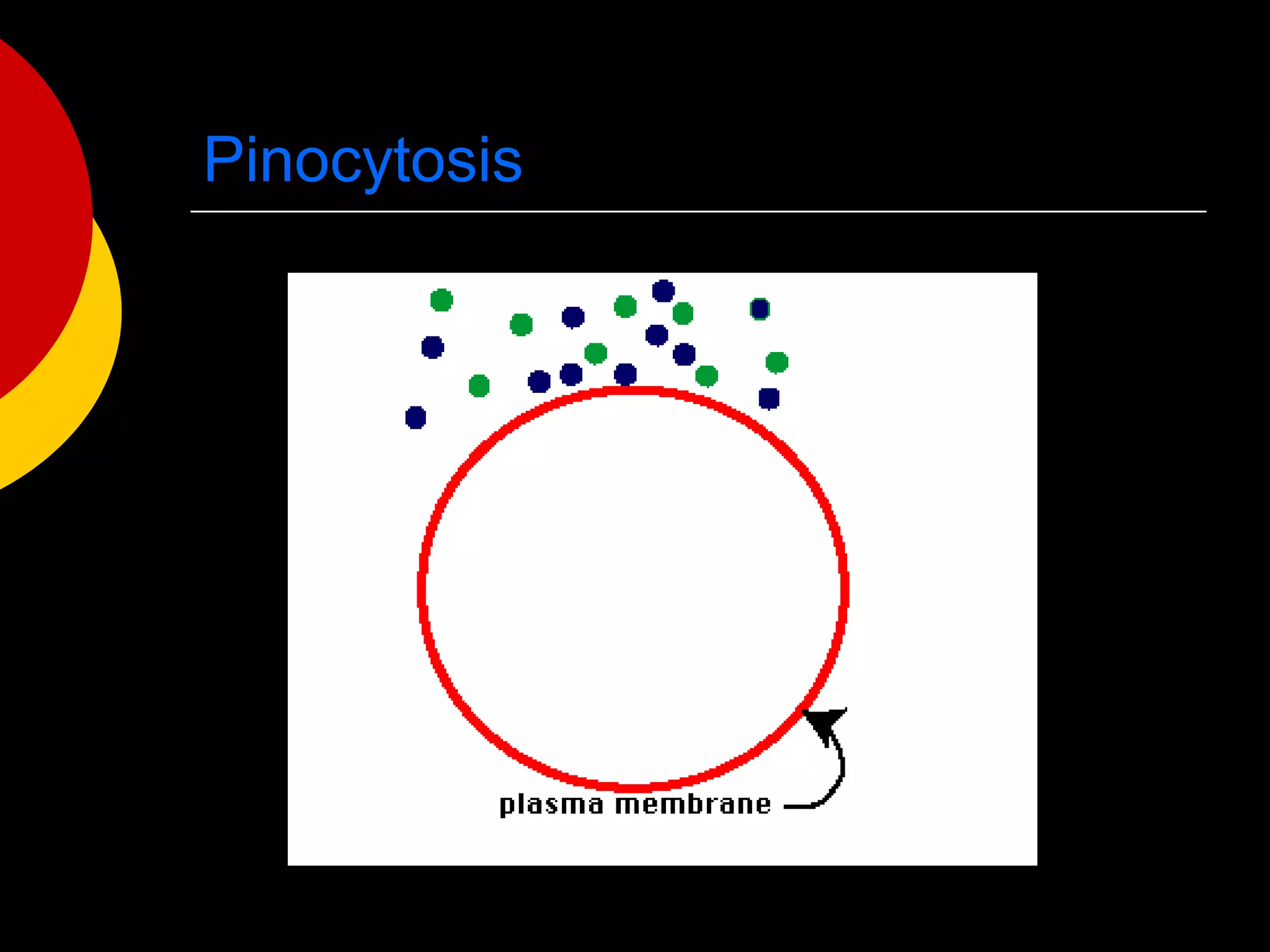
This document provides an overview of cell structure and function. It outlines several key discoveries and concepts in cell biology, including:
1) The cell theory states that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
2) Cells can be either unicellular (single-celled) or multicellular (many-celled). Multicellular organisms have cell specialization where cells perform specific functions.
