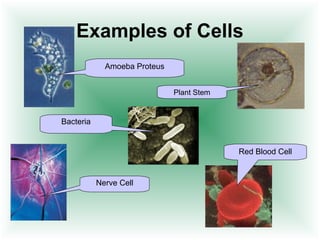
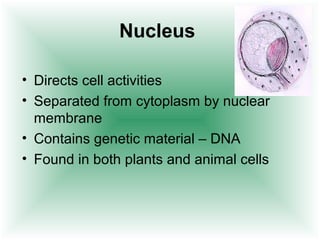
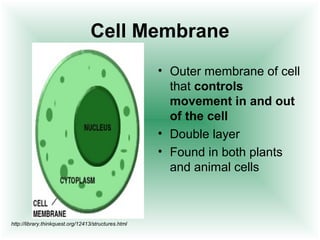
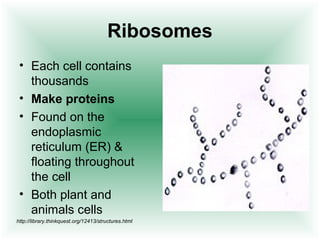
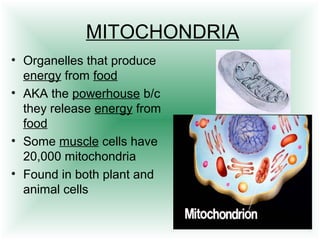
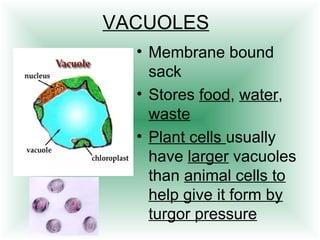
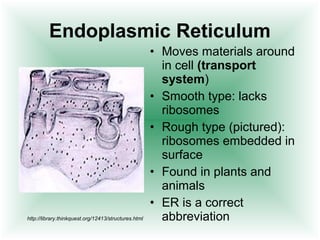
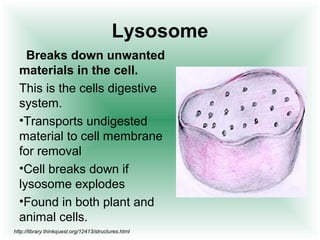
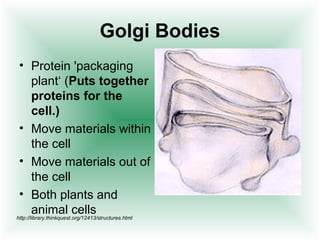
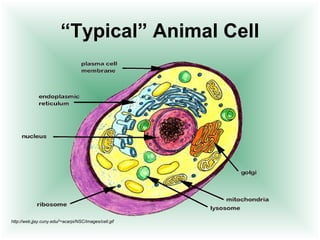
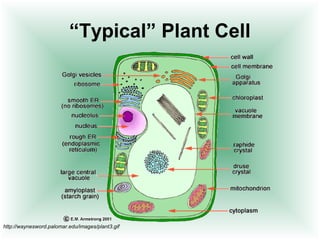
This document defines cells and describes their basic structures and functions. It explains that cells are the smallest unit capable of life functions and lists examples like amoebas, plant stems, red blood cells, and bacteria. It then describes the structures common to plant and animal cells, including the nucleus that directs the cell, the cell membrane that controls what enters and exits, the cytoplasm where organelles float, and ribosomes that produce proteins. Organelles like mitochondria that produce energy, vacuoles that store materials, and chloroplasts that conduct photosynthesis in plant cells are also outlined. Lastly, diagrams of a typical animal and plant cell are provided.