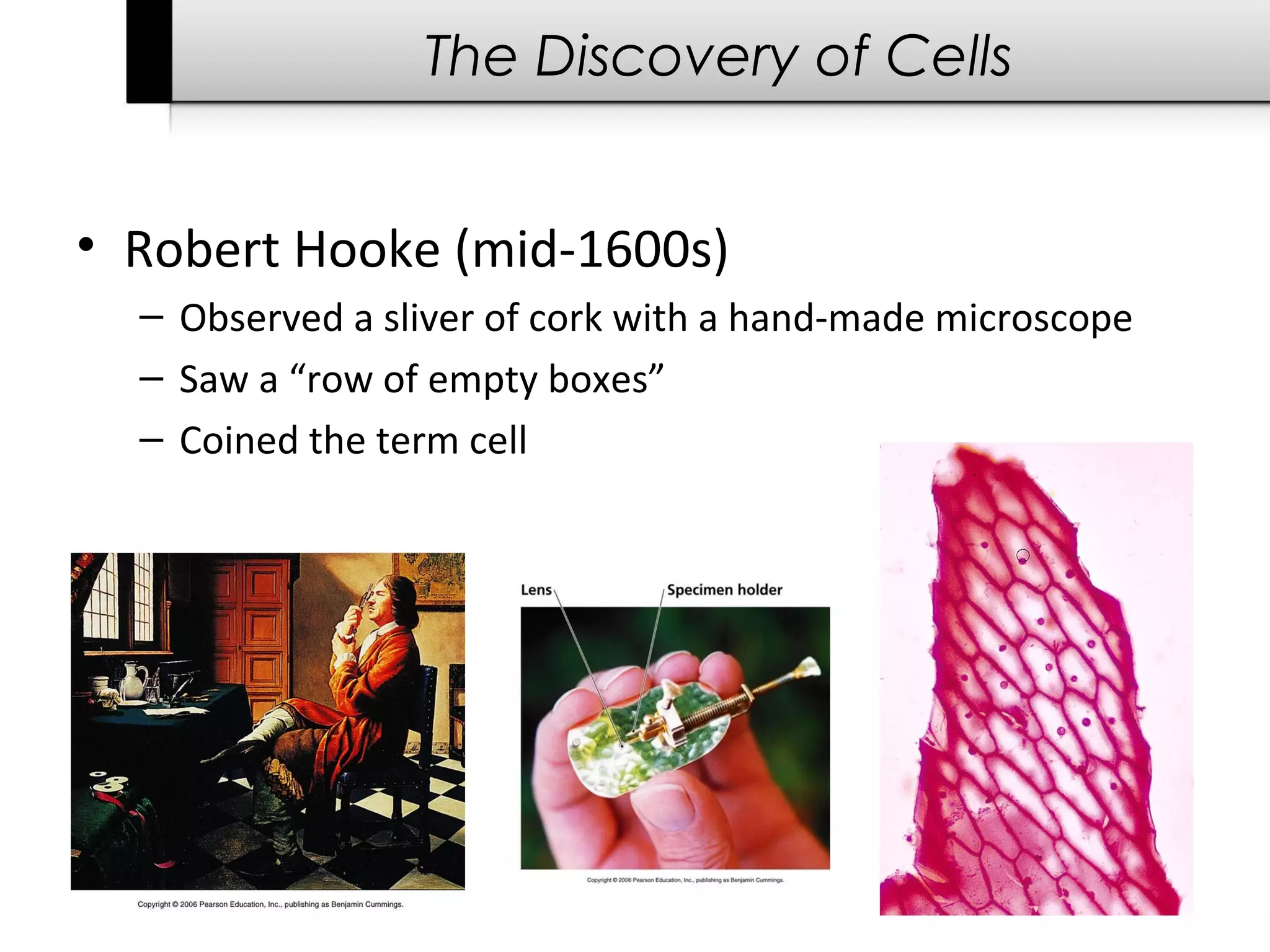
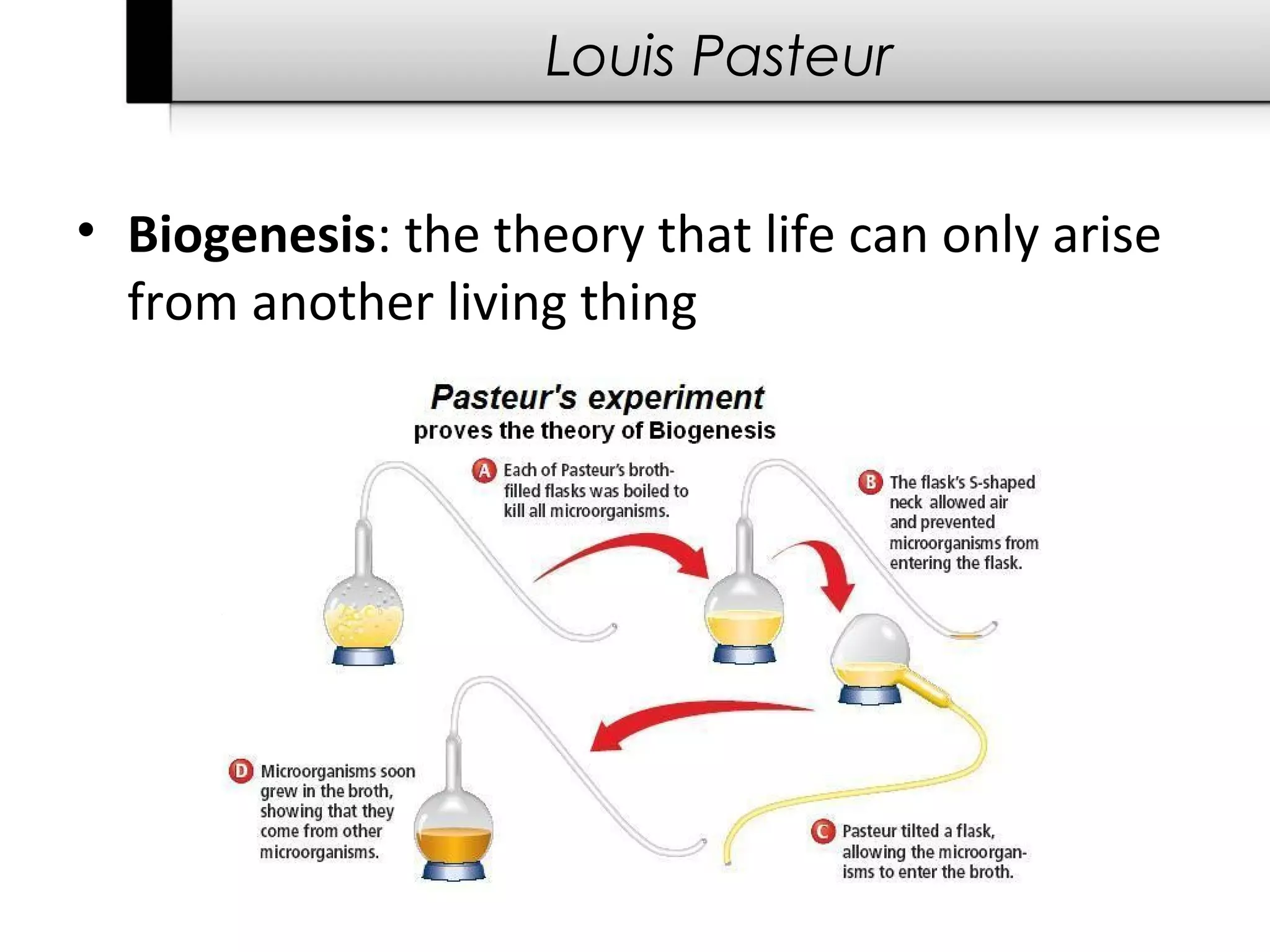
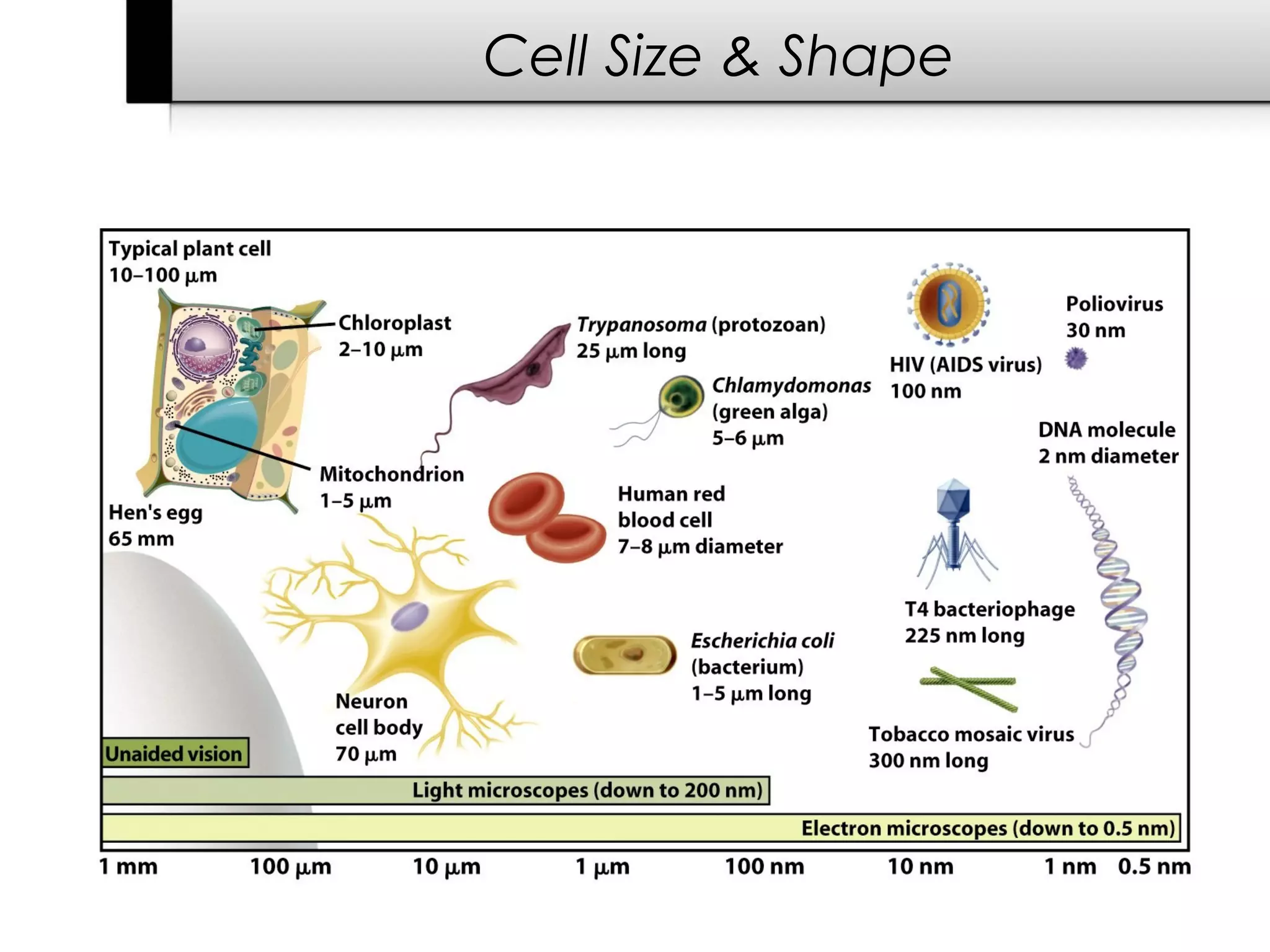
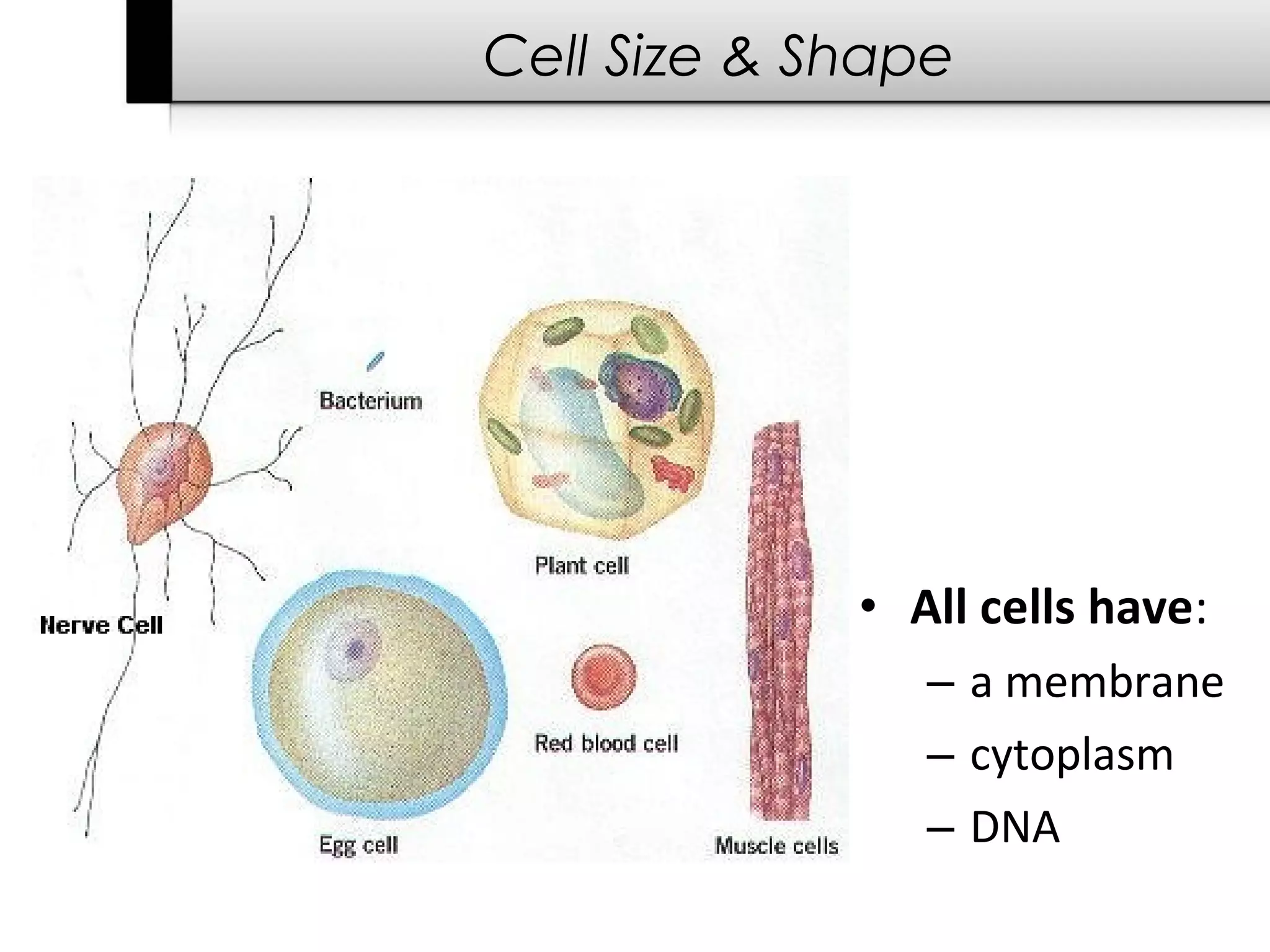
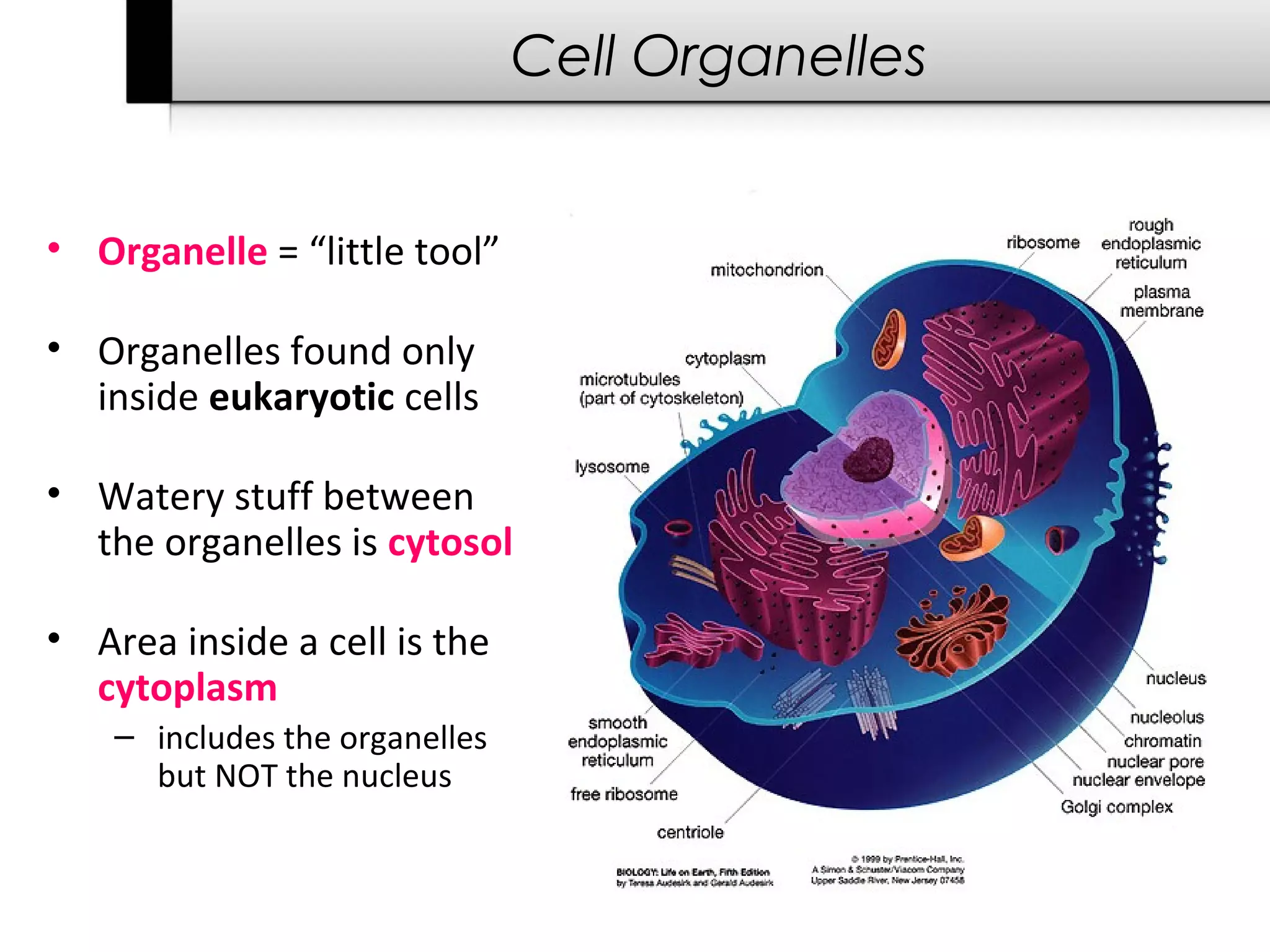
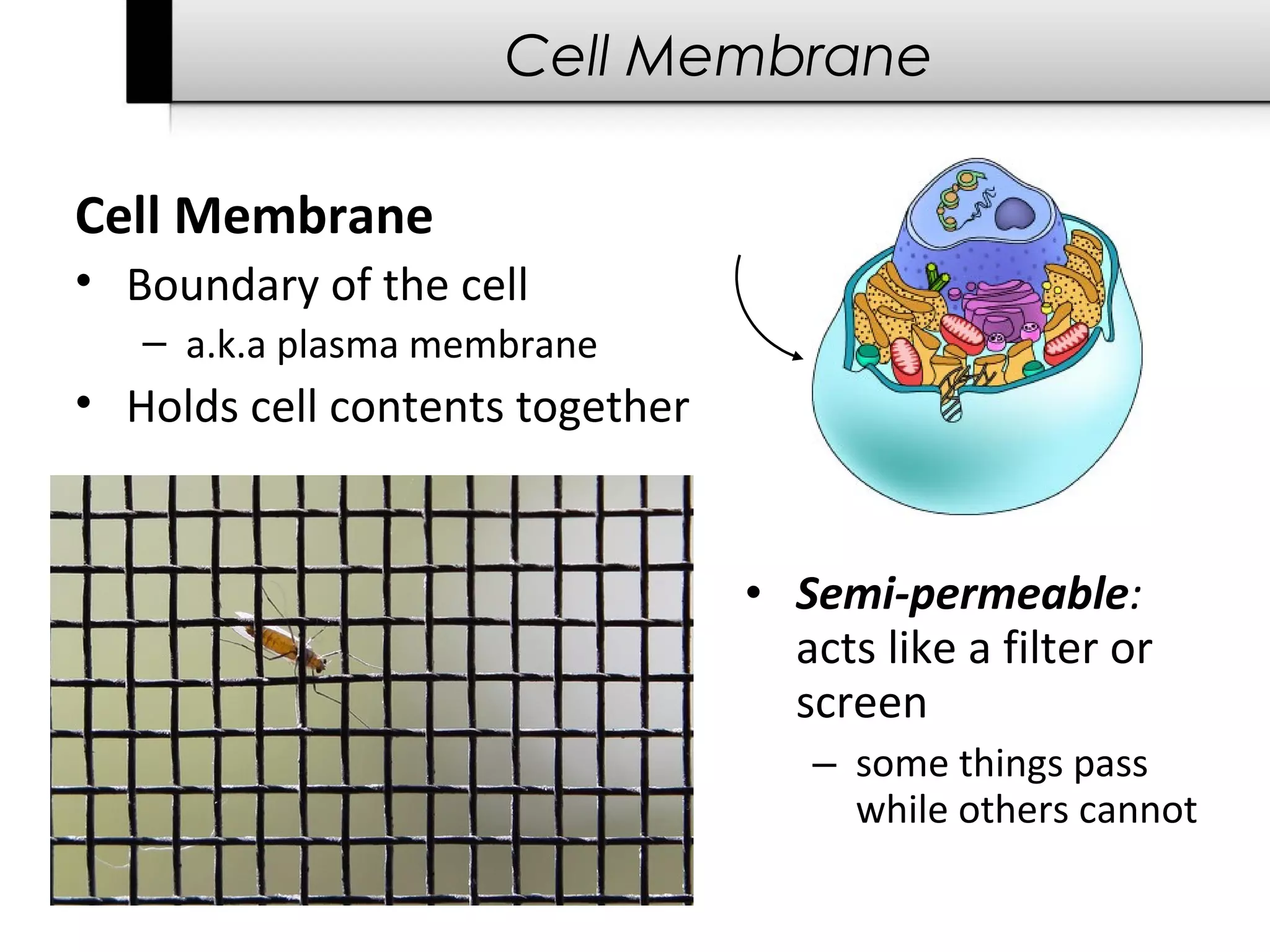
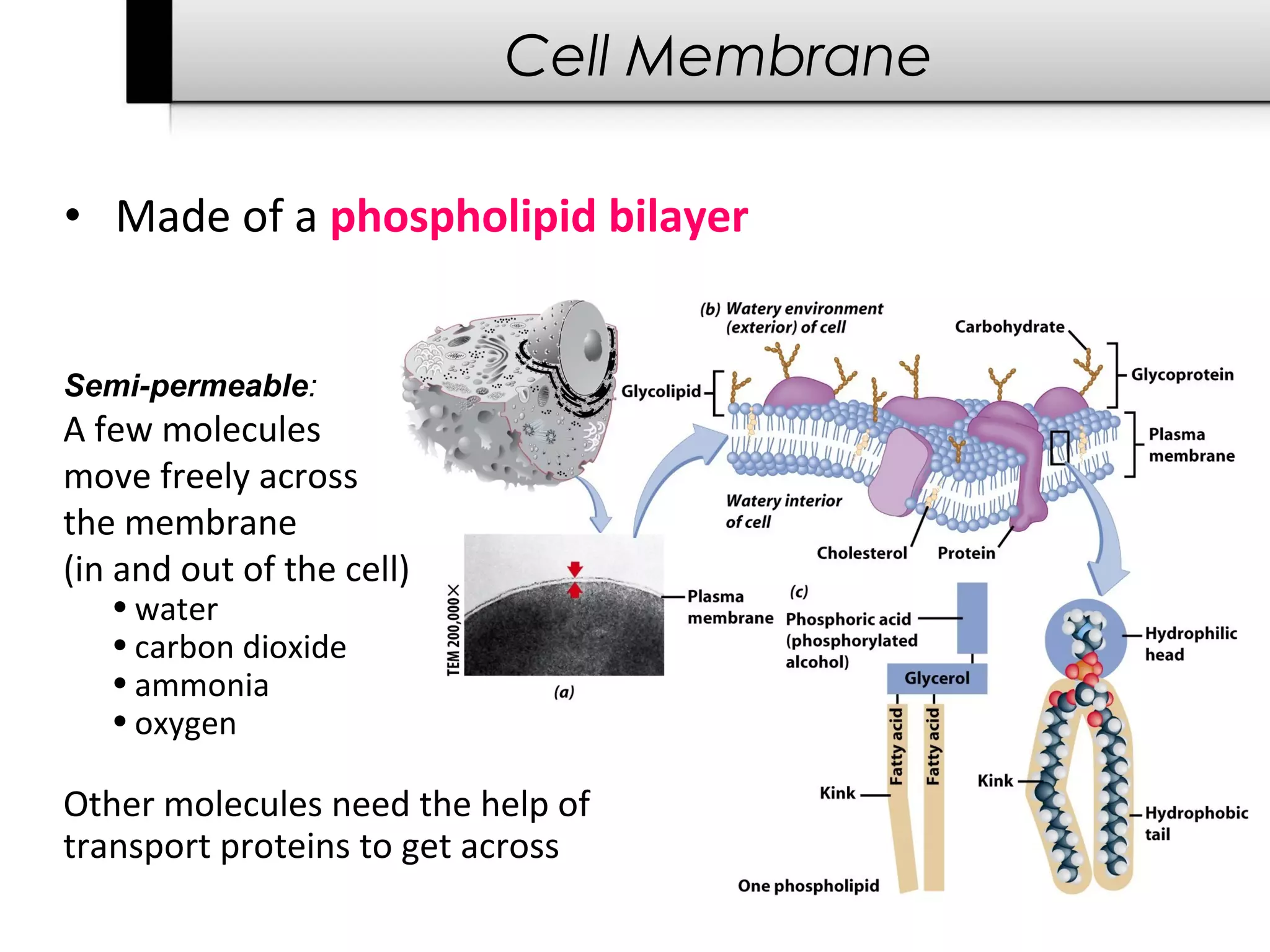
