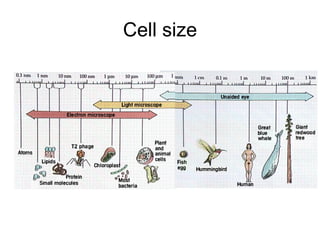
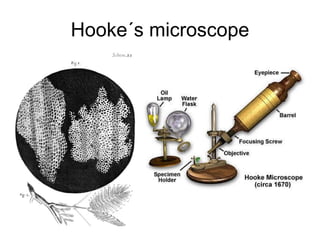
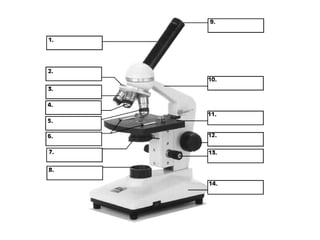
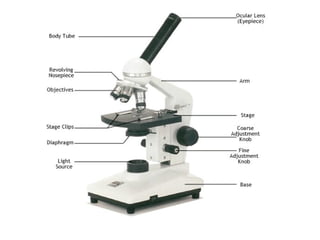
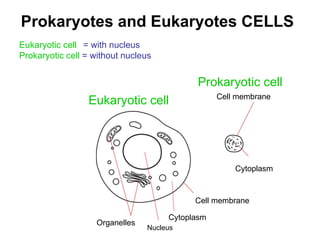
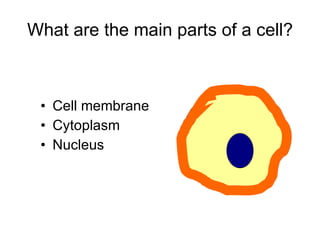
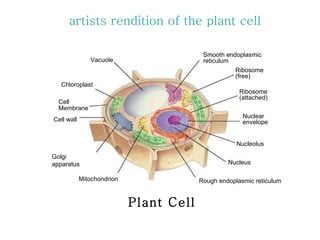
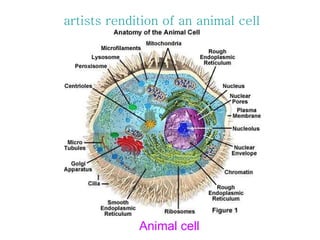
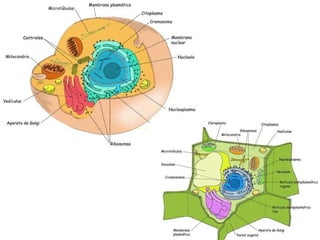
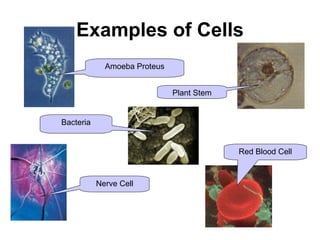
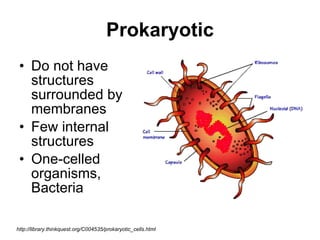
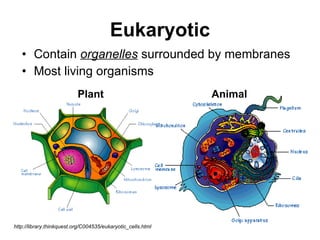
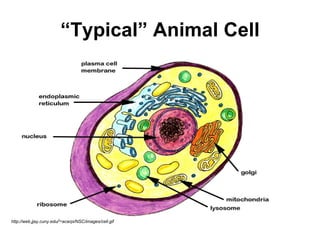
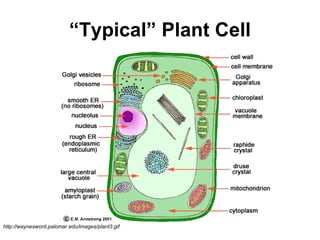
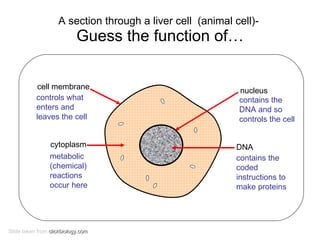
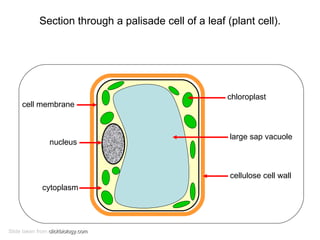
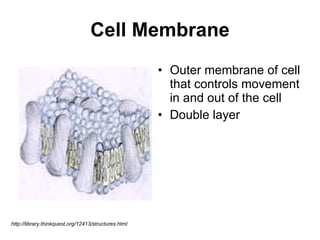
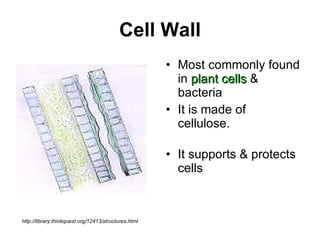
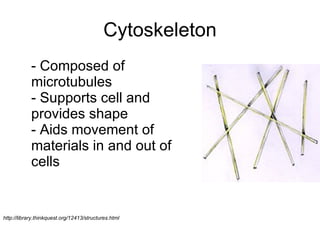
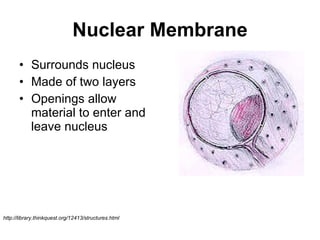