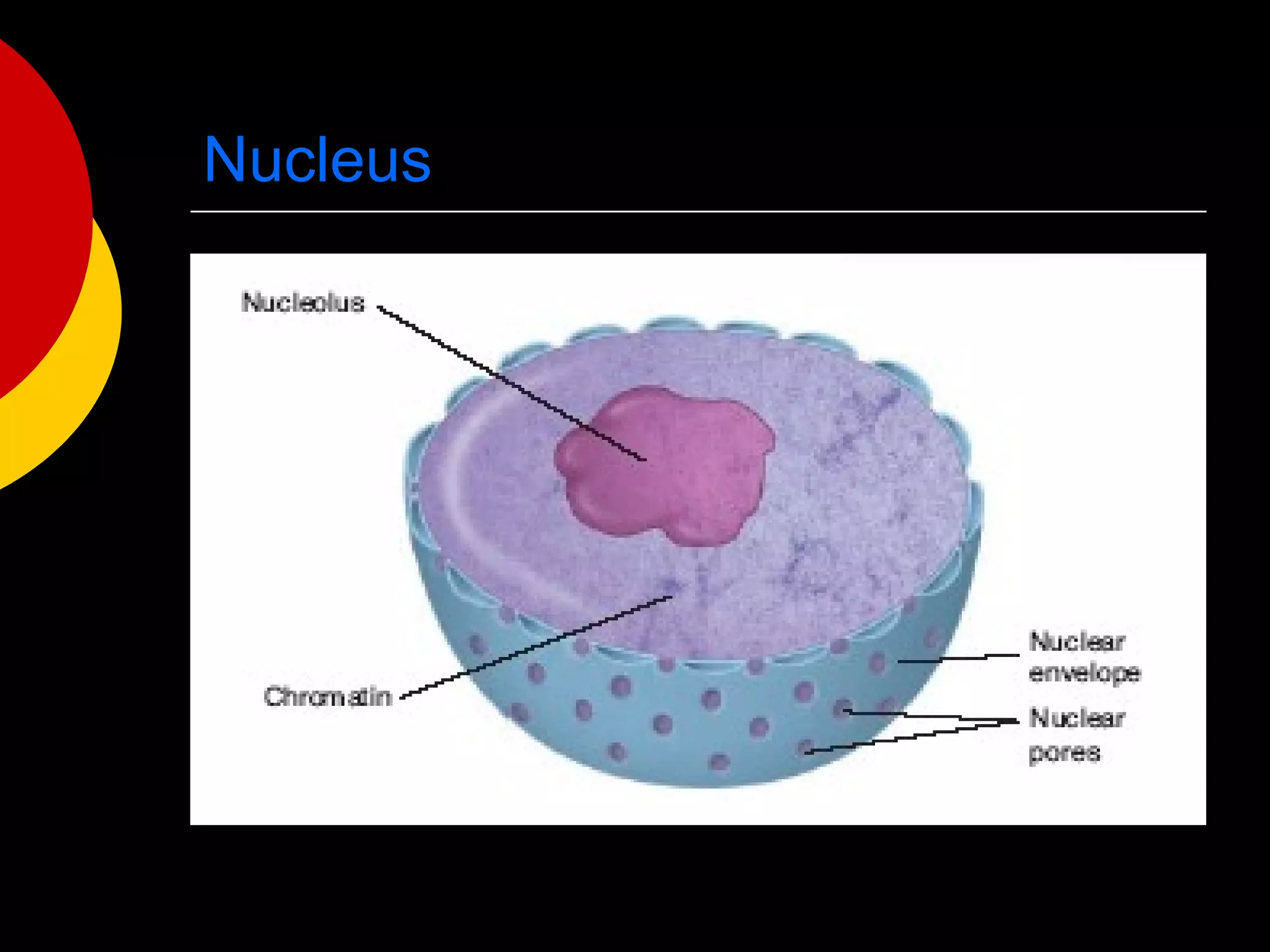
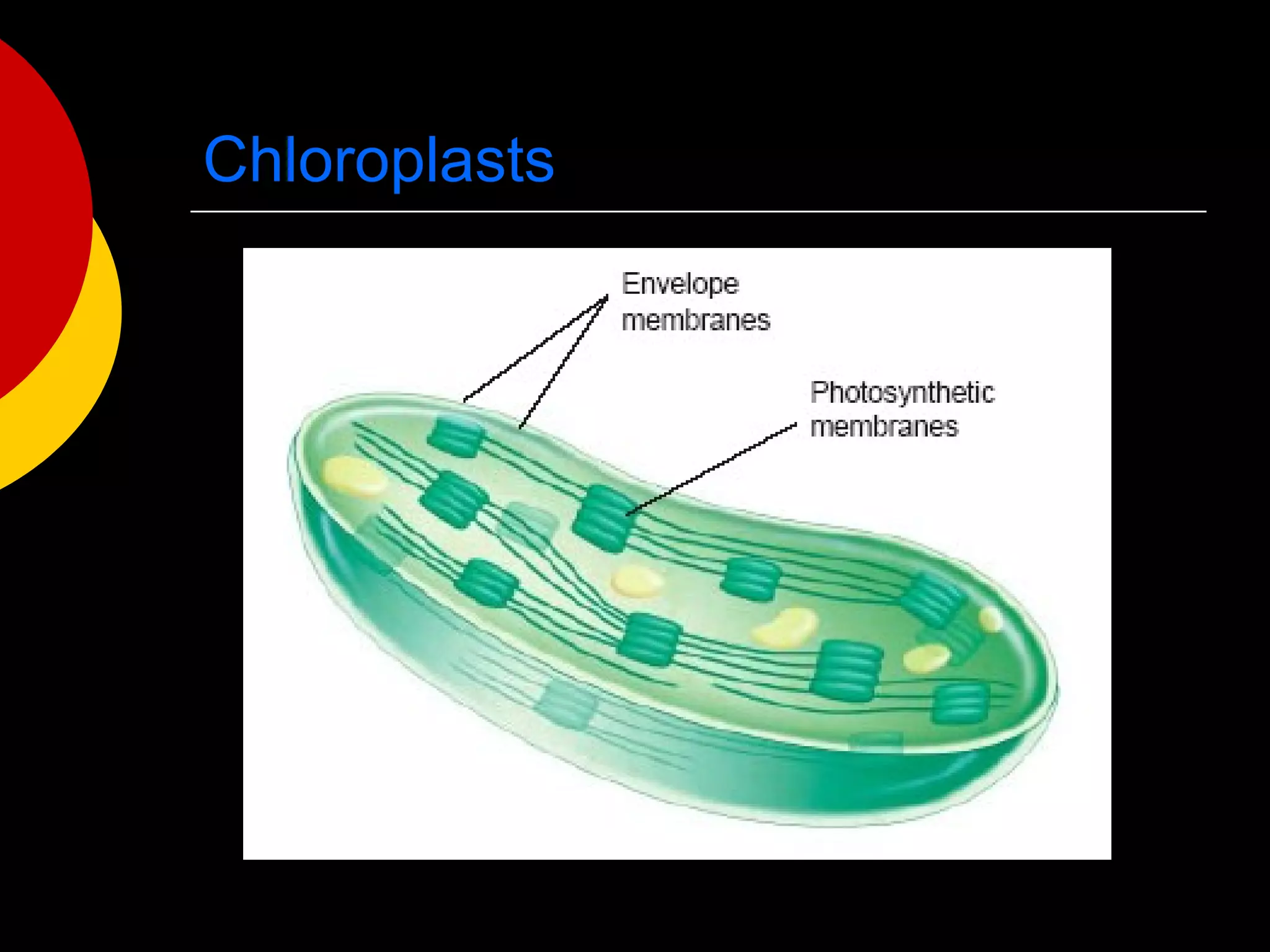