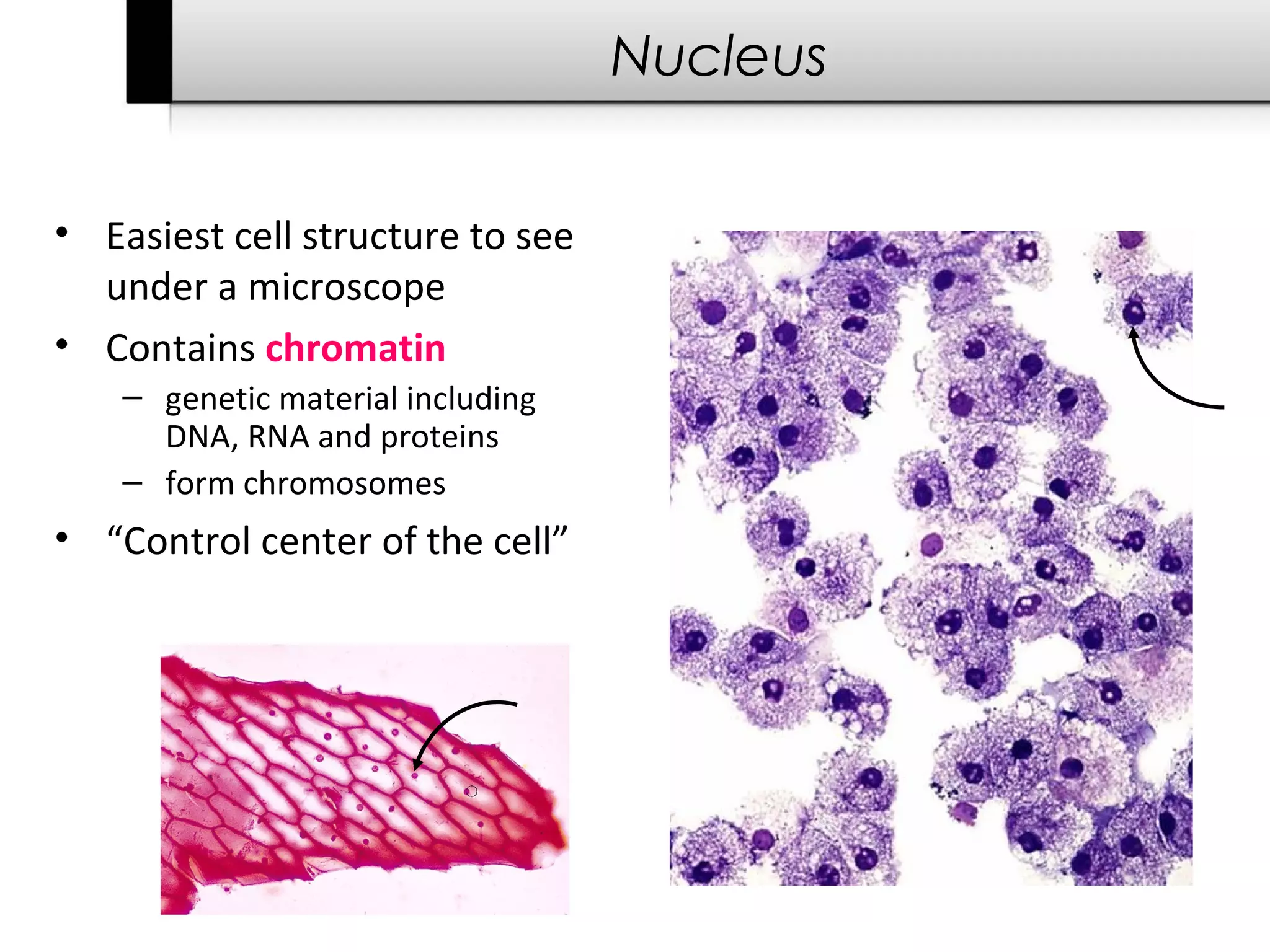
The document provides information about cells including:
1. It summarizes the cell theory which states that cells are the basic units of life, all living things are made of cells, and new cells come from existing cells.