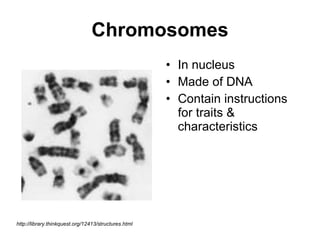
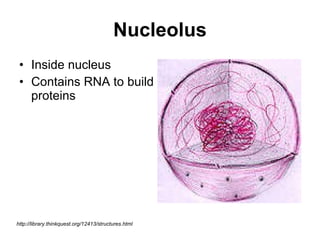
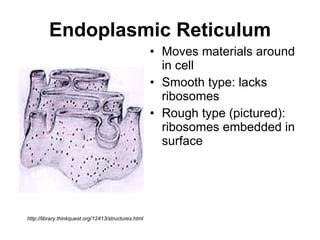
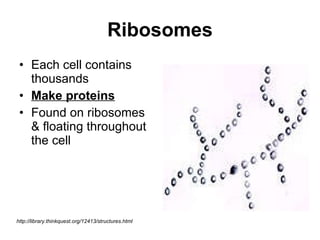
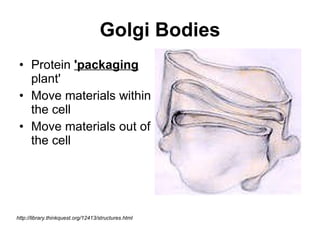
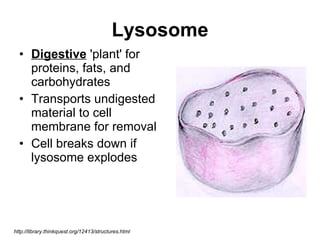
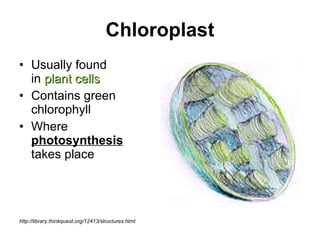
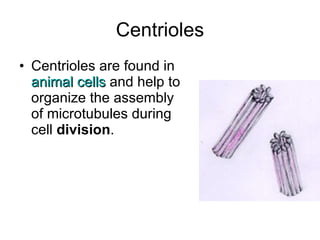
The document covers the fundamental concepts of cell theory, detailing that all living things are composed of cells, which are the basic units of life. It distinguishes between prokaryotic cells (without a nucleus) and eukaryotic cells (with a nucleus), and outlines the various parts of eukaryotic cells, such as the nucleus, organelles, and cell membrane. Additionally, it highlights the vital functions that differentiate living from non-living things, emphasizing the roles of nutrition, interaction, and reproduction.