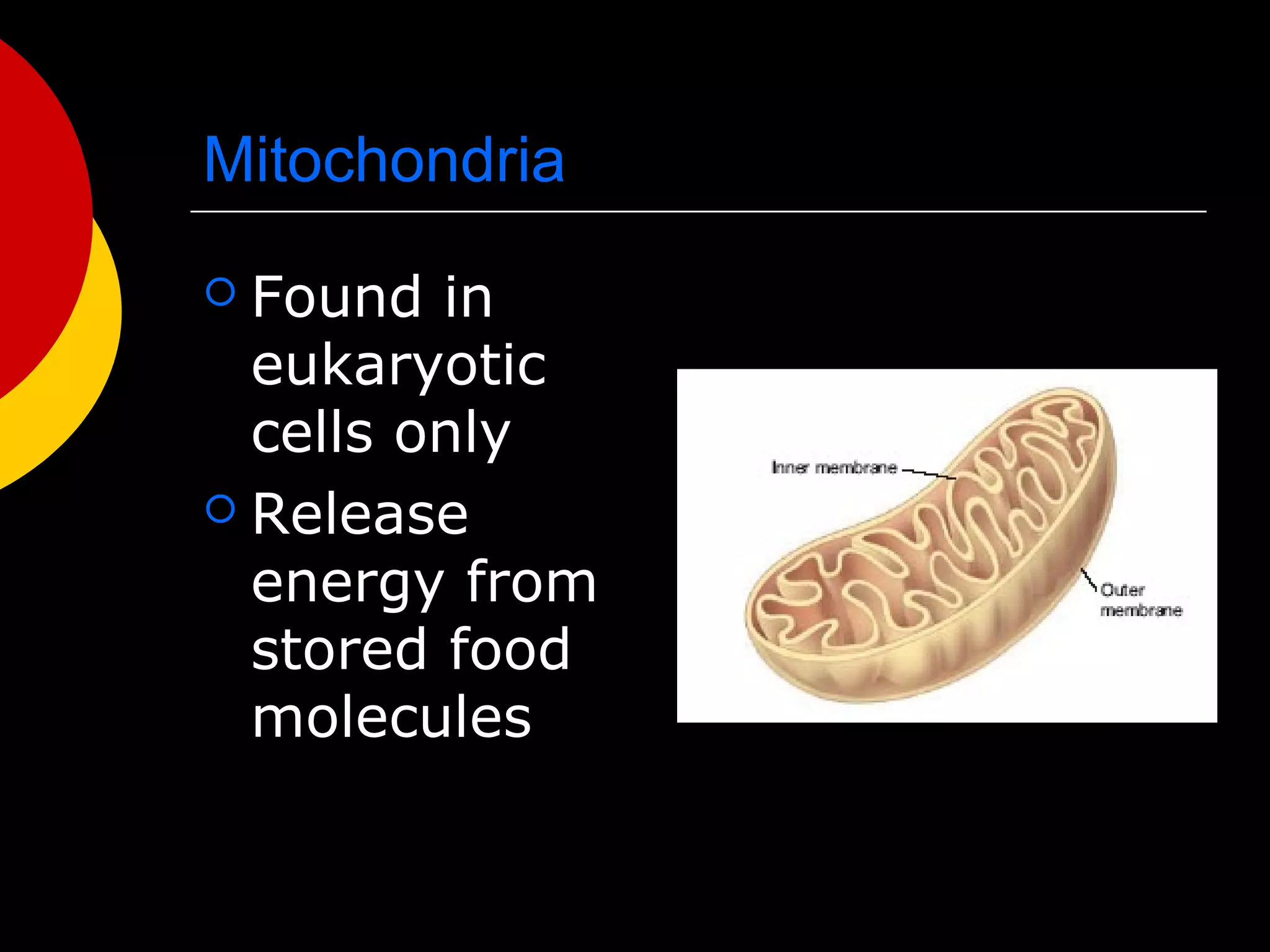
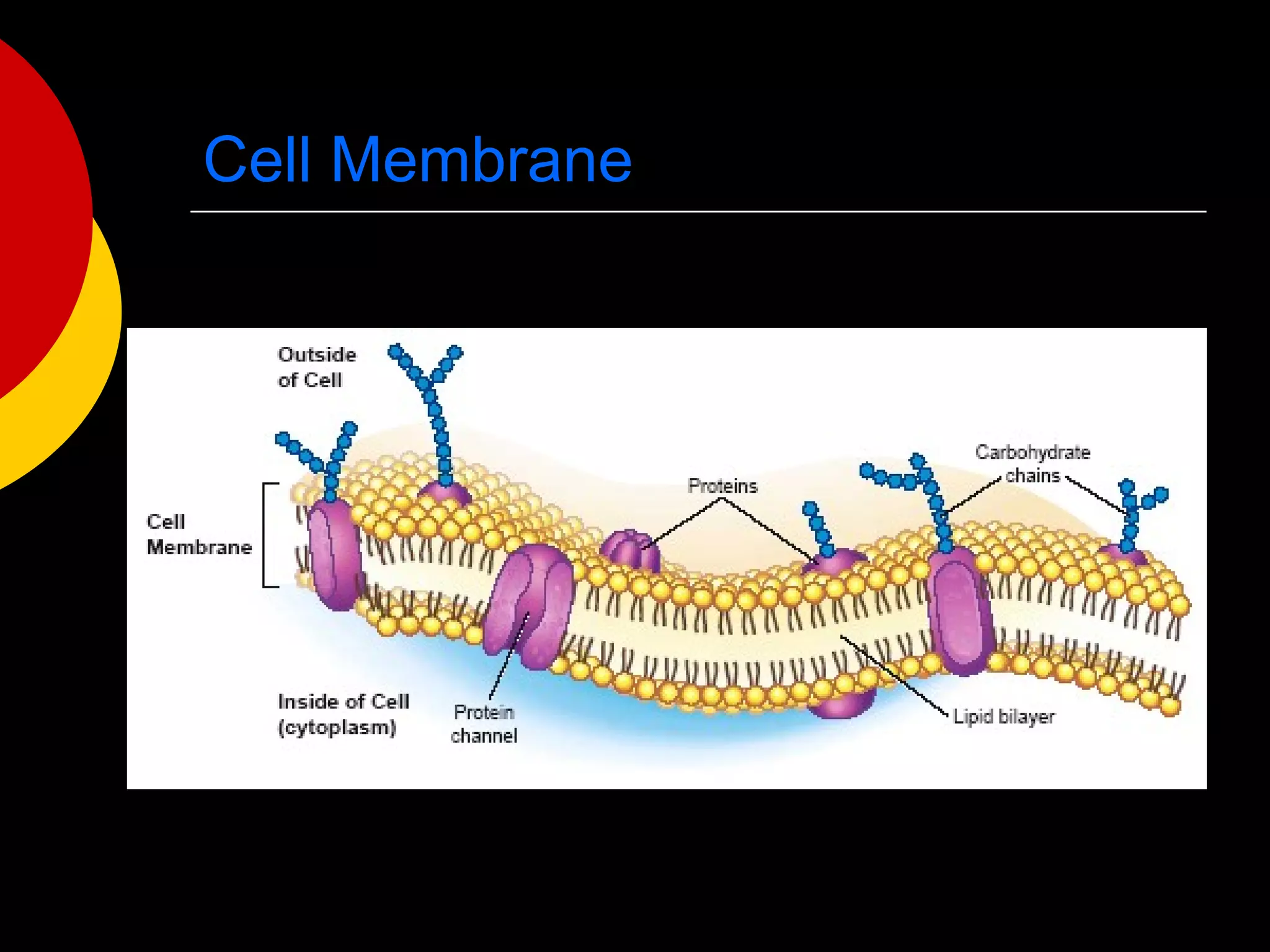