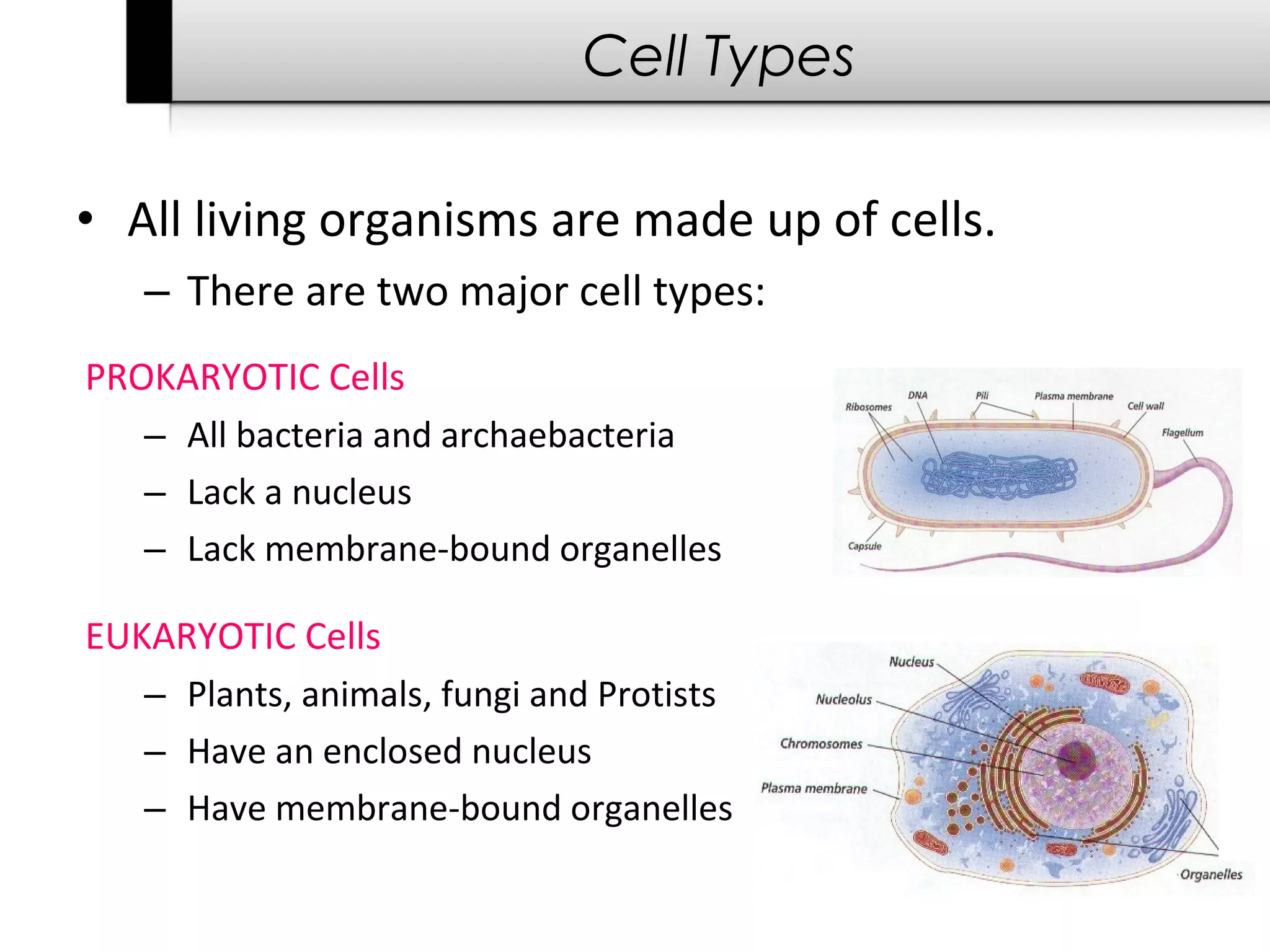
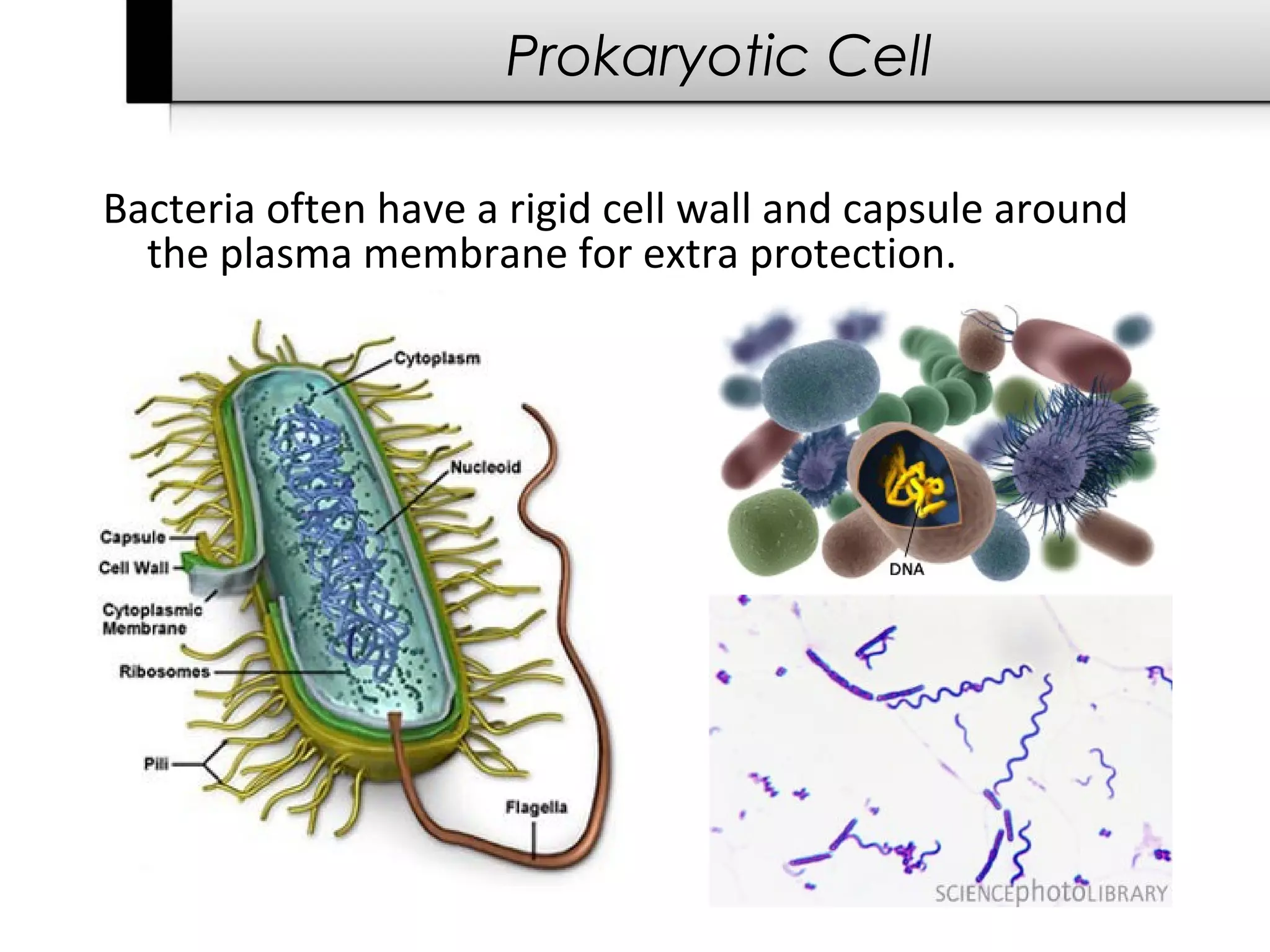
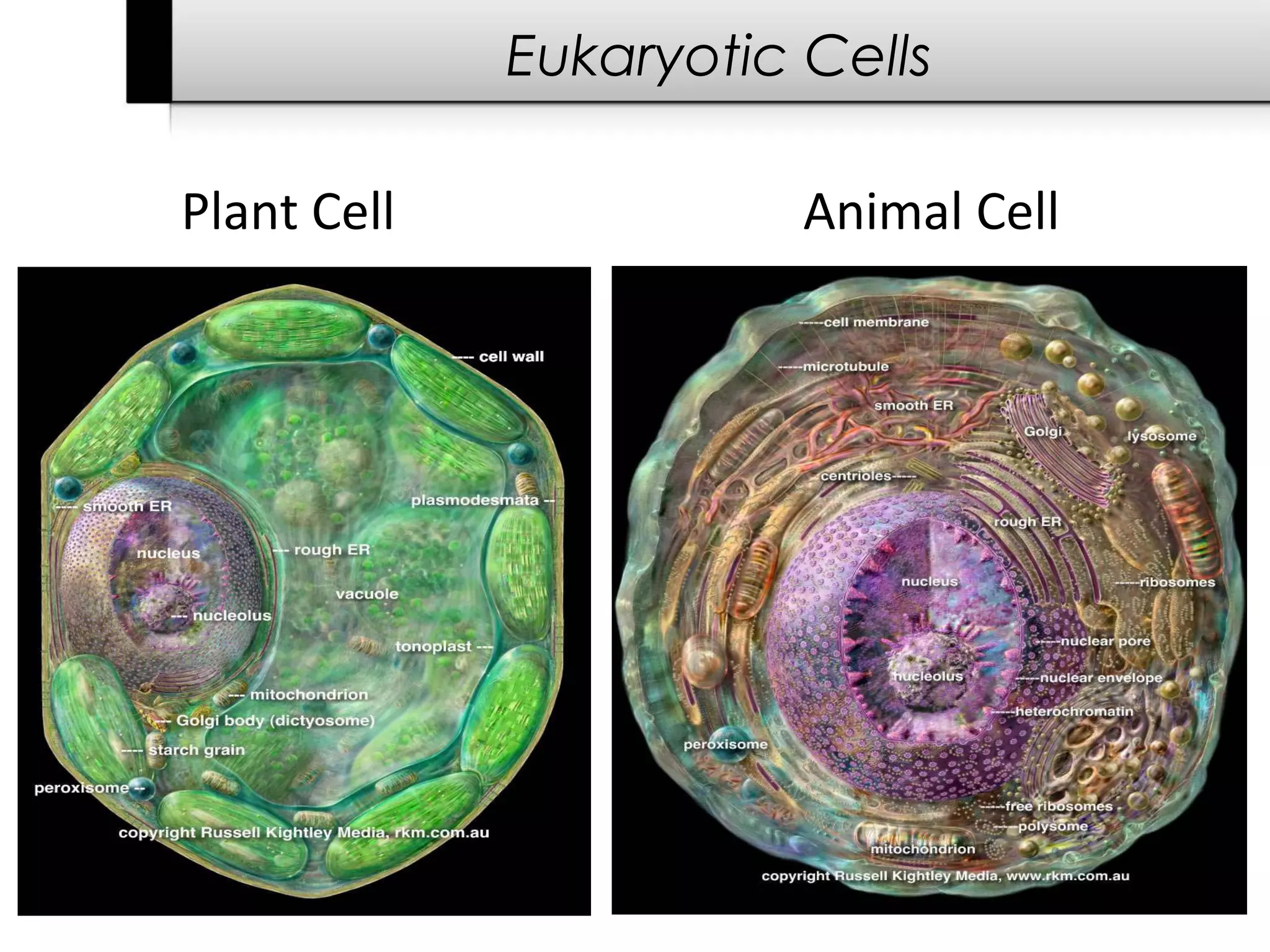
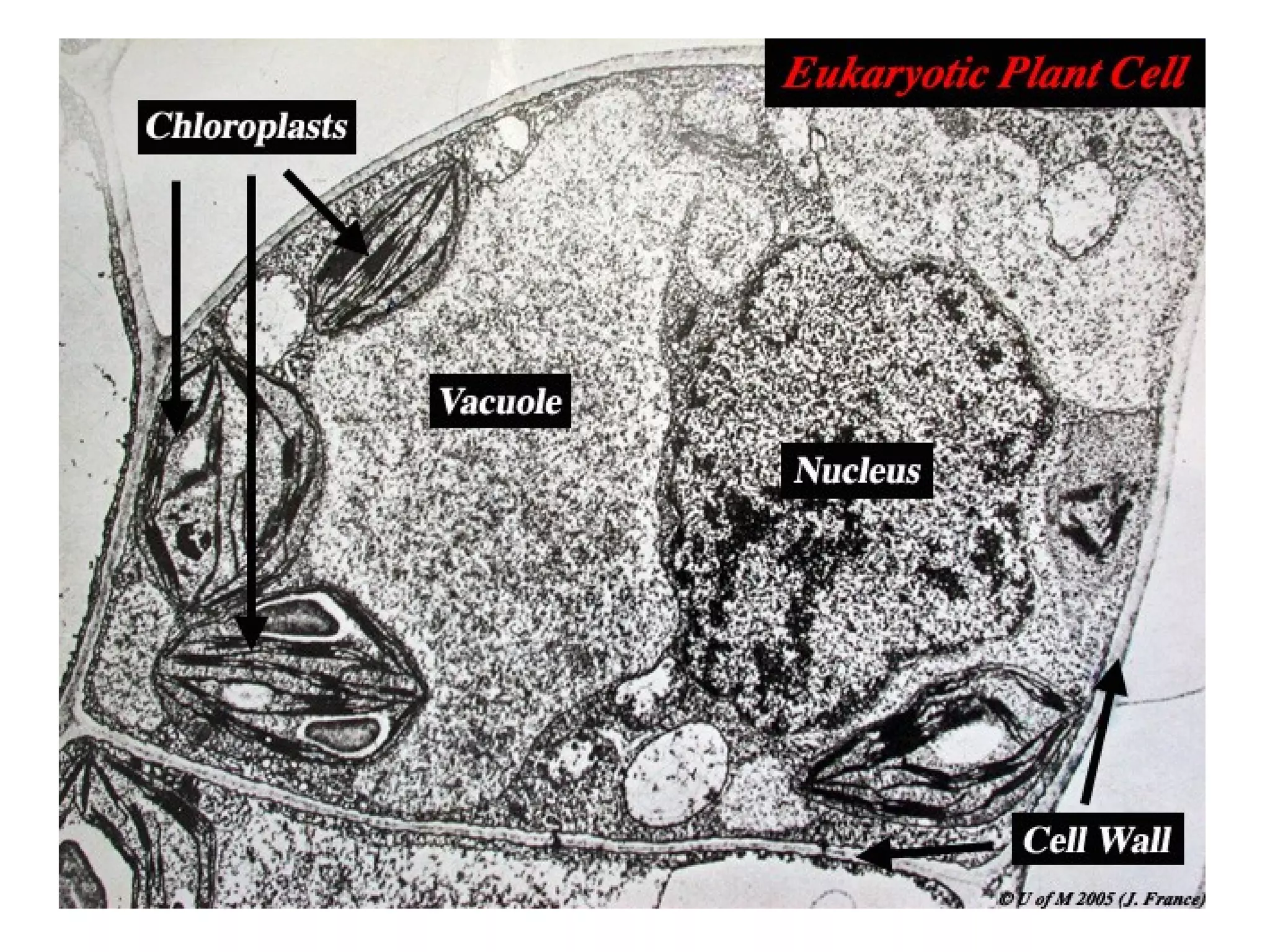
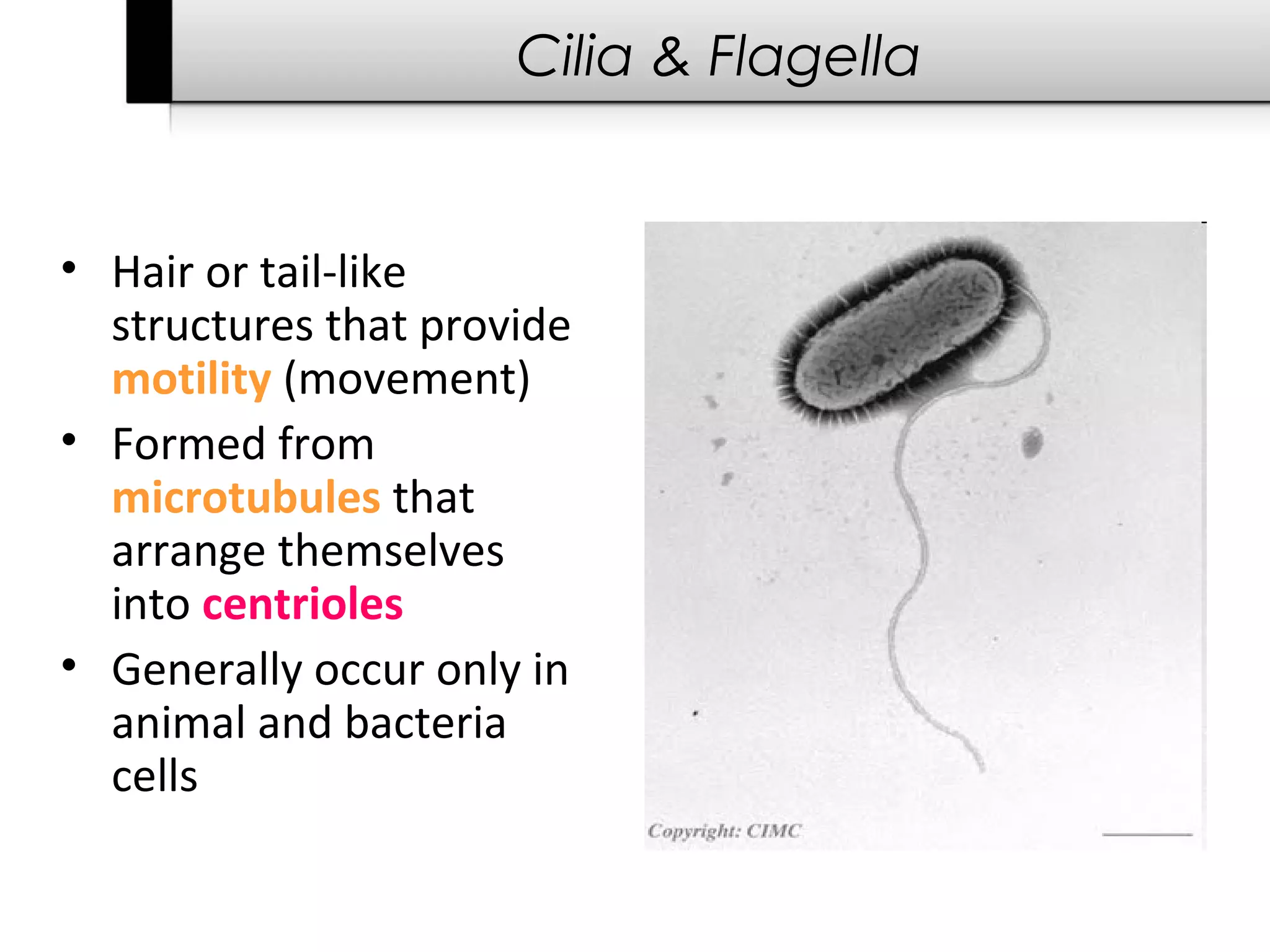
