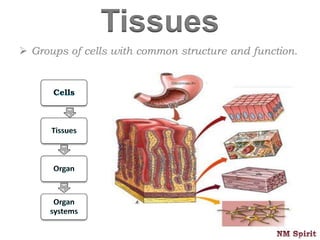
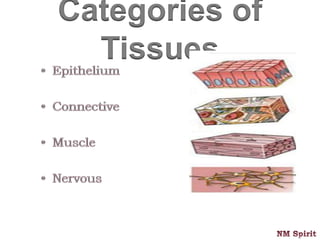
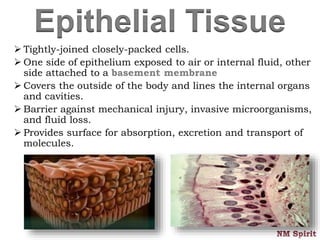
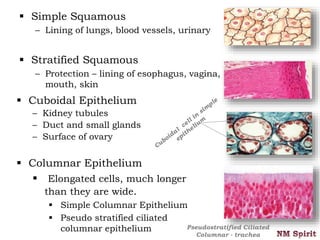
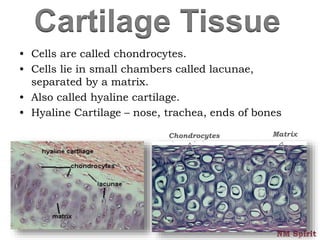
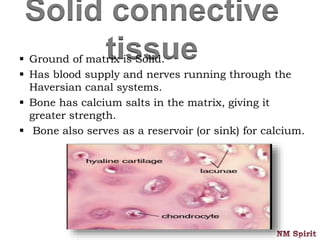
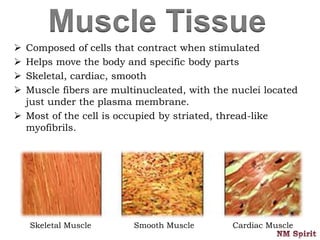
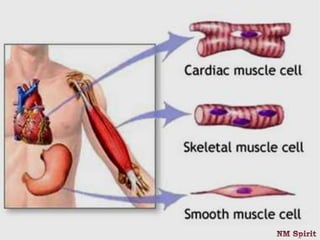
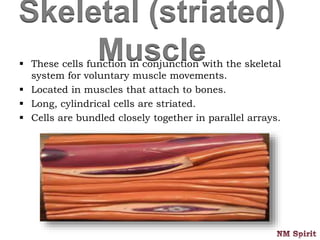
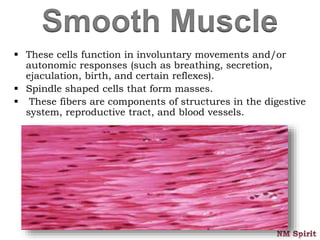
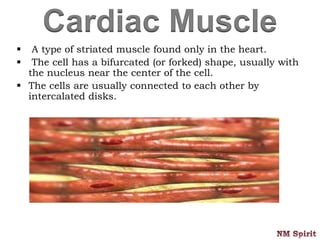
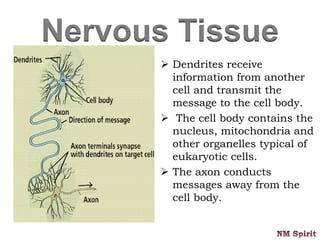
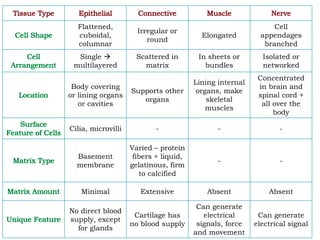
This document discusses the four main types of tissues in the human body - epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue.
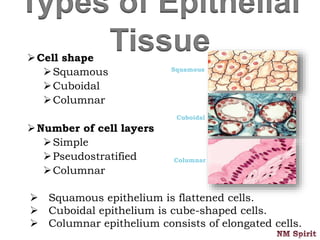
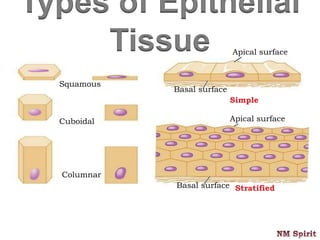
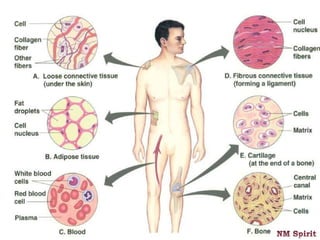
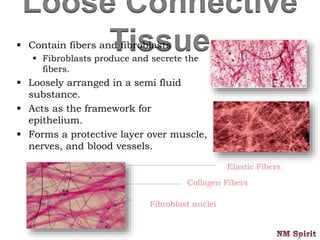
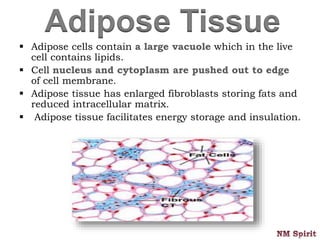
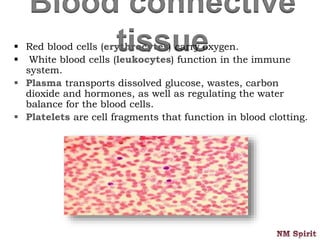
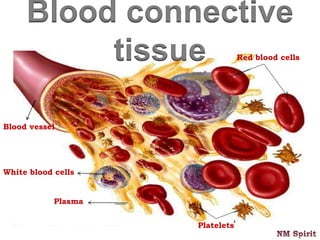
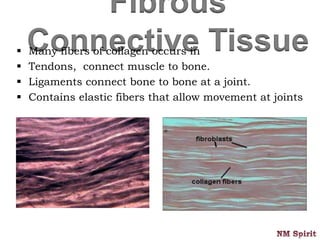
It describes epithelial tissue as sheets of cells that cover surfaces and line organs. There are several types classified by cell shape and layer thickness. Connective tissue binds other tissues together and has fibers within a fluid or solid matrix. Examples include loose connective, adipose, blood and fibrous tissues. Muscle tissue contains contractile cells in skeletal, cardiac and smooth configurations. Nervous tissue is made up of neurons that transmit electrical signals through dendrites, cell bodies and axons.