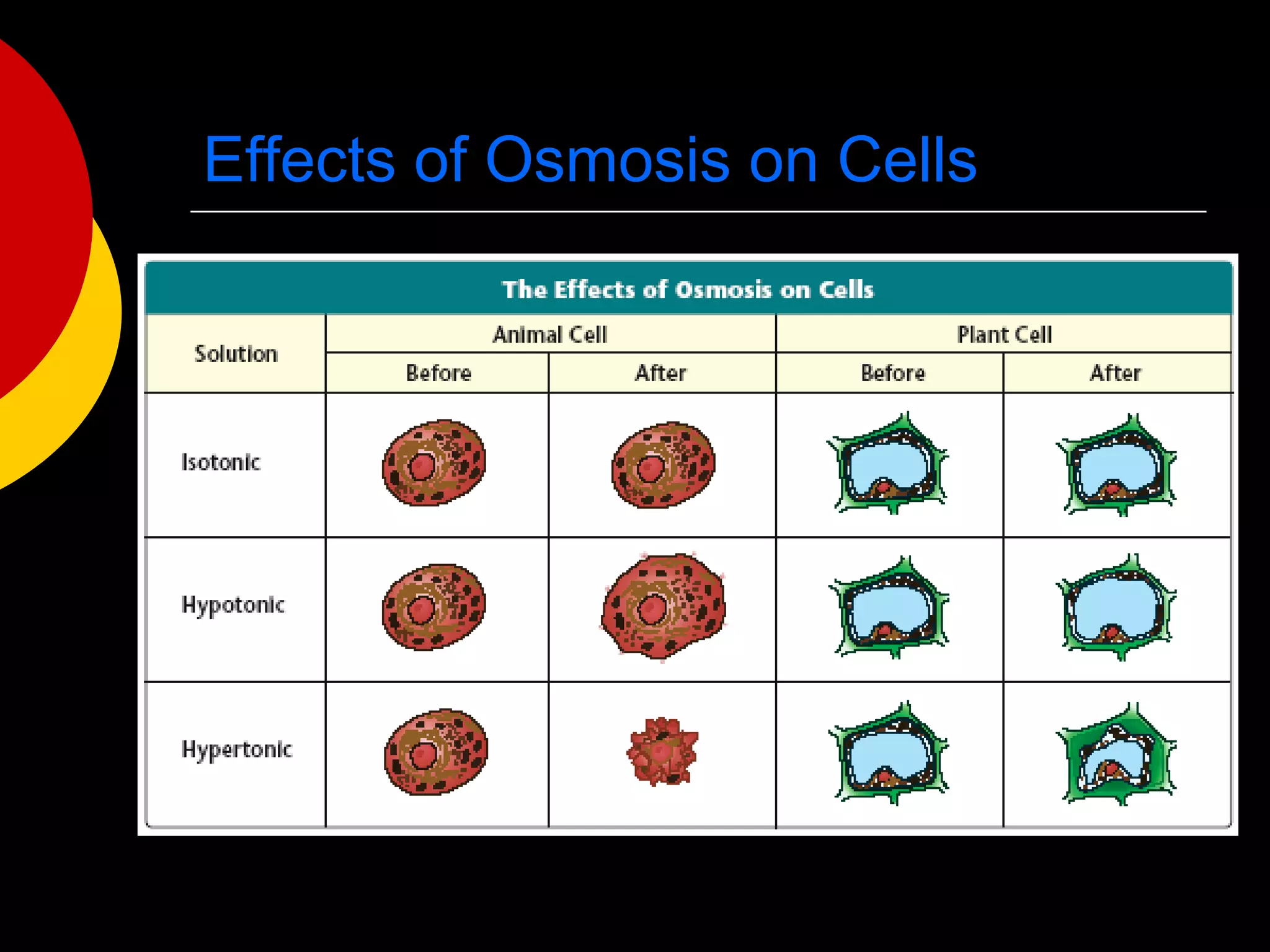