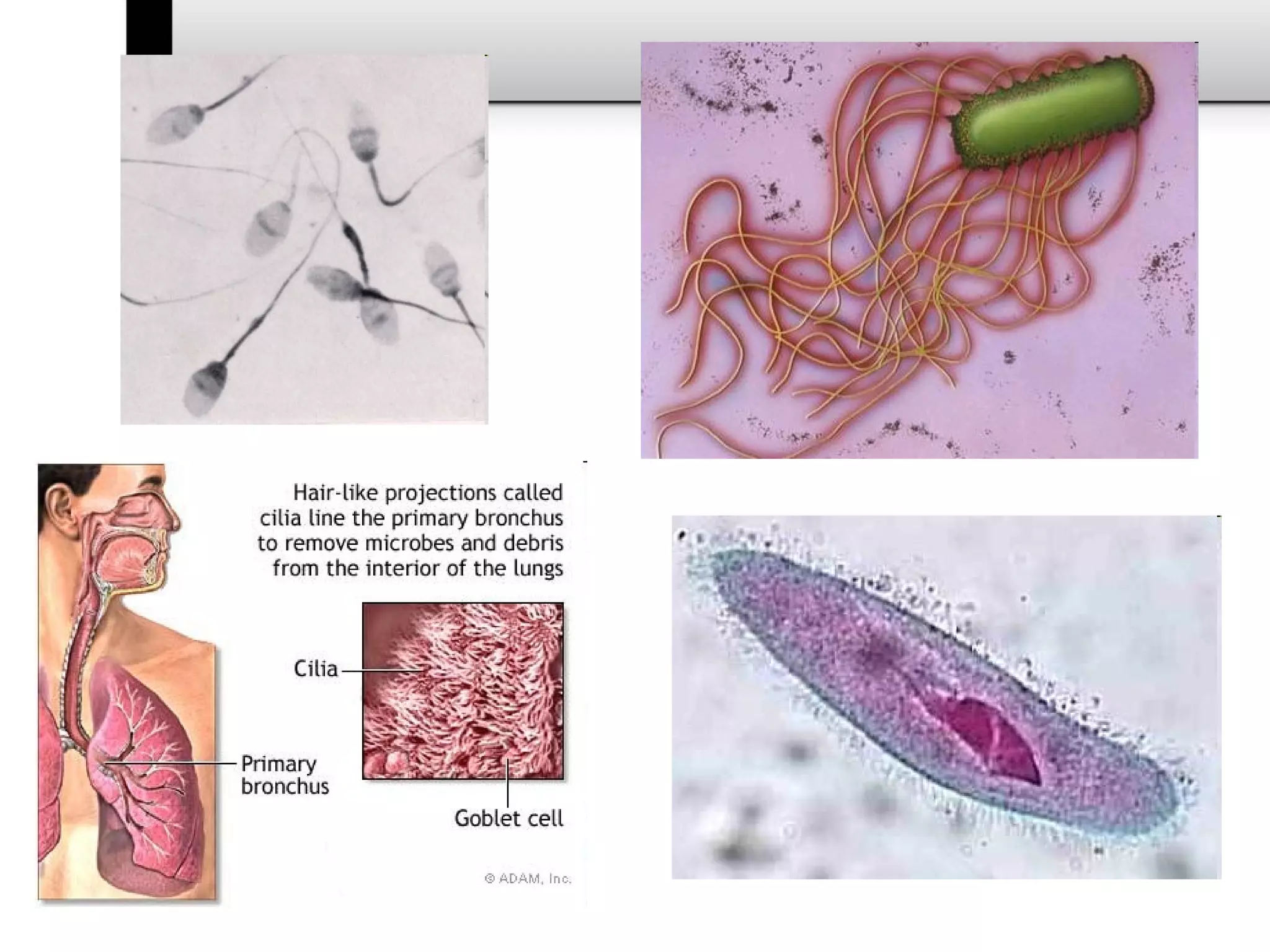
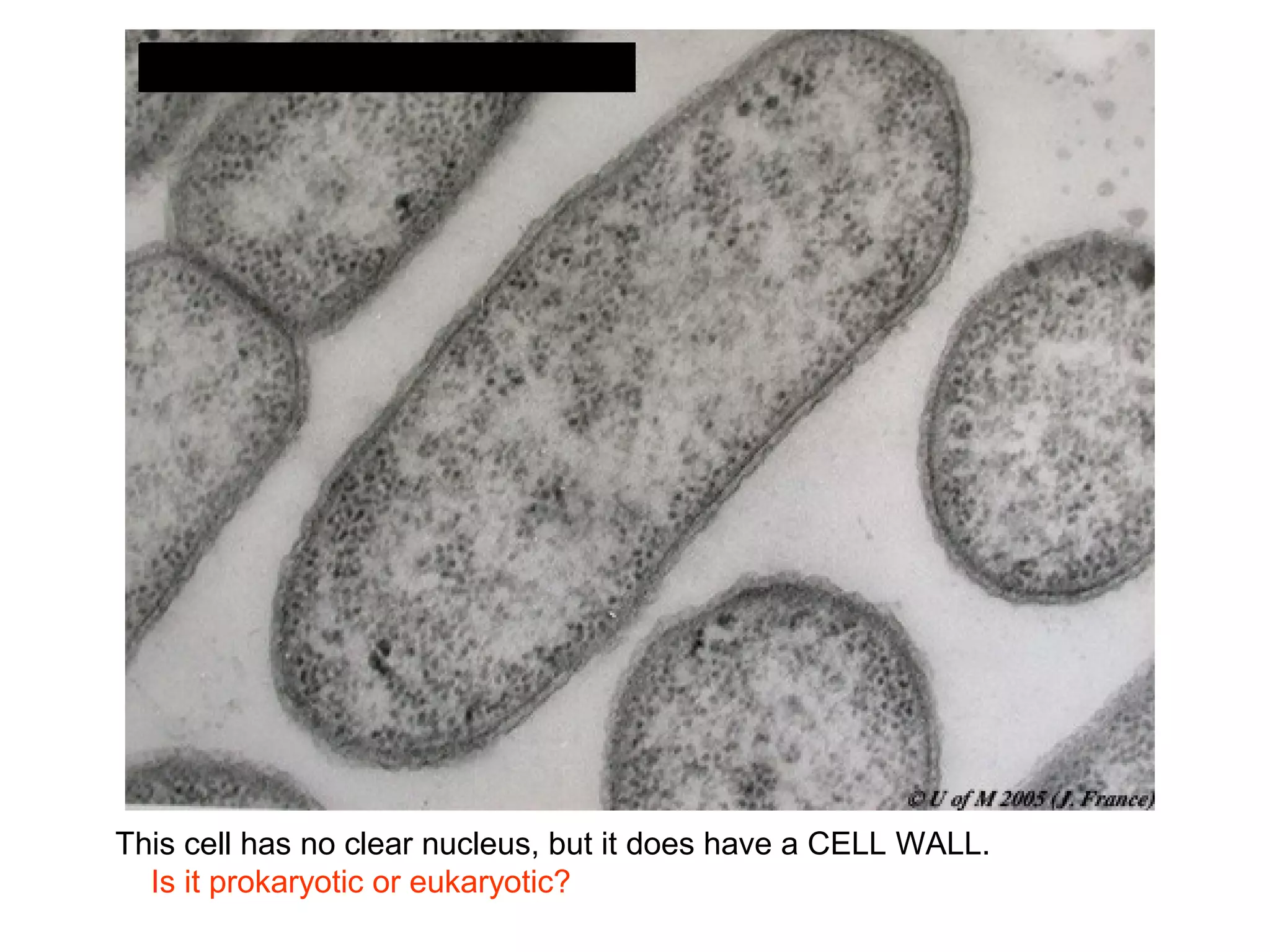
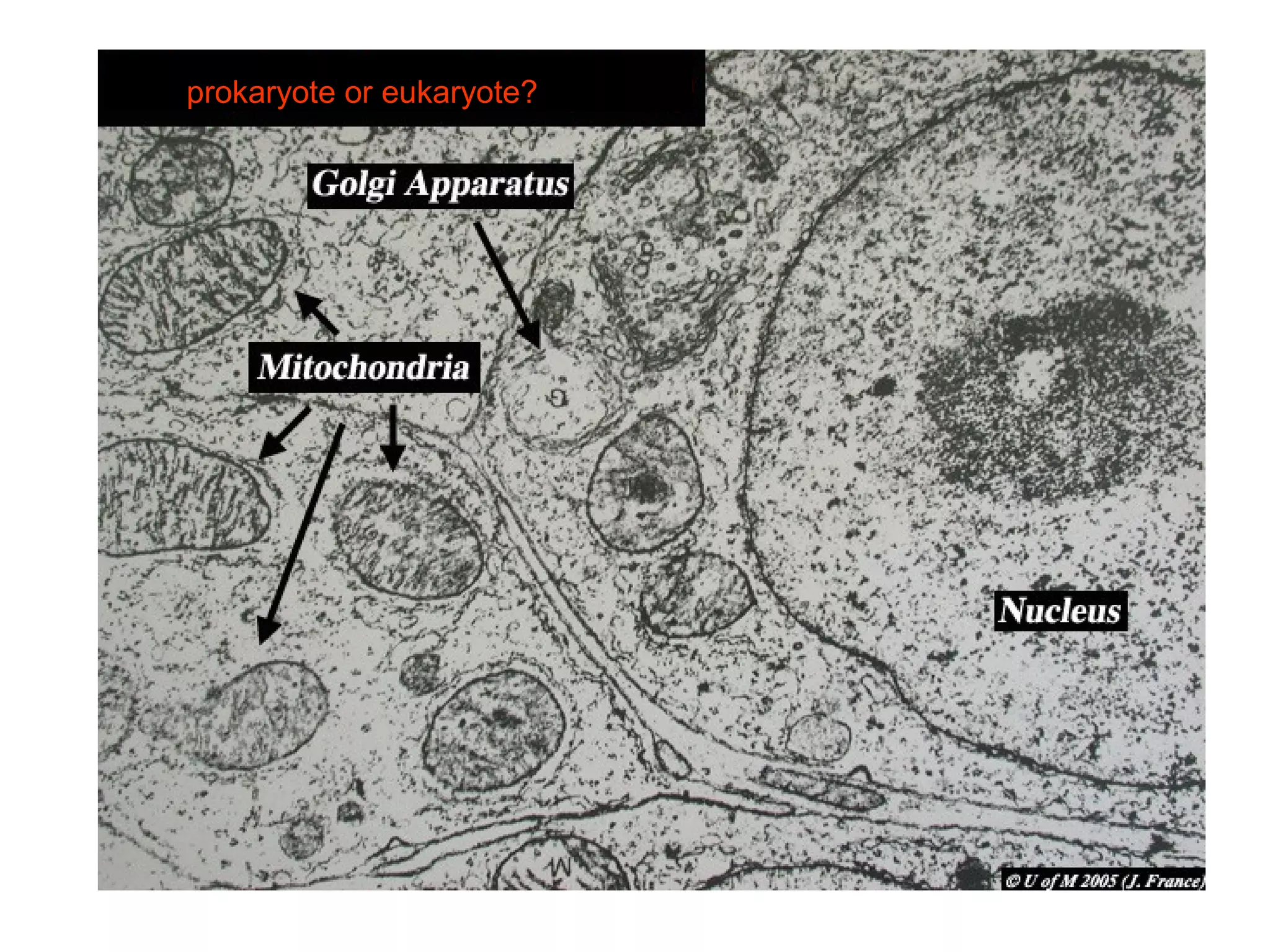
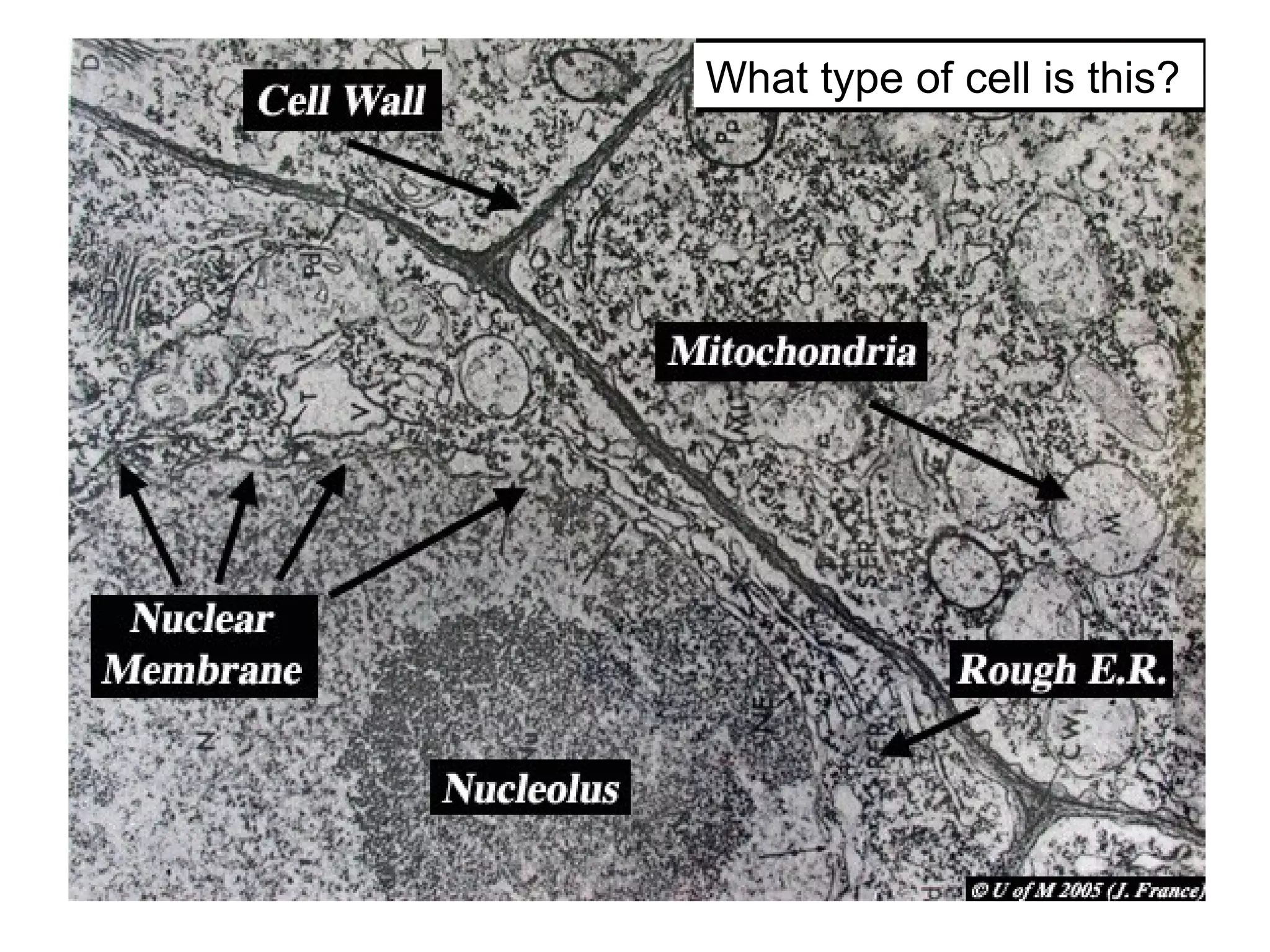
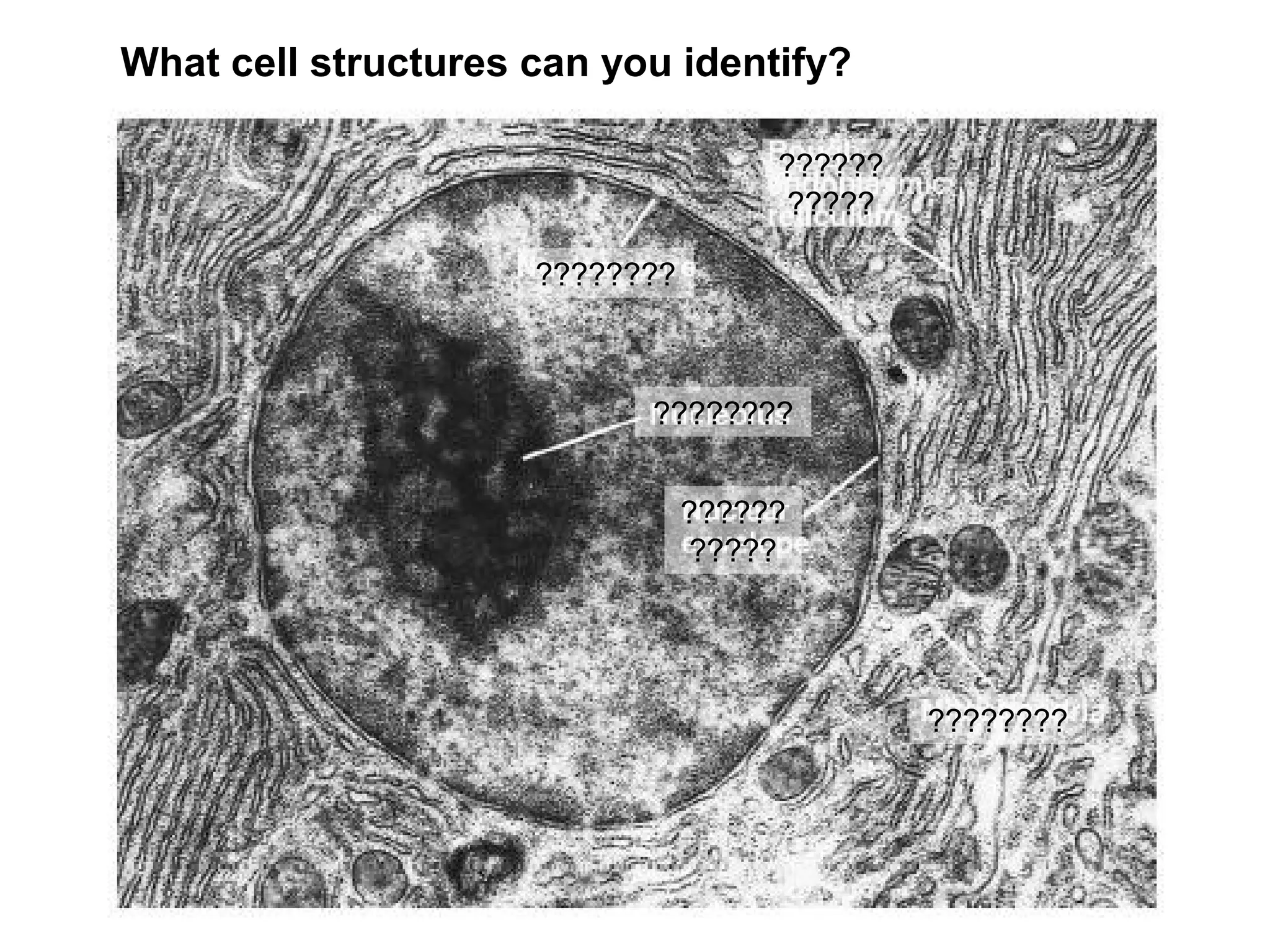
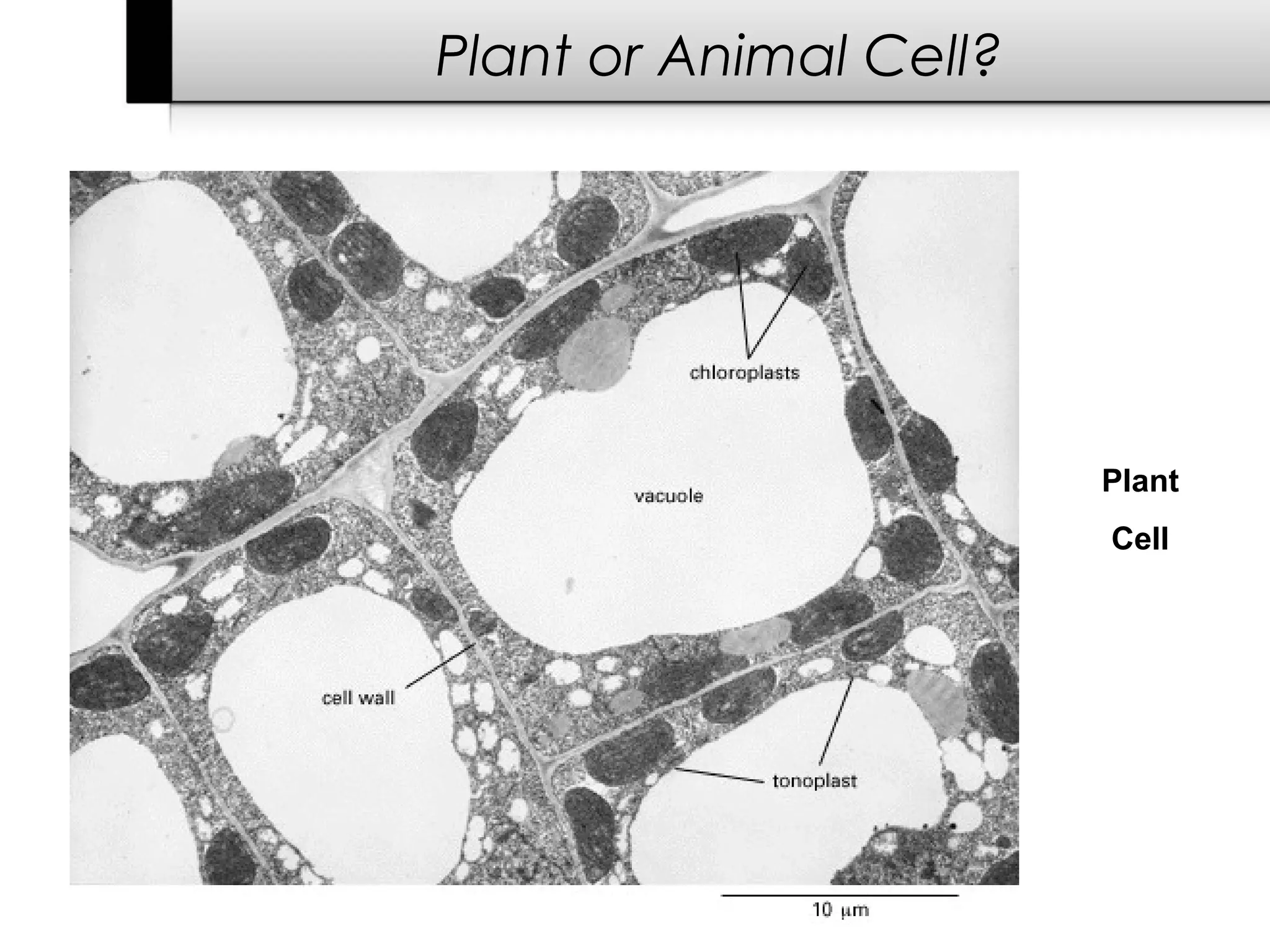
