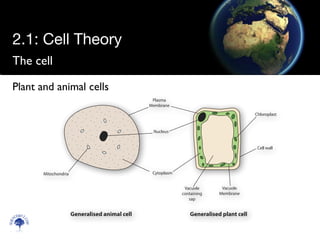
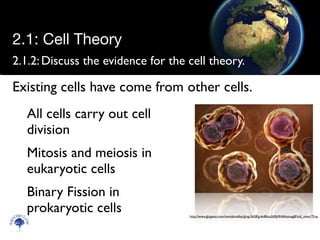
The cell theory states that all living things are made of cells, cells are the smallest unit of life, and existing cells come from other cells. Evidence for the cell theory includes observations of organisms under microscopes appearing to be made of cells, Hooke and van Leeuwenhoek's early microscopic observations of cells, cells carrying out functions but components not surviving independently, and all cells undergoing cell division. Unicellular organisms carry out all the functions of life such as metabolism, sensitivity, homeostasis, growth, reproduction, nutrition, and movement within a single cell.