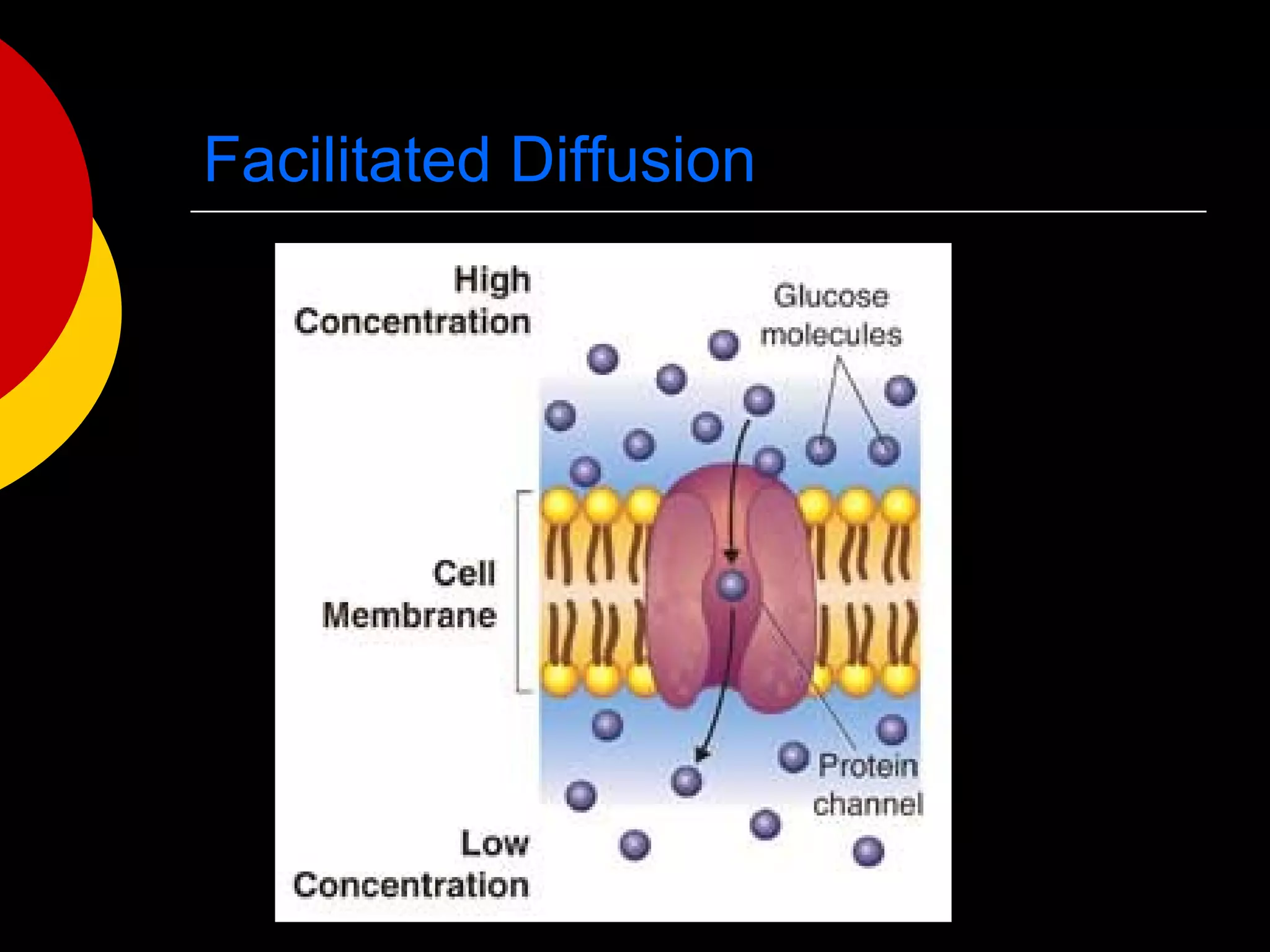
3) The basic structures of cells include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles that have specific functions like the mitochondria, chloroplasts, and endoplasmic reticulum.
4)