2. It describes the two main types of cells - prokaryotic cells which lack a nucleus and organelles, and eukaryotic cells which have a nucleus and organelles.
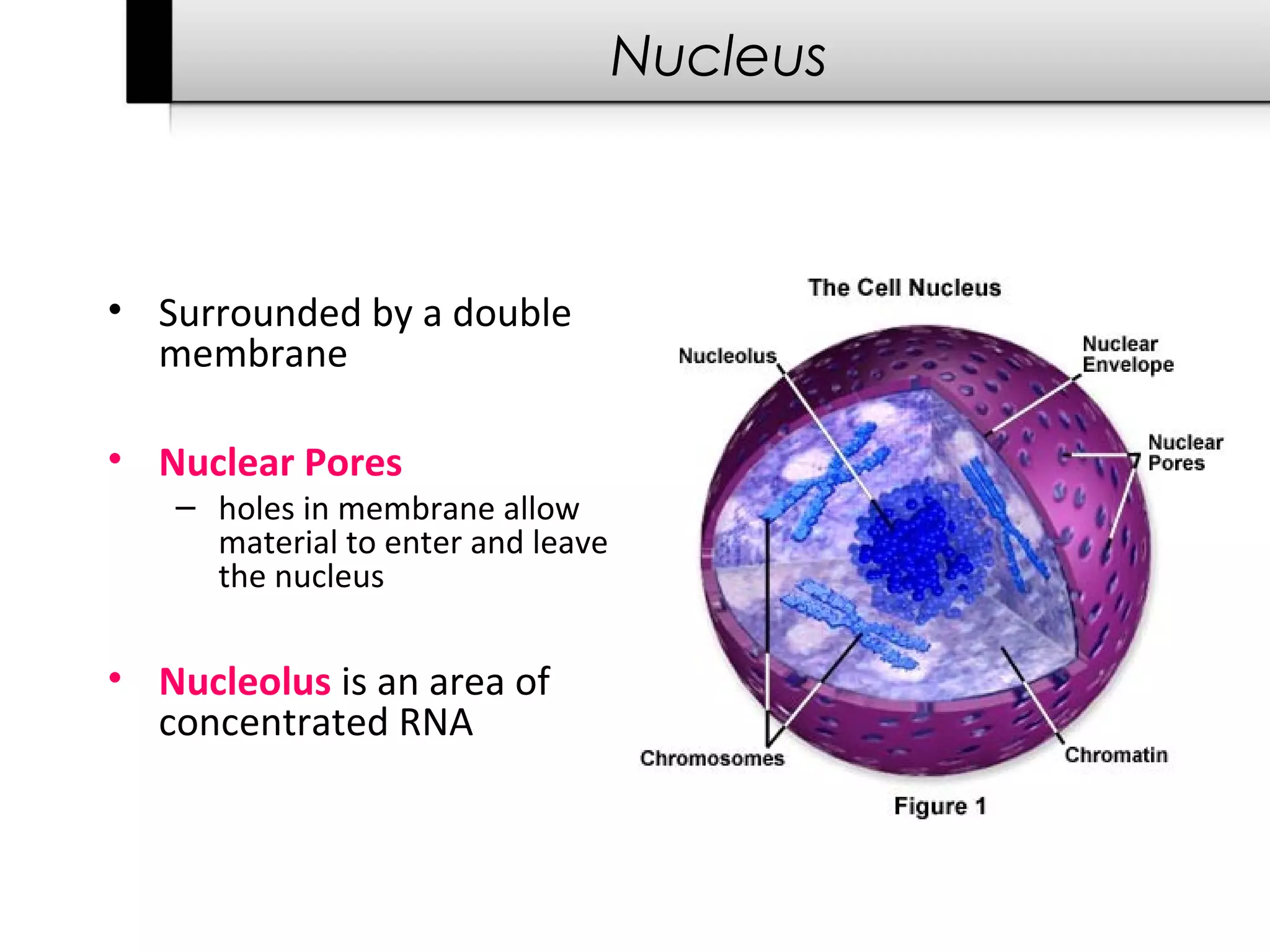
