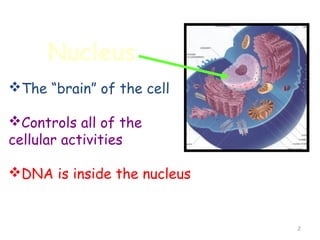
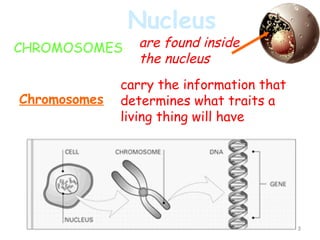
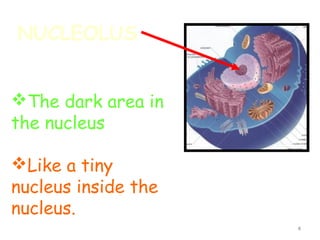
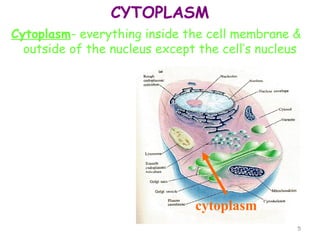
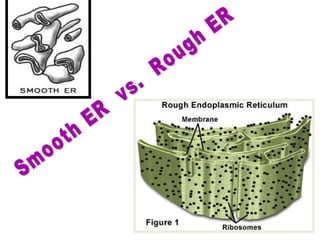
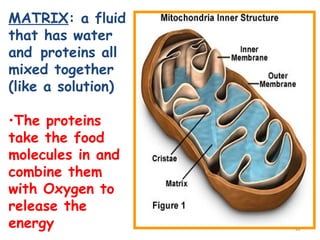
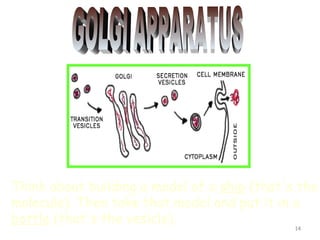
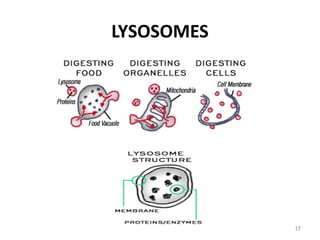
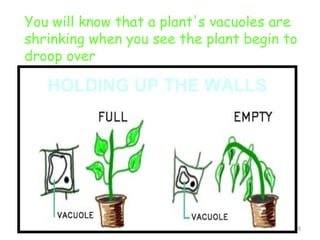
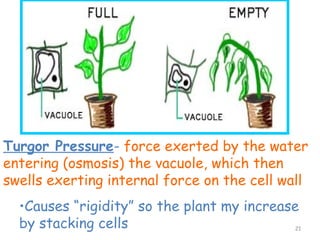
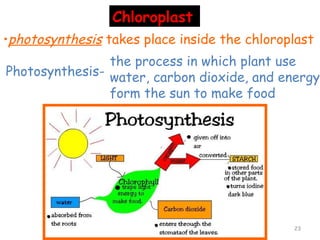
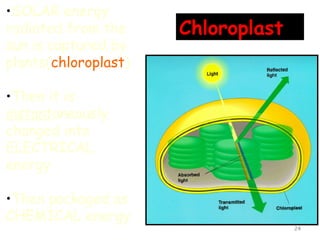
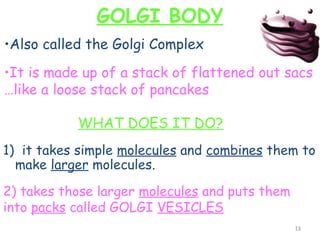The document describes several key organelles in plant and animal cells. It defines the nucleus as the "brain" of the cell that controls cellular activities. It also describes the nucleolus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi body, lysosomes, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes. Each organelle is defined in one to three sentences explaining its structure and main function.