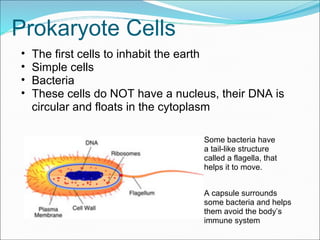
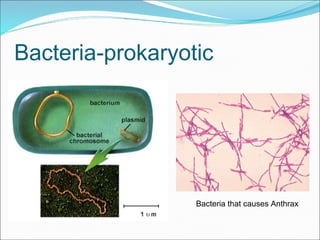
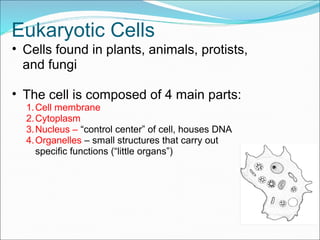
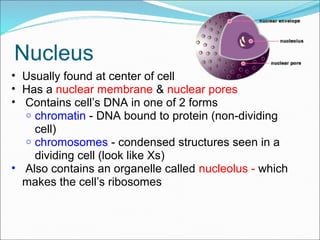
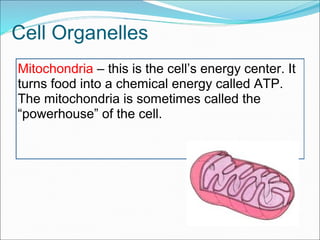
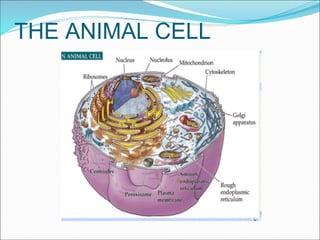
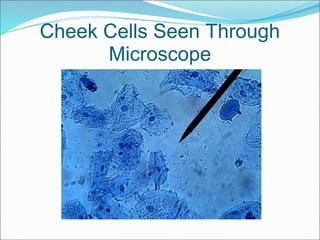
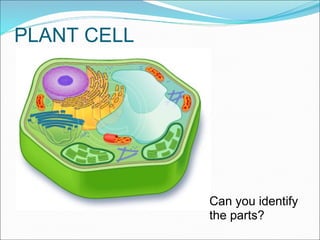
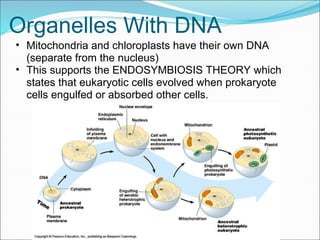
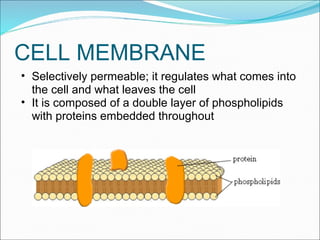
The document summarizes key aspects of cell theory and cell structure. It discusses scientists like Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schwann, and Virchow who contributed to early observations of cells. The cell theory states that all living things are made of cells, the cell is the basic unit of structure and function, and cells only arise from pre-existing cells. The document compares prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, describing their components like DNA, organelles, and membranes. Key organelles in plant and animal cells are also outlined.