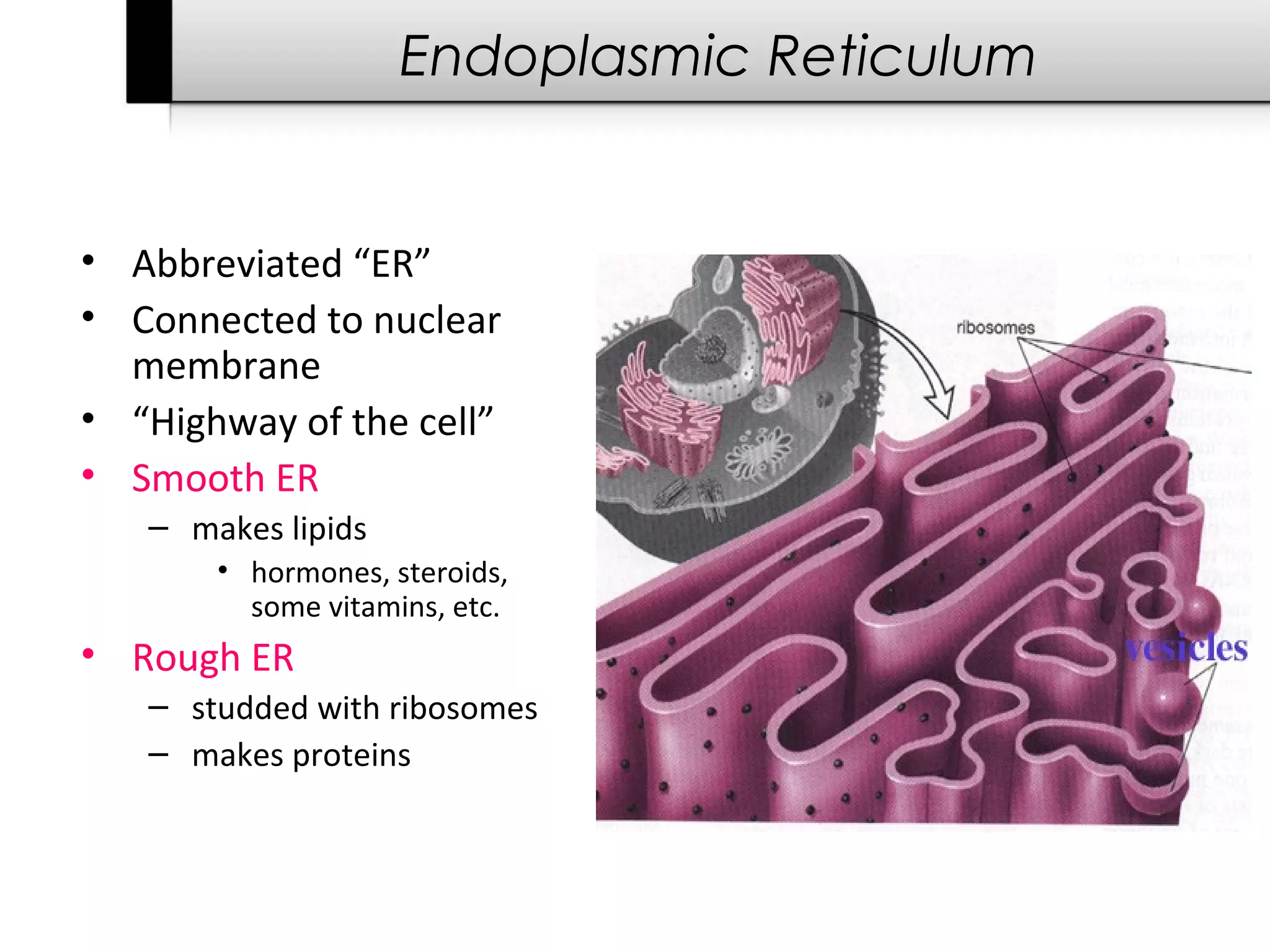
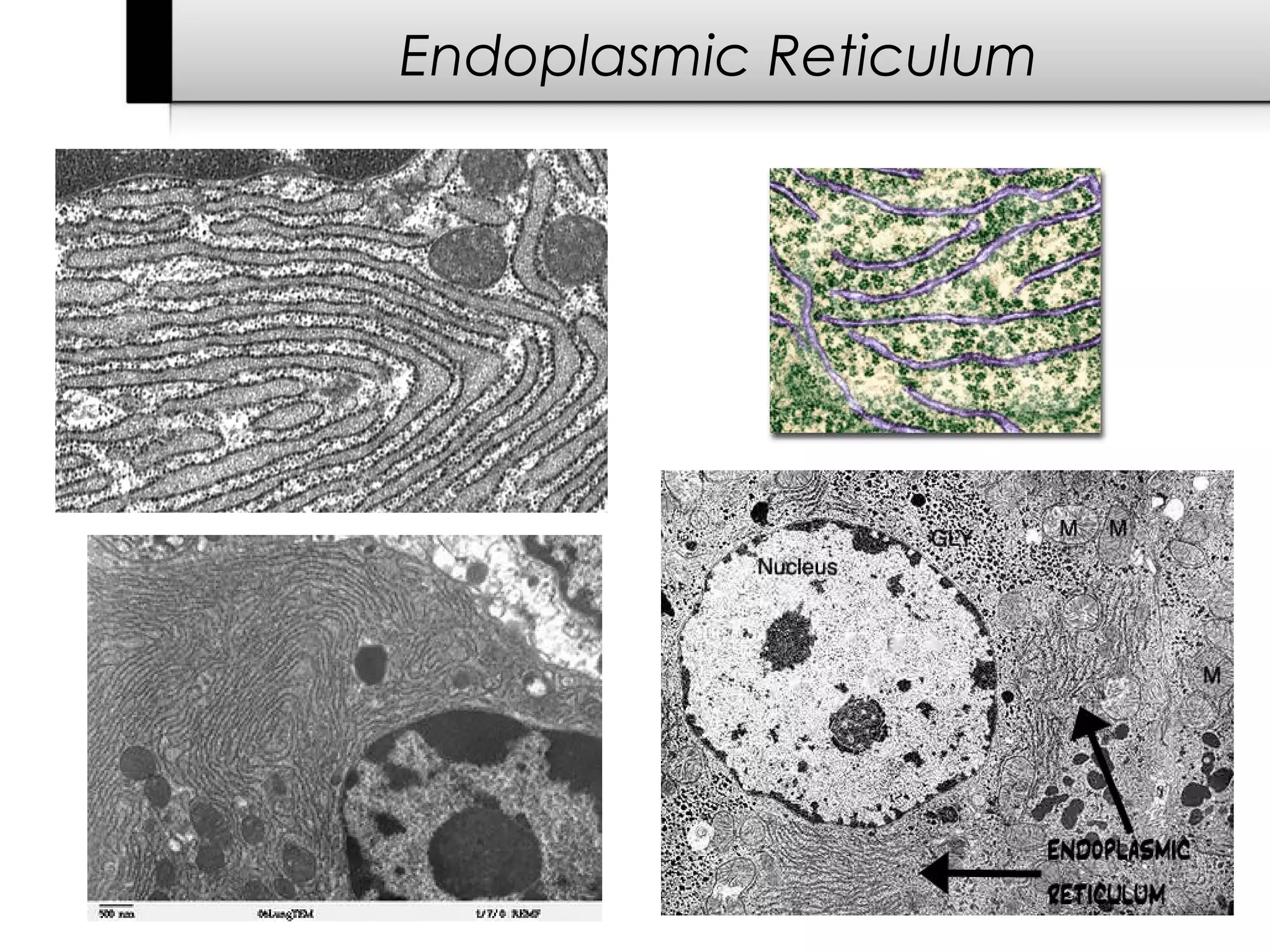
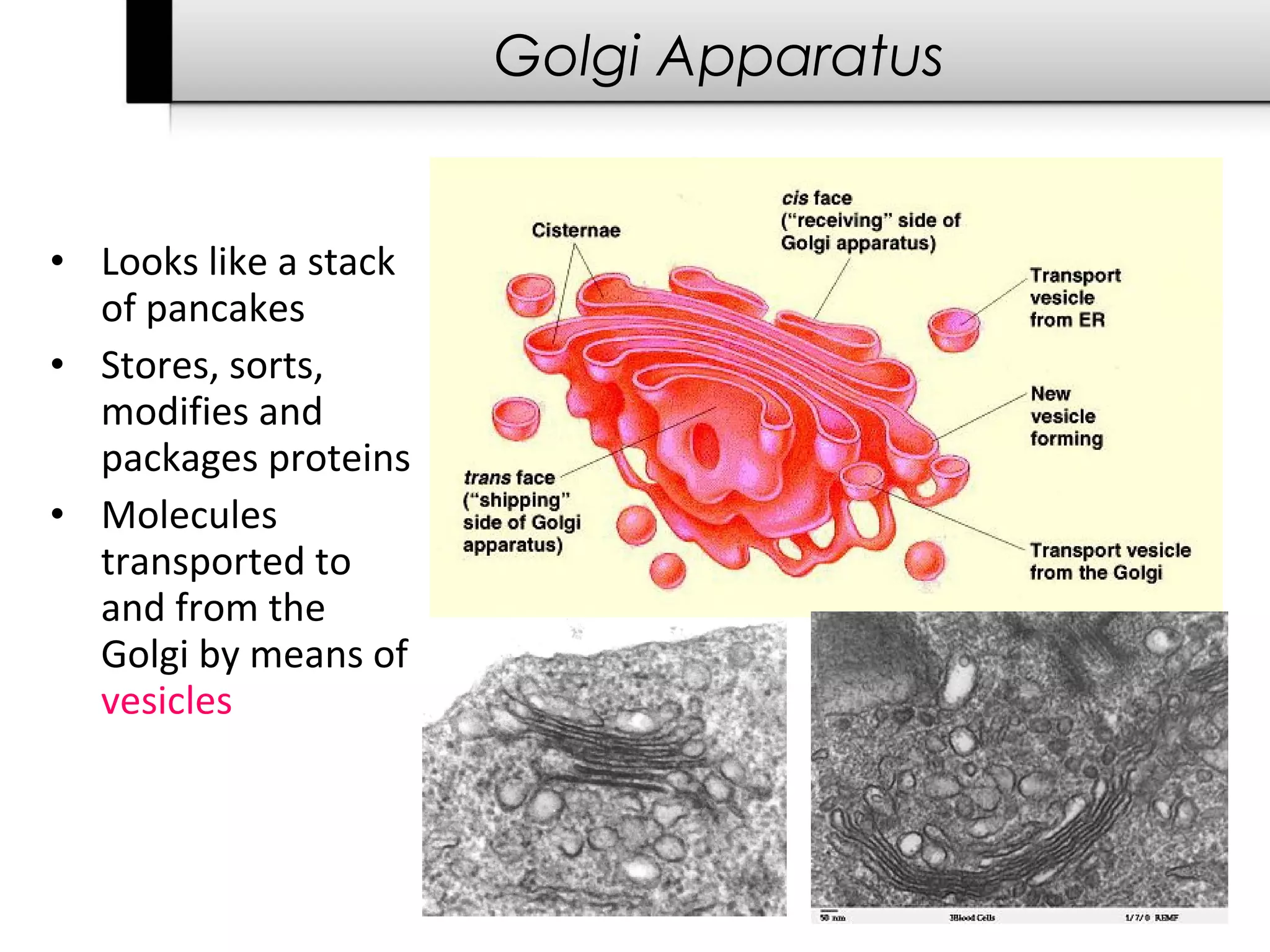
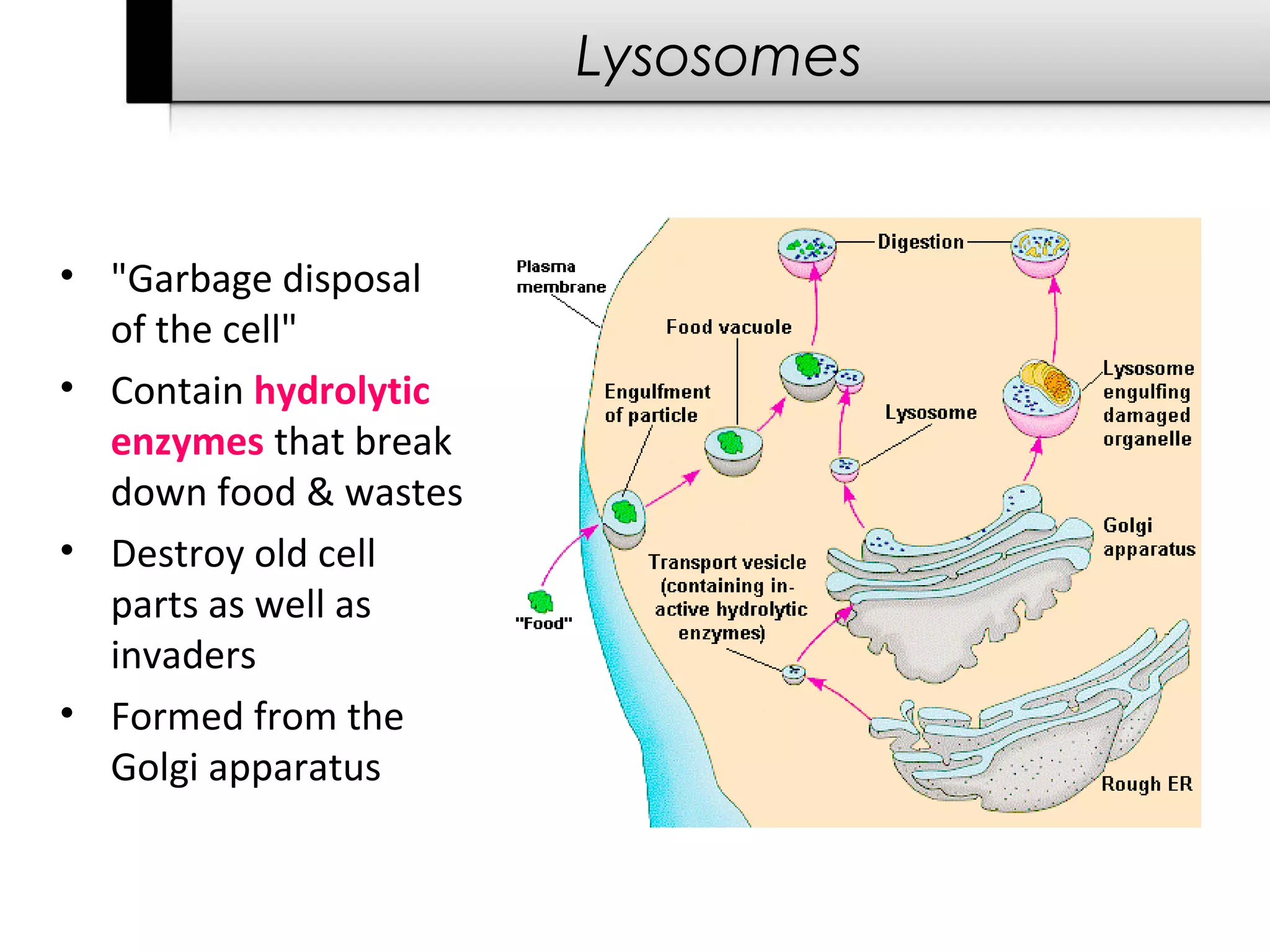
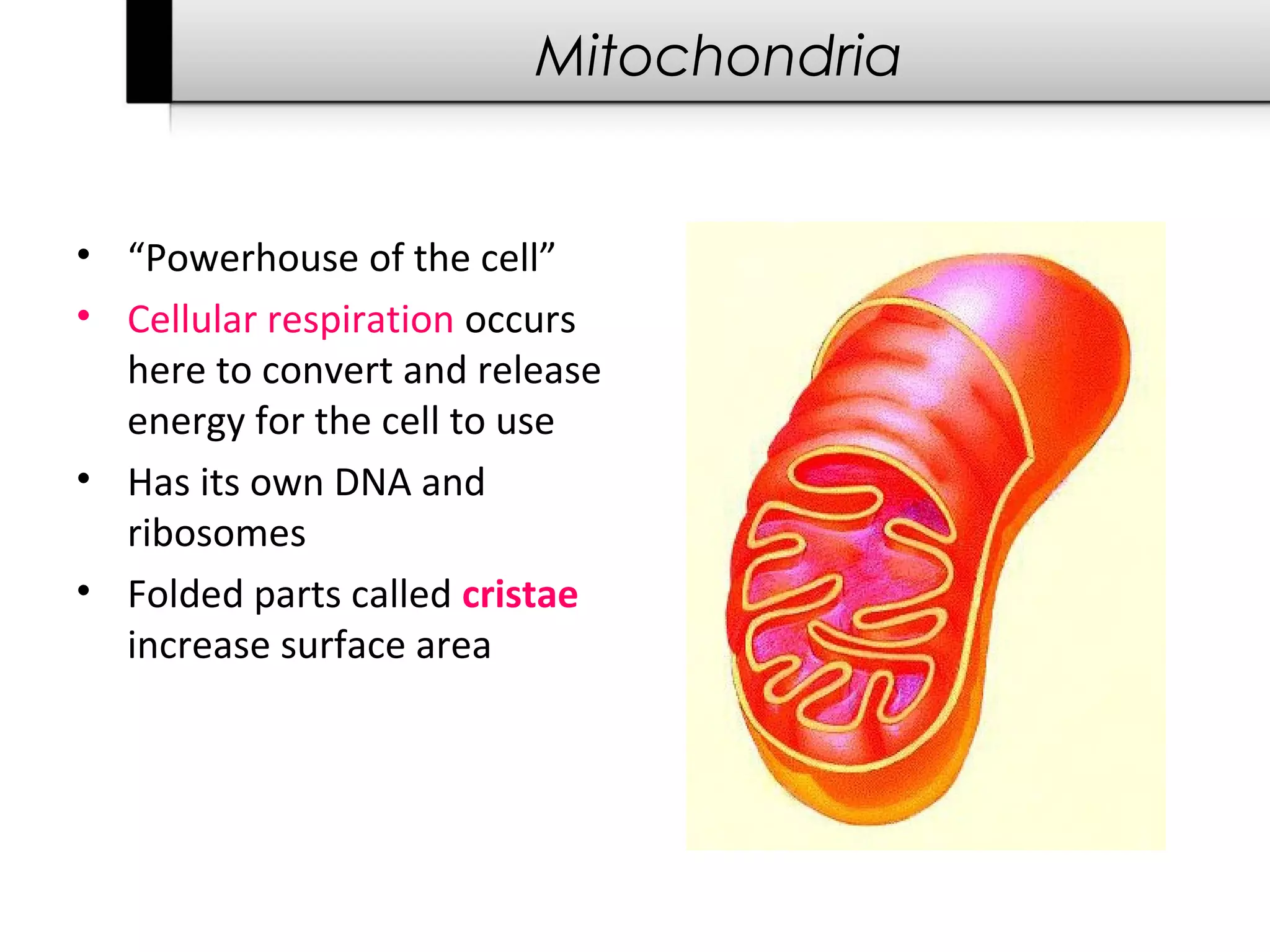
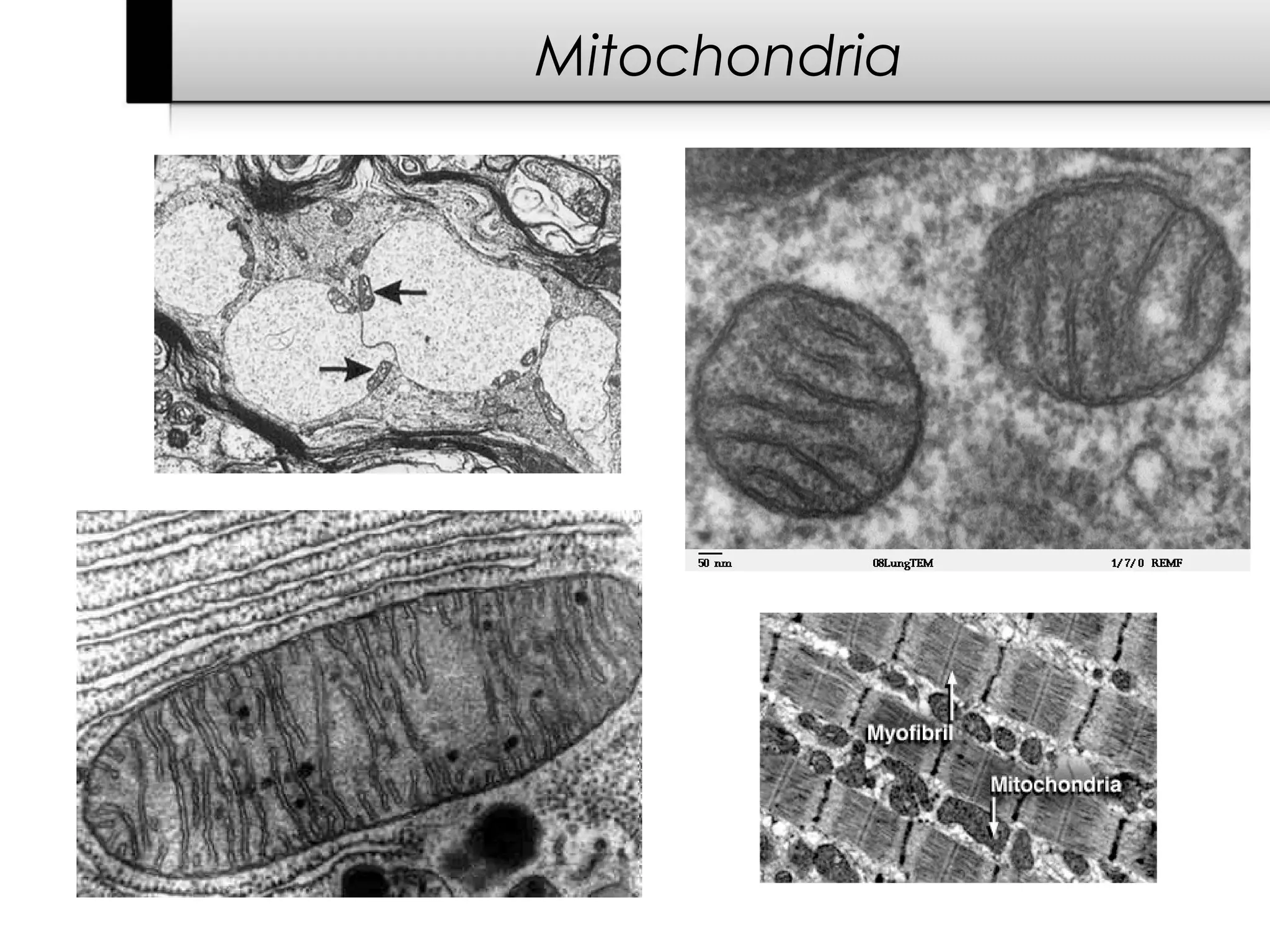
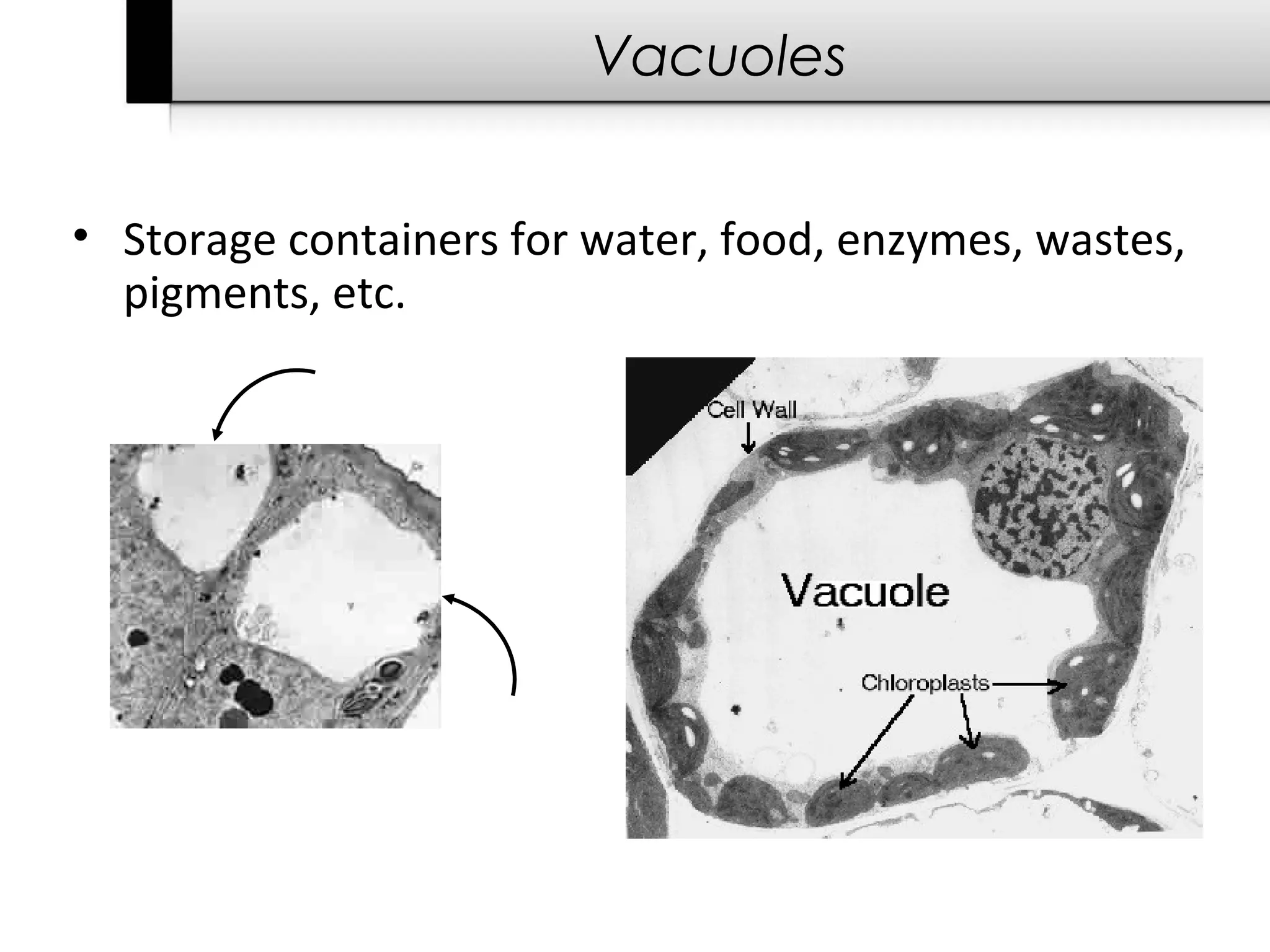
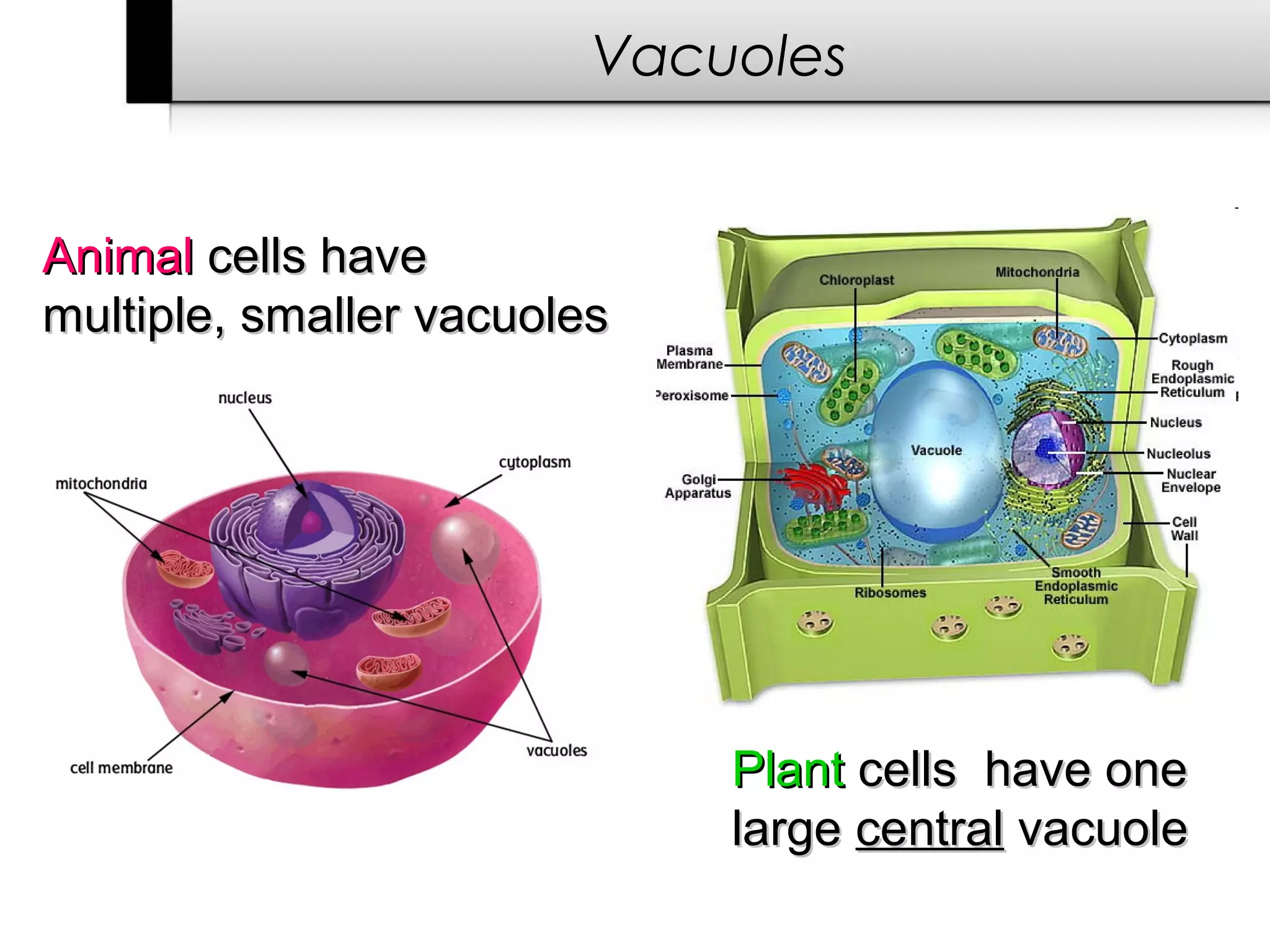
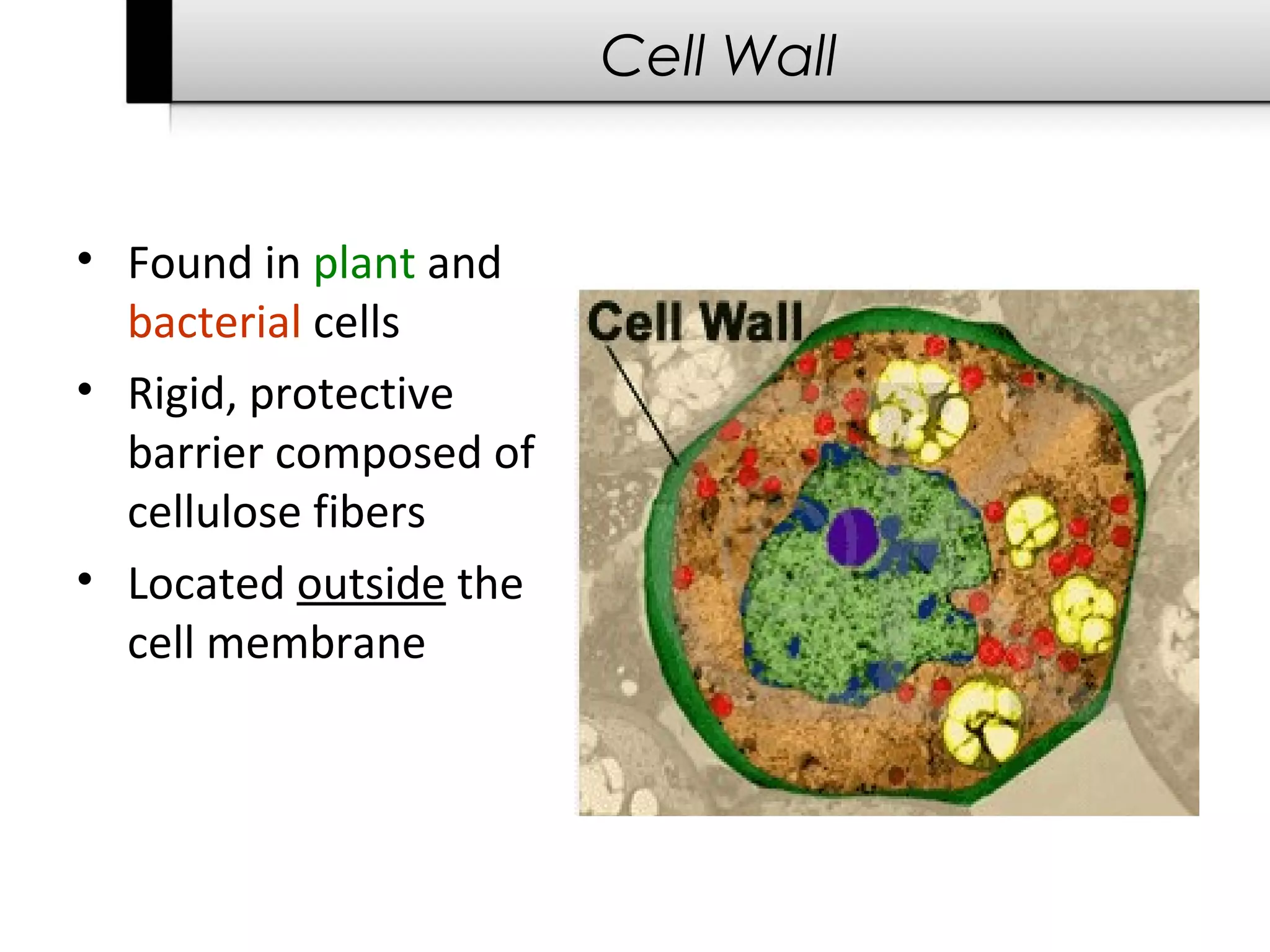
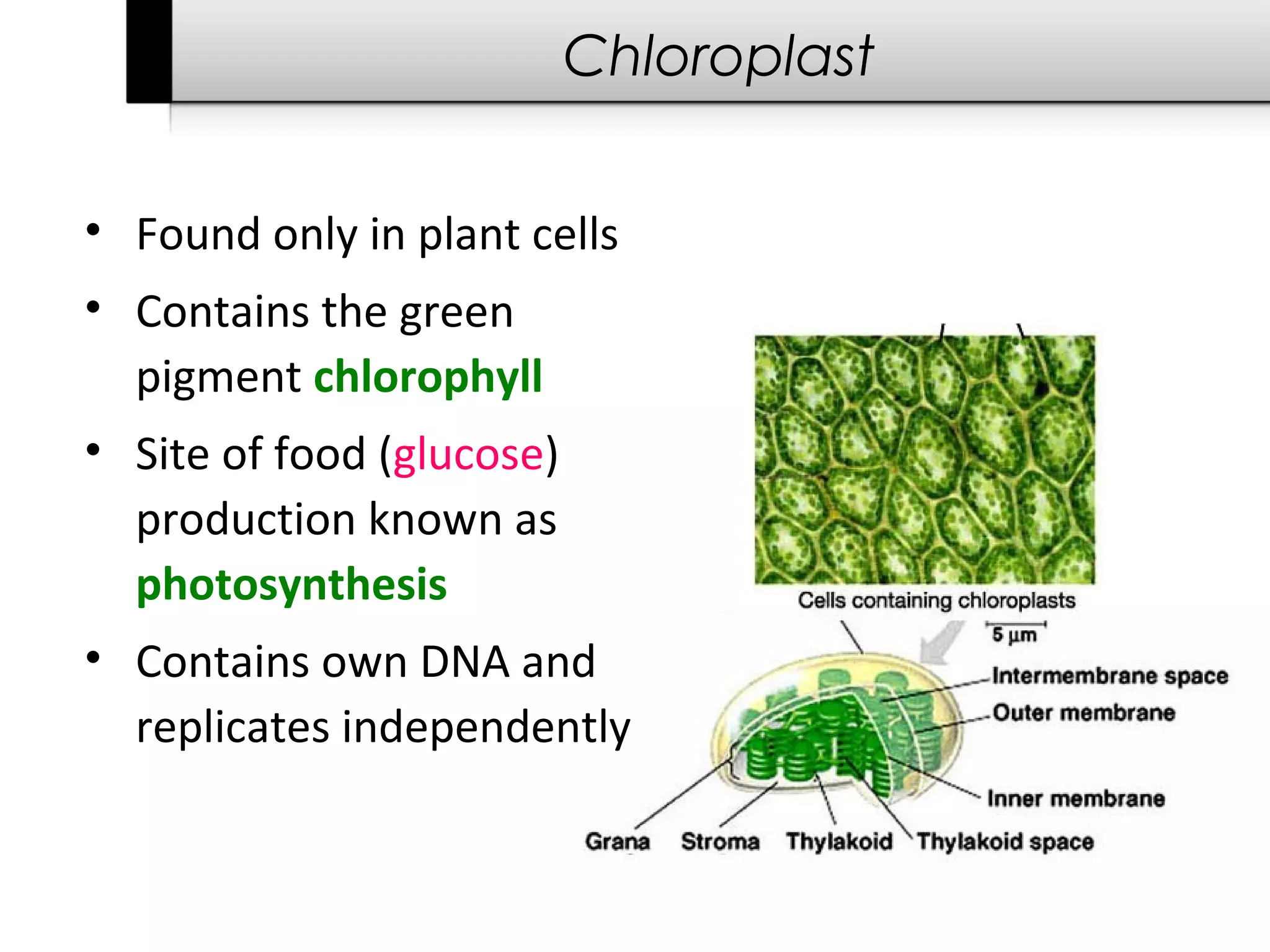
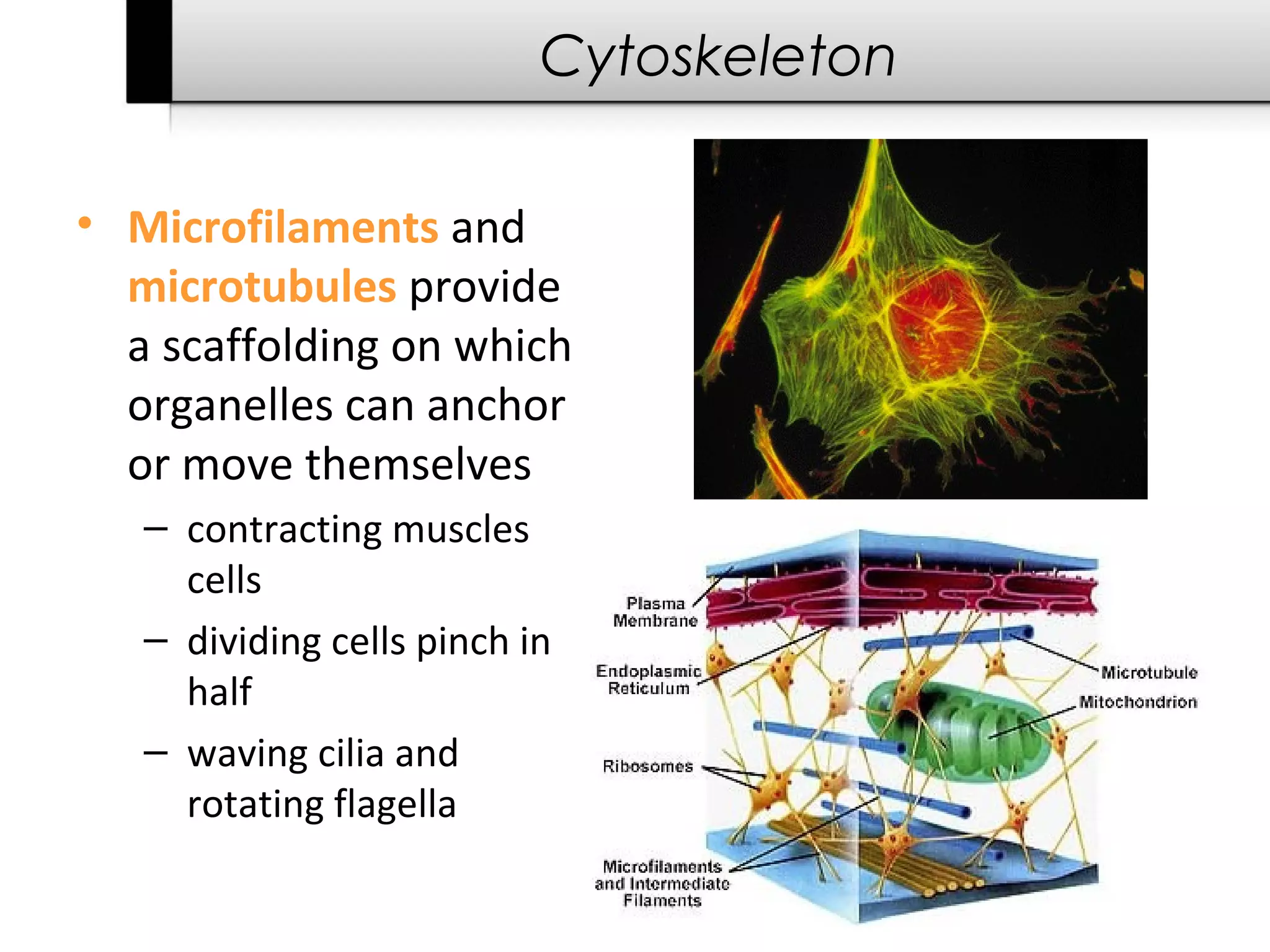
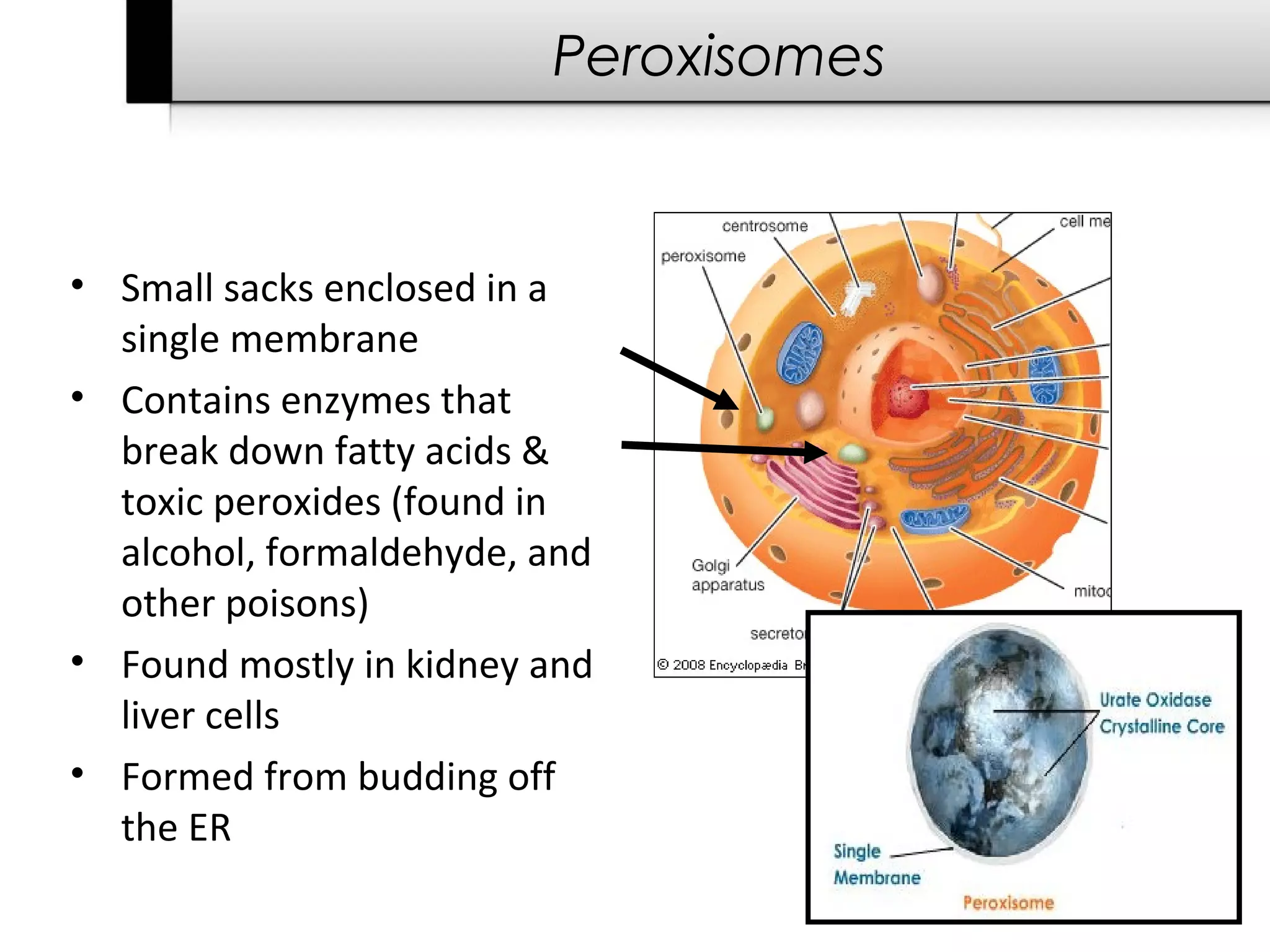
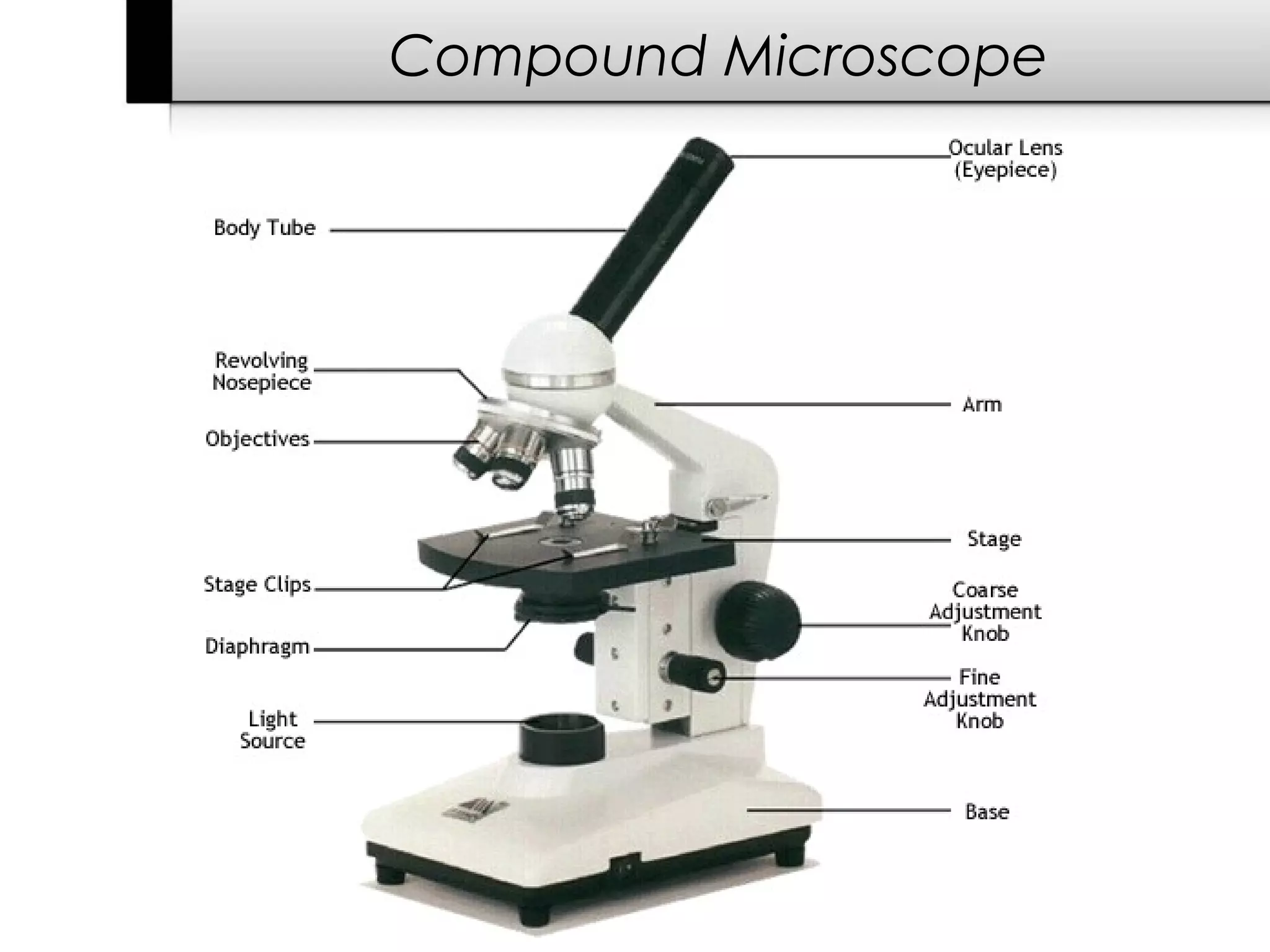
3. It details several organelles found in eukaryotic cells and their functions